Land Transportation Office (Philippines)
The Land Transportation Office (Filipino: Tanggapan ng Transportasyong-Lupa or LTO) is an agency of the Philippine government under the Department of Transportation and is responsible for all land transportation in the Philippines. Functions of the Land Transportation Office include the inspection and registration of motor vehicles, issuance of license and permits, enforcement of land transportation rules and regulations, adjudication of traffic cases, and the collection of revenues for the government of the Philippines.[1]
| Tanggapan ng Transportasyong-Lupa | |
 | |
| Agency overview | |
|---|---|
| Formed | June 20, 1964 |
| Superseding agency |
|
| Headquarters | East Avenue, Diliman, Quezon City |
| Agency executives |
|
| Parent agency | Department of Transportation |
| Website | www |
Its primary mission is to rationalize the land transportation services and facilities and to effectively implement the various transportation laws, rules, and regulations. It believes that it is the responsibility of those involved in the public service to be more vigilant in their part in the over-all development scheme of national leadership. Hence, the promotion of safety and comfort in land travel is one of LTO's continuing commitments.[2] It aims to be a frontline government agency that showcases fast and efficient public service for a progressive land transport sector.[3]
History
There were several predecessors before the formation of the present Land Transportation Office.
Automobile Section
In order to regulate and license of operators for motor vehicles in the Philippines, Act No. 2159 was enacted in 1912 under the American colonial Insular Government. This was the first formal law on land transportation in the country. It created the Automobile Section under the Administrative Division of the Bureau of Public Works.[4]
In 1926, Act No. 3045 compiled and incorporated all laws governing motor vehicles. The Automobile Section was upgraded to the Automobile Division but still under the supervision of the Bureau of Public Works. Act No. 3992 (Revised Motor Vehicle Law) was enacted in 1933, amending Act No. 3045. The Automobile Division was renamed Division of Motor Vehicles.
Motor Vehicles Office
In 1945, the Department of Public Works and Highways issued Department Order No. 4 for the reorganization of the Division. It took effect after the Philippines were liberated from the Japanese during World War II. Executive Order No. 94 was promulgated in 1947 reorganizing the different executive

departments, bureaus, and offices. Under Section 82 of E.O. 94, the Division of Motor Vehicles was upgraded into the Motor Vehicles Office (MVO) with the category of the Bureau. However, the Motor Vehicle Office was abolished in 1964 by Republic Act No. 4136 or the Land Transportation and Traffic Code. The Land Transportation and Traffic Code was an act that compiled all the laws relative to transportation and traffic rules, to create a land transportation commission and for other purposes.[5] This act was eventually replaced by the Land Transportation Commission. The Land Transportation Commission was tasked with the registration and operation of motor vehicles and the licensing of conductors and drivers. In order for the commission to effectively carry out its duty, regional offices were established in various parts of the country.[6] Additionally, the powers, functions, and duties previously conferred on the Chief of the Motor Vehicles are now performed by the Land Transportation Commissioner.[5]
Land Transportation Commission
During the Marcos dictatorship, Executive Order No. 546 was promulgated in 1979, creating the Ministry of Transportation and Communications (MOTC). The Land Transportation Commission was renamed into Bureau of Land Transportation and was absorbed into that ministry. The creation of the Board of Transportation and the Bureau of Land Transportation was nullified in 1985 by Executive Order 1011. The E.O. established the Land Transportation Commission, which was tasked to perform functions such as registering motor vehicles, licensing of drivers and conductors, franchising of public utility vehicles and enforcing land transportation rules and regulations.
Establishment of the Land Transportation Office
The Land Transportation Commission was abolished in 1987, and two offices were created, namely the Land Transportation Office (LTO) and the Land Transportation Franchising and Regulatory Board (LTFRB). The LTO took over the functions of the former BLT while the LTFRB took over the functions of the BOT. The MOTC was likewise renamed as the Department of Transportation and Communications (DOTC).[7]
Functions and Mandate
License and Permit Issuance
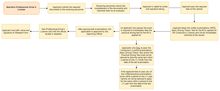
The LTO is in charge of the issuance, renewal, and regulation of driver's licenses. It can issue licenses to both citizens and foreigners provided that they meet the requirements for those licenses. The LTO provides the non-professional driver's license, which allows holders to operate vehicles under the restriction codes 1,2, and 4. It also provides the professional driver's license, which allows the bearer to operate vehicles under all 8 restriction codes. The LTO also issues student permits (SP), which are a primary requirement for both the non-professional and professional driver's licenses. All applicants are also required to pass both a written and practical examination to be granted their license. The application process for any license or permit may be done at any LTO Licensing Center and District/Extension Office.
Motor Vehicle Registration
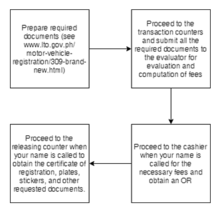
The LTO is responsible for the registration of motor vehicles and renewals. It can register brand new vehicles, including locally manufactured vehicles, imported vehicles, light electric vehicles, low speed vehicles, three wheeled vehicles, and tax exempt vehicles. Each category has an obligatory set of requirements and procedures to follow to be fully registered. Renewals are also obligated to submit the necessary requirements and to follow procedures to be fully renewed. The LTO also oversees miscellaneous transactions, specifically transactions requiring change of certificate of registration, and transactions that do not require the change of certificate of registration.[8]
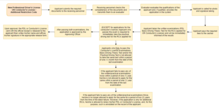
Law Enforcement and Adjudication of Cases
One of the main functions of the LTO is to strictly implement and enforce the laws regarding land transportation. Necessary requirements and procedures are to be followed in settlements of admitted cases and contested cases of motor vehicles, plates, and driver's licenses. The LTO also follows a strict procedure in settlements of impounded violations. It also allows private and for hire motor vehicles to apply for duplicate plates.
Furthermore, the LTO is in charge of ensuring that public land transportation services abide by the fares set by the LTFRB. It has sanctions for the overcharging and undercharging of fares, and for non-issuance of fare tickets.[9]
Manufacturers, Assemblers, Importers, and Dealers Reporting (MAIDR)
The LTO grants accreditation to certain manufacturers, assemblers, importers, and dealers who wish to transact business with the LTO. A firm, person, or corporation must file an application for accreditation with Assistant Secretary of the Land Transportation Office containing certain requirements and qualifