Natural regions of Chile
Because Chile extends from a point about 625 kilometers north of the Tropic of Capricorn to a point hardly more than 1,400 kilometers north of the Antarctic Circle, within its territory can be found a broad selection of the Earth's climates.

In 1950, CORFO defined, following criteria of geographic and economic homogeneity, six regions in continental Chile: Norte Grande, Norte Chico, Núcleo Central, Concepción y La Frontera, Los Lagos and Los Canales.[1]
Although this territorial division was never used to define administrative entities (as the current Regions of Chile), the natural regions continue to be used for reference purposes.
Overview
These natural regions are ordered from north to south and reduced to five natural regions:[2] Each has its own characteristic vegetation, fauna, climate, and, despite the omnipresence of both the Andes and the Pacific, its own distinct topography.
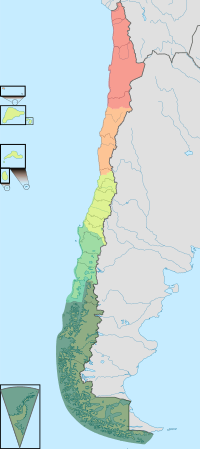
| Natural Regions | Regions of Chile | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Norte Grande (Far North) | Arica & Parinacota Region | Desert climate with areas of extreme aridity. Coastal cliffs, high coast range, intermediate depression and Andes. Plateaus in the Andes. Salt flats, copper and saltpeter deposits in the interior. Puna grassland with summer precipitation in the eastern fringes. |
| Tarapacá Region | ||
| Antofagasta Region | ||
| North Atacama Region | ||
| Copiapó River (27° S) | ||
| Norte Chico (Near North) | South Atacama Region | Semi-arid climate. Coast range and Andes merge, transversal east-west valleys instead of intermediate depression. Agriculture limited to narrow valley bottoms. Periodic flowering in parts of the desert. No volcanism. Important gold, copper and iron deposits. |
| Coquimbo Region | ||
| North Valparaíso Region | ||
| Aconcagua River (33° S) | ||
| Zona Central (Central Chile) | South Valparaíso Region | Mediterranean climate and Matorral vegetation. The Andes is massive and high. Coast range and Andes lose height as they separate from each other to the south, fertile intermediate depression. Summer runoff of large rivers is heavily dependent on glacier and snowmelt. |
| Santiago Metropolitan Region | ||
| O'Higgins Region | ||
| Maule Region | ||
| Ñuble Region | ||
| North Bío-Bío Region | ||
| Bío-Bío River (37° S) | ||
| Zona Sur (Southern Zone) | South Bío-Bío Region | Temperate oceanic climate and Valdivian vegetation. Coast range and Andes are low, intermediate depression near sea level. Lakes of glacial origin, intensive volcanic and geothermal activity. |
| Araucanía Region | ||
| Los Ríos Region | ||
| North Los Lagos Region | ||
| Chacao Channel (42° S) | ||
| Zona Austral (Austral Zone) | South Los Lagos Region | Subpolar oceanic climate in the west and steppe climate in the east. Magellanic forest and Magellanic moorland vegetation in the west, grasslands in the east. Glacial landscape; Coast range consists of islands, intermediate depression absent or under sea level. Fjords and ice fields in the Andes. |
| Aisén Region | ||
| Magallanes Region | ||
Norte Grande
Most of the region is covered by the Atacama Desert and has a dry arid climate. The coast range has peaks over 2000 m and ends in cliffs in the coast.[3] There are large salt flats in the Intermediate depression and the Andes. Norte Grande has Chile's highest mountains including Ojos del Salado (6,891 m) but host also the Altiplano and puna high plateaus.
Norte Chico
The region has semi-arid climate, characterized by the transition from the Atacama Desert to the Mediterranean Matorral vegetation. The coast range and the Andes merges in this zone leaving no space for the Intermediate depression which is "replaced" by several tranversal (east-west) valleys. The lack of an intermediate depression and absence of volcanic activity are believed to be the result of the flat-slab subduction of the Juan Fernández Ridge.
Zona Central
Mediterranean climate, vegetation of the Chilean Matorral. The Intermediate Depression of central Chile extends from Santiago to the south as a fertile region and is considered the agricultural heartland of Chile. After the Destruction of Seven Cities (1598–1604), all major settlements within the colonial Captaincy General of Chile came to be confined in central Chile, excepting only La Serena and the Chiloé Archipelago.
Zona Sur

Temperate oceanic climate, vegetation of Valdivian temperate rain forests. The coast range is lower than further north with no peak over 1,500 m. The Intermediate depression is close to sea level. There are features from the last glacial maximum in the Andes and the Intermediate depression such as moraines and glacial lakes. Intensive volcanism in the Andes in form of volcanoes and hot springs.
Zona Austral
Covers all of Chilean Patagonia, and the Chiloé Archipelago. Zona austral has a subpolar oceanic climate and a vegetation of Magellanic subpolar forests in the west and Patagonian grasslands in the east. The former Patagonian Ice Sheet have eroded the coast range so that it now of islands and is not present south of Taitao Peninsula. The Intermediate depression is under the sea level. Fjords penetrate the Andes where there are also two ice sheets and several glacial lakes.
Notes
- Geografía económica de Chile. Corporación de fomento de la producción. (CORFO) Fundación Pedro Aguirre Cerda. Varios Autores. Imprenta Universitaria. Santiago de Chile 1950
- Note that the correspondence between regions is approximate in general.
- Quezada, Jorge; Cerda, José Luis; Jensen, Arturo (2010). "Efectos de la tectónica y el clima en la configuración morfológica del relieve costero del norte de Chile". Andean Geology (in Spanish). 37 (1): 78–109. Retrieved 5 December 2015.
