Levi-Civita connection
In Riemannian or pseudo Riemannian geometry (in particular the Lorentzian geometry of general relativity), the Levi-Civita connection is the unique connection on the tangent bundle of a manifold (i.e. affine connection) that preserves the (pseudo-)Riemannian metric and is torsion-free.
The fundamental theorem of Riemannian geometry states that there is a unique connection which satisfies these properties.
In the theory of Riemannian and pseudo-Riemannian manifolds the term covariant derivative is often used for the Levi-Civita connection. The components of this connection with respect to a system of local coordinates are called Christoffel symbols.
History
The Levi-Civita connection is named after Tullio Levi-Civita, although originally "discovered" by Elwin Bruno Christoffel. Levi-Civita,[1] along with Gregorio Ricci-Curbastro, used Christoffel's symbols[2] to define the notion of parallel transport and explore the relationship of parallel transport with the curvature, thus developing the modern notion of holonomy.[3]
The Levi-Civita notions of intrinsic derivative and parallel displacement of a vector along a curve make sense on an abstract Riemannian manifold, even though the original motivation relied on a specific embedding
since the definition of the Christoffel symbols make sense in any Riemannian manifold. In 1869, Christoffel discovered that the components of the intrinsic derivative of a vector transform as the components of a contravariant vector. This discovery was the real beginning of tensor analysis. It was not until 1917 that Levi-Civita interpreted the intrinsic derivative in the case of an embedded surface as the tangential component of the usual derivative in the ambient affine space.
Remark
In 1906, L. E. J. Brouwer was the first mathematician to consider the parallel transport of a vector for the case of a space of constant curvature.[4][5] In 1917, Levi-Civita pointed out its importance for the case of a hypersurface immersed in a Euclidean space, i.e., for the case of a Riemannian manifold embedded in a "larger" ambient space.[1] In 1918, independently of Levi-Civita, Jan Arnoldus Schouten obtained analogous results.[6] In the same year, Hermann Weyl generalized Levi-Civita's results.[7][8]
Notation
- (M, g) denotes a Riemannian or pseudo-Riemannian manifold.
- TM is the tangent bundle of M.
- g is the Riemannian or pseudo-Riemannian metric of M.
- X, Y, Z are smooth vector fields on M, i. e. smooth sections of TM.
- [X, Y] is the Lie bracket of X and Y. It is again a smooth vector field.
The metric g can take up to two vectors or vector fields X, Y as arguments. In the former case the output is a number, the (pseudo-)inner product of X and Y. In the latter case, the inner product of Xp, Yp is taken at all points p on the manifold so that g(X, Y) defines a smooth function on M. Vector fields act (by definition) as differential operators on smooth functions. In a local coordinates , the action reads
where Einstein's summation convention is used.
Formal definition
An affine connection ∇ is called a Levi-Civita connection if
- it preserves the metric, i.e., ∇g = 0.
- it is torsion-free, i.e., for any vector fields X and Y we have ∇XY − ∇YX = [X, Y], where [X, Y] is the Lie bracket of the vector fields X and Y.
Condition 1 above is sometimes referred to as compatibility with the metric, and condition 2 is sometimes called symmetry, cf. Do Carmo's text.
Fundamental theorem of (pseudo) Riemannien Geometry
Theorem Every pseudo Riemannian manifold has a unique Levi Civita connection .
proof: If a Levi-Civita connection exists, it must be unique. To see this, write condition 1 as
By the symmetry of the metric tensor g we then find:
By condition 2, the right hand side is equal to
so we find the Koszul formula
Hence, if a Levi-Civita connection exists, it must be unique, because Z is arbitrary, is non degenerate, and the right hand side does not depend .
To prove existence, note that for given vector field X and Y, the right hand side of the Koszul expression is function-linear in the vector field Z, not just real linear. Hence by the non degeneracy of , the right hand side uniquely defines some new vector field which we suggestively denote ∇XY as in the left hand side. One now checks that for all vector fields X, Y, Z, and all functions f
Hence the Koszul expression does, in fact, define a connection, and this connection is compatible with the metric and is torsion free, i.e. is a (hence the) Levi-Civita connection.
Note that with minor variations the same proof shows that there is a unique connection that is compatible with the metric and has prescribed torsion.
Christoffel symbols
Let ∇ be an affine connection on the tangent bundle. Choose local coordinates x1 … xn with coordinate basis vector fields and write ∇j for . The Christoffel symbols Γljk of ∇ with respect to these coordinates are defined as
The Christoffel symbols conversely define the connection ∇ on the coordinate neighbourhood because
ie.
An affine connection ∇ is compatible with a metric iff
i.e. iff
An affine connection ∇ is torsion free iff
i.e. iff
is symmetric in its lower two indices.
As one checks by taking X, Y, Z coordinate vectorfields (or computes directly), the Koszul expression of the Levi-Civita connection derived above is equivalent to a definition of the Christoffel symbols in terms of the metric as
where as usual gij are the coefficients of the dual metric tensor, i.e. the entries of the inverse of the matrix (gkl).
Derivative along curve
The Levi-Civita connection (like any affine connection) also defines a derivative along curves, sometimes denoted by D.
Given a smooth curve γ on (M, g) and a vector field V along γ its derivative is defined by
Formally, D is the pullback connection γ*∇ on the pullback bundle γ*TM.
