Lands of the Bohemian Crown (1526–1648)
Although the Kingdom of Bohemia, both of the Lusatias, the Margraviate of Moravia, and Silesia were all under Habsburg rule, they followed different paths of development. Moravians include Silesia had accepted the hereditary right of the Austrian Habsburgs to rule and thus escaped the intense struggle between native estates and the Habsburg monarchy that was to characterize Bohemian history. In contrast, the Bohemian Kingdom had entrenched estates that were ready to defend what they considered their rights and liberties. The Habsburgs pursued a policy of centralization and conflict arose, which was further complicated by ethnic and religious issues
Lands of the Bohemian Crown | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||
 Flag
 Coat of arms of Frederick V of the Palatinate as king of Bohemia
| |||||||||
.svg.png) Lands of the Bohemian Crown within the Holy Roman Empire (1618) | |||||||||
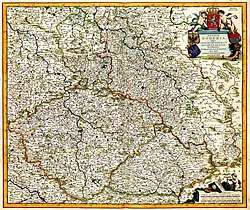 Lands of the Bohemian Crown around 1620 | |||||||||
| Status | States of the Holy Roman Empire Crown lands of the Habsburg Monarchy (after 1526) | ||||||||
| Capital | Prague | ||||||||
| Common languages | Czech, German, Latin | ||||||||
| Religion | Lutheran Hussite Protestant (Utraquist, Brethren) Roman Catholic Reformed Judaistic | ||||||||
| Government | Hereditary monarchy Confederation (1619–1620) | ||||||||
| King | |||||||||
• 1526–1564 | Ferdinand I (first Habsburg on the throne) | ||||||||
• 1619–1620 | Frederick V | ||||||||
| History | |||||||||
| 1526 | |||||||||
• Treaty of Westphalia | 1648 | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| Today part of | |||||||||
History of the Lands of the Bohemian Crown (1526–1648)
Initial clashes (16th century)
Habsburg rule brought two centuries of conflict between the Bohemian estates and the monarchy. As a result of this struggle, the Czechs lost a major portion of their native aristocracy, their particular form of religion (Hussitism), and even the widespread use of the Czech language. The Habsburg policy of centralization began with its first ruler, King Ferdinand (1526–64). His efforts to eliminate the influence of the Bohemian estates were met with resistance. But the Bohemian estates were themselves divided, primarily on religious lines. By several adroit political maneuvers, Ferdinand was able to establish hereditary succession to the Bohemian crown for the Habsburgs. The estates' inability to establish the principle of electing or even confirming a monarch made their position considerably weaker.
The conflict in Bohemia was complicated further by the Reformation and the subsequent wars of religion in Central Europe. Adherents of the Czech Reformed Church (Hussites) opposed the Roman Catholic Habsburgs, who were in turn supported by the Czech and German Catholics. The Lutheran Reformation of 1517 introduced an added dimension to the struggle: much of the German burgher population of Bohemia adopted one of the new Protestant creeds (both Lutheran and Calvinist); the Hussites split, and one faction allied with the German Protestants. In 1537, Ferdinand conceded to the Czechs, recognized the Compacts of Basel, and accepted moderate Utraquism. The reconciliation, however, was of brief duration.
In 1546 German Protestants united in the Schmalkaldic League to wage war against the Holy Roman Emperor, Charles V. Whereas Ferdinand wanted to aid his brother, the Hussite and pro-Protestant Czech nobility sympathized with the German Protestant princes. Armed conflict between Ferdinand and the Bohemian estates broke out in 1547. But the Bohemians were not unified; victory went to Ferdinand, and reprisals against the Czech rebels followed. The property of Czech Utraquist nobility was confiscated and their privileges abrogated. Four rebels (two lesser nobles and two burghers) were executed in the square before the royal palace. Members of the Unity of the Brethren, a Hussite church that had figured prominently in the rebellion, were bitterly persecuted. Their leader, Bishop Jan Augusta, was sentenced to sixteen years' imprisonment. Ferdinand, now Holy Roman Emperor (1556–64), attempted to extend the influence of Catholicism in Bohemia by forming the Jesuit Academy in Prague and by bringing Jesuit missionaries into Bohemia.
Battle of White Mountain

Discord between Habsburgs and Czechs and between Catholics and the followers of the reformed creeds erupted again into an open clash in the early seventeenth century. At that time, the Czechs were able to take advantage of the struggle between two contenders to the imperial throne, and in 1609 they extracted a Letter of Majesty from Emperor Rudolf II (1576–1612) that promised toleration of the Czech Reformed Church, gave control of Charles University to the Czech estates, and made other concessions. Rudolf's successor, Matthias (1612–17), proved to be an ardent Catholic and quickly moved against the estates. Violation of promises contained in the Letter of Majesty regarding royal and church domains and Matthias's reliance on a council composed of ardent Catholics further increased tensions.
In 1618 two Catholic imperial councillors were thrown out of a window of Prague Castle (one of the so-called Defenestrations of Prague), signaling an open revolt by the Bohemian estates against the Habsburgs and started the Thirty Years' War. The Bohemian estates decided to levy an army, decreed the expulsion of the Jesuits, and proclaimed the Bohemian throne to be elective. They elected a Calvinist, Frederick of the Palatinate, to the Bohemian throne. Frederick then tried to muster further support for the Bohemian cause, even attempting to convince the Ottoman Empire to provide military support in exchange for tribute.[1] On November 8, 1620, the Czech estates confronted the imperial forces in the Battle of White Mountain near Prague and were decisively defeated.
Consequences of the defeat (1620–1648)
The Czech defeat at the Battle of White Mountain was followed by measures that effectively secured Habsburg authority and the dominance of the Roman Catholic Church. Many Czech nobles were executed; most others were forced to flee the kingdom. An estimated five-sixths of the Czech nobility went into exile soon after the Battle of White Mountain, and their properties were confiscated. Large numbers of Czech and German Protestant burghers emigrated. In 1622, Charles University was merged with the Jesuit Academy, and the entire education system of the Bohemian Kingdom was placed under Jesuit control. In 1624 all non-Catholic priests were expelled by royal decree.
The Revised Ordinance of the Land (1627) established a legal basis for Habsburg absolutism. All Czech lands were declared hereditary property of the Habsburg family. The German language was made equal to the Czech language. The legislative function of the diets of both Bohemia and Moravia was revoked; all subsequent legislation was to be by royal decree, receiving only formal approval from the diets. The highest officials of the kingdom, to be chosen from among the local nobility, would be strictly subordinate to the king. Thus, little remained of an autonomous and distinct Bohemian Kingdom.
Habsburg rule was further buttressed by the large-scale immigration into Bohemia of Catholic Germans from south German territories. The Germans received most of the land confiscated from Czech owners and came to constitute the new Bohemian nobility. The remaining Czech Catholic nobles gradually abandoned Czech particularism and became loyal servants of the imperial system. German Catholic immigrants took over commerce and industry as well.
The religious wars continued after the Czech defeat. The Thirty Years' War (1618–48) of the German Protestant princes against the Holy Roman Emperor involved foreign powers and extended beyond German territory. Czechs fought on all sides: most of the rebellious Czech generals joined Protestant armies; Albrecht of Wallenstein was the most prominent Czech defector to the imperial cause. Bohemia served as a battlefield throughout the war. Prince Bethlen Gabor's Hungarian forces, reinforced by Turkish mercenaries, fought against the emperor and periodically devastated Slovakia and Moravia. Protestant German armies and, later, Danish and Swedish armies, laid waste the Czech provinces. Cities, villages, and castle fortresses were destroyed. Lusatia was incorporated into Saxony in 1635.
In 1648 the Treaty of Westphalia confirmed the incorporation of the Bohemian Kingdom into the Habsburg imperial system, which established its seat in Vienna. The Bohemian Kingdom de facto lost its independence (de jure only under Maria Theresa).
Legacy
Part of a series on the |
|---|
| History of the Czech lands |
 |
|
Early history |
|
Middle Ages
|
|
Early modern period
|
|
Czech Republic |
|
|
Czechs call the following period, from 1620/1648 till the late 18th century, the "Dark Age." It is characterized by devastation by foreign troops; Germanization; and economic and political decline. The struggle between the Bohemian estates and Habsburg absolutism resulted in the complete subordination of the Bohemian estates to Habsburg interests. In the aftermath of the defeat at White Mountain, the Czechs lost their native noble class, their reformed religion, and a vibrant Czech Protestant culture. The German language became more prominent in government and polite society.
The Kingdom of Bohemia became little more than a province of the Habsburg realm.
After the Thirty Years' War (1618 and 1648), from the original 2.6 million inhabitants of Bohemia and Moravia, there remained approximately 950,000 inhabitants in Bohemia and only 600,000 inhabitants in Moravia.
See also
- Kingdom of Bohemia
- Habsburg Bohemia
- History of the Lands of the Bohemian Crown (1648–1867)
- History of the Lands of the Bohemian Crown (1867–1918)
- Czech lands under Habsburg rule
References
- The Thirty Years War: Europe's Tragedy - Peter Hamish Wilson - Google Books. Books.google.com. Retrieved 2013-09-18.
