Mount Glasgow
Mount Glasgow is a prominent 2,935-metre (9,629 ft) pyramid-shaped summit located between the Elbow River valley and Little Elbow River valley of Kananaskis Country in the Canadian Rockies of Alberta, Canada.[2] The peak is visible from Calgary, weather permitting. Mount Glasgow's nearest higher peak is Mount Cornwall, 2.0 km (1.2 mi) to the southwest.[1]
| Mount Glasgow | |
|---|---|
 Mount Glasgow seen from Elbow River valley | |
| Highest point | |
| Elevation | 2,935 m (9,629 ft) [1] |
| Prominence | 283 m (928 ft) [1] |
| Parent peak | Mount Cornwall (2970 m)[1] |
| Listing | Mountains of Alberta |
| Coordinates | 50°45′20″N 114°55′55″W [2] |
| Geography | |
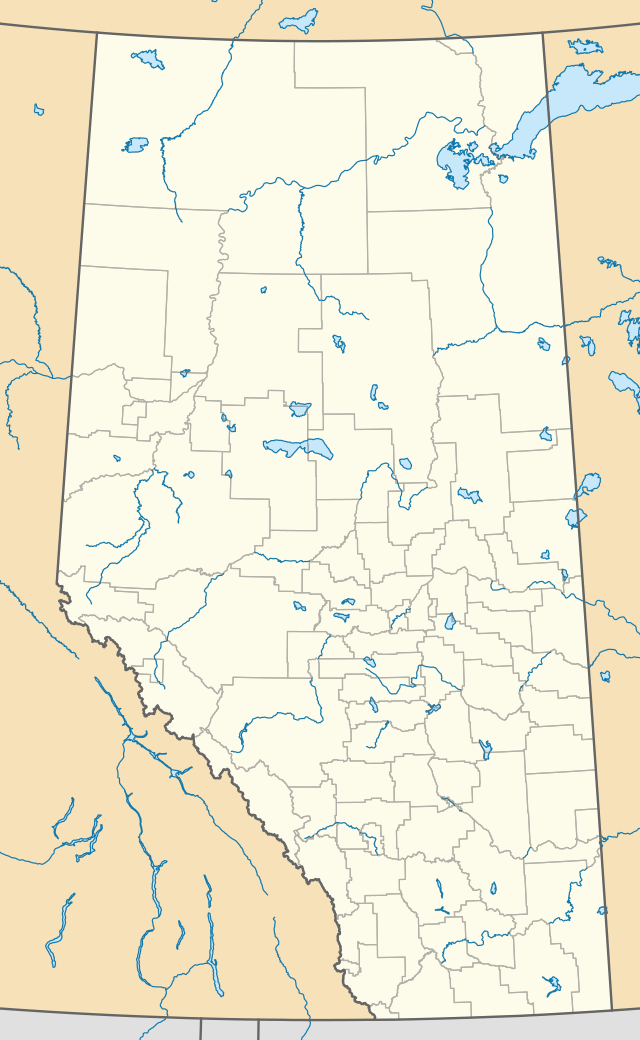 Mount Glasgow Location of Mount Glasgow in Alberta  Mount Glasgow Mount Glasgow (Canada) | |
| Location | Alberta, Canada |
| Parent range | Opal Range[3] Canadian Rockies |
| Topo map | NTS 82J/15[2] |
| Geology | |
| Age of rock | Cambrian |
| Type of rock | limestone |
| Climbing | |
| First ascent | 1949, A Choquette[1] |
| Easiest route | Scramble East and west ridges |
History
Peter Fidler, the first non-native to visit southern Alberta, took bearings on this identifiable peak as he traveled south across the prairies near present-day Calgary. He wrote of it: "a remarkable high cliff, very much resembling a pyramid - from which very near resemblance I shall call it by that name." This is the first known instance of a non-native naming a peak in the Canadian Rockies.[4]
However, the Pyramid name did not stick, and Mount Glasgow was named in 1922 for HMS Glasgow, a British warship involved in the Battle of the Falkland Islands during the First World War in the South Atlantic.[5] The mountain's name became official in 1939 by the Geographical Names Board of Canada.[2]
The first ascent of the peak was made in 1949 by Arnold Choquette.[1]
Geology
Mount Glasgow is composed of sedimentary rock laid down during the Precambrian to Jurassic periods. Formed in shallow seas, this sedimentary rock was pushed east and over the top of younger rock during the Laramide orogeny.[6]
Climate
Based on the Köppen climate classification, Mount Glasgow is located in a subarctic climate with cold, snowy winters, and mild summers.[7] Temperatures can drop below −20 °C (−4 °F) with wind chill factors below −30 °C (−22 °F). Precipitation runoff from the mountain drains into the Elbow River which is a tributary of the Bow River.
References
- "Mount Glasgow". Bivouac.com. Retrieved 2018-11-15.
- "Mount Glasgow". Geographical Names Data Base. Natural Resources Canada. Retrieved 2018-12-23.
- "Mount Glasgow, Alberta". Peakbagger.com. Retrieved 2020-01-31.
- "Mount Glasgow". PeakFinder.com. Retrieved 2020-01-31.
- Place-names of Alberta. Ottawa: Geographic Board of Canada. 1928. p. 57.
- Gadd, Ben (2008). "Geology of the Rocky Mountains and Columbias". Missing or empty
|url=(help) - Peel, M. C.; Finlayson, B. L. & McMahon, T. A. (2007). "Updated world map of the Köppen−Geiger climate classification". Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 11: 1633–1644. ISSN 1027-5606.
Gallery
 Mount Glasgow from Forget-me-not Pond
Mount Glasgow from Forget-me-not Pond Mount Glasgow in winter
Mount Glasgow in winter Mount Glasgow (right) seen from the Alberta plains
Mount Glasgow (right) seen from the Alberta plains
External Links
- Mount Glasgow weather web site: Mountain Forecast
- Mt. Glasgow photo: Flickr