In particular, is a vector field along the curve γ itself. If vanishes, the curve is called a geodesic of the covariant derivative. Formally, the condition can be restated as the vanishing of the pullback connection applied to :
If the covariant derivative is the Levi-Civita connection of a certain metric, then the geodesics for the connection are precisely those geodesics of the metric that are parametrised proportionally to their arc length.
Parallel transport
In general, parallel transport along a curve with respect to a connection defines isomorphisms between the tangent spaces at the points of the curve. If the connection is a Levi-Civita connection, then these isomorphisms are orthogonal – that is, they preserve the inner products on the various tangent spaces.
The images below show parallel transport of the Levi-Civita connection associated to two different Riemannian metrics on the plane, expressed in polar coordinates. The metric of left image corresponds to the standard Euclidean metric , while the metric on the right has standard form in polar coordinates, and thus preserves the vector tangent to the circle. This second metric has a singularity at the origin, as can be seen by expressing it in Cartesian coordinates:
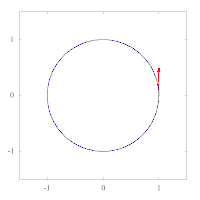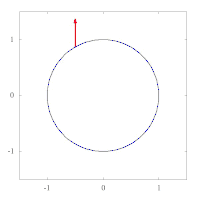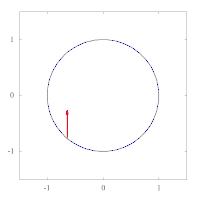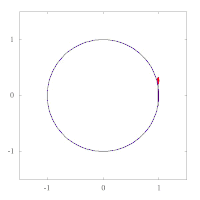
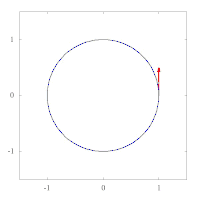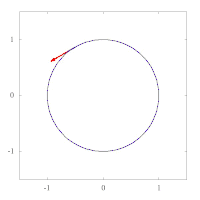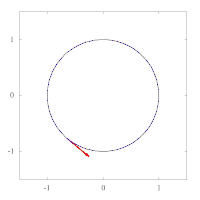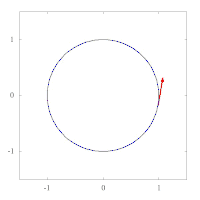
Example: the unit sphere in R3
Let ⟨ , ⟩ be the usual scalar product on R3. Let S2 be the unit sphere in R3. The tangent space to S2 at a point m is naturally identified with the vector subspace of R3 consisting of all vectors orthogonal to m. It follows that a vector field Y on S2 can be seen as a map Y : S2 → R3, which satisfies
Denote as dmY(X) the covariant derivative of the map Y in the direction of the vector X. Then we have:
- Lemma: The formula
- defines an affine connection on S2 with vanishing torsion.
- Proof: It is straightforward to prove that ∇ satisfies the Leibniz identity and is C∞(S2) linear in the first variable. It is also a straightforward computation to show that this connection is torsion free. So all that needs to be proved here is that the formula above does indeed define a vector field. That is, we need to prove that for all m in S2
- Consider the map f that sends every m in S2 to ⟨Y(m), m⟩, which is always 0. The map f is constant, hence its differential vanishes. In particular
- The equation (1) above follows. Q.E.D.
In fact, this connection is the Levi-Civita connection for the metric on S2 inherited from R3. Indeed, one can check that this connection preserves the metric.
See also
- Weitzenböck connection
Notes
- Levi-Civita, Tullio (1917). "Nozione di parallelismo in una varietà qualunque" [The notion of parallelism on any manifold]. Rendiconti del Circolo Matematico di Palermo (in Italian). 42: 173–205. doi:10.1007/BF03014898. JFM 46.1125.02.
- Christoffel, Elwin B. (1869). "Ueber die Transformation der homogenen Differentialausdrücke zweiten Grades". Journal für die reine und angewandte Mathematik. 1869 (70): 46–70. doi:10.1515/crll.1869.70.46.
- See Spivak, Michael (1999). A Comprehensive introduction to differential geometry (Volume II). Publish or Perish Press. p. 238. ISBN 0-914098-71-3.
- Brouwer, L. E. J. (1906). "Het krachtveld der niet-Euclidische, negatief gekromde ruimten". Koninklijke Akademie van Wetenschappen. Verslagen. 15: 75–94.
- Brouwer, L. E. J. (1906). "The force field of the non-Euclidean spaces with negative curvature". Koninklijke Akademie van Wetenschappen. Proceedings. 9: 116–133.
- Schouten, Jan Arnoldus (1918). "Die direkte Analysis zur neueren Relativiteitstheorie". Verhandelingen der Koninklijke Akademie van Wetenschappen Te Amsterdam. 12 (6): 95.
- Weyl, Hermann (1918). "Gravitation und Elektrizitat". Sitzungsberichte Berliner Akademie: 465–480.
- Weyl, Hermann (1918). "Reine Infinitesimal geometrie". Mathematische Zeitschrift. 2 (3–4): 384–411. doi:10.1007/bf01199420.
References
- Boothby, William M. (1986). An introduction to differentiable manifolds and Riemannian geometry. Academic Press. ISBN 0-12-116052-1.
- Kobayashi, Shoshichi; Nomizu, Katsumi (1963). Foundations of differential geometry. John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 0-470-49647-9. See Volume I pag. 158
External links
- "Levi-Civita connection", Encyclopedia of Mathematics, EMS Press, 2001 [1994]
- MathWorld: Levi-Civita Connection
- PlanetMath: Levi-Civita Connection
- Levi-Civita connection at the Manifold Atlas