Leuconostocaceae
The Leuconostocaceae are a family of Gram-positive bacteria, placed within the order of Lactobacillales. Representative genera include Fructobacillus, Leuconostoc, Oenococcus, and Weissella. Bacteria that belong to these three genera are non-spore-forming, round or elongated in shape, and anaerobic or aerotolerant. They usually inhabit nutrient-rich environments such as milk, meat, vegetable products, and fermented drinks.[1] Lactic acid is the main end product of their characteristic heterofermentative carbohydrate metabolism. The phylogeny of the family Leuconostocaceae has recently been evaluated.[2]
| Leuconostocaceae | |
|---|---|
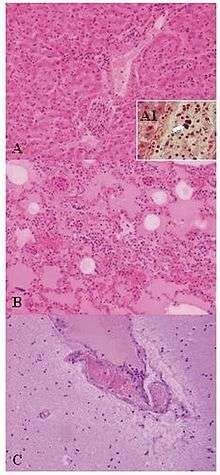 | |
| Lesions of Weissella confusa in the mona monkey (hematoxylin and eosin stain): A) liver: portal triads with neutrophilic infiltration (x10); A1, presence of bacterial emboli inside the vein (arrow) (x40). B) acute pneumonia: edema, congestion, and leukocyte cells exudation in the pulmonary alveoli (x10). C) encephalitis: congestion and marginalized neutrophils in nervous vessels (x10) | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| Division: | |
| Class: | |
| Order: | Lactobacillales |
| Family: | Leuconostocaceae Garrity et al. 2001 |
| Genera | |
|
Convivina | |
References
- Björkroth, Johanna; Holzapfel, Wilhelm (2006). "Genera Leuconostoc, Oenococcus and Weissella". The Prokaryotes. pp. 267–319. doi:10.1007/0-387-30744-3_9. ISBN 978-0-387-25494-4.
- Chelo, Ivo M.; Zé-Zé, Líbia; Tenreiro, Rogério (2007). "Congruence of evolutionary relationships inside the Leuconostoc-Oenococcus-Weissella clade assessed by phylogenetic analysis of the 16S rRNA gene, dnaA, gyrB, rpoC and dnaK". International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology. 57 (2): 276–86. doi:10.1099/ijs.0.64468-0. PMID 17267964.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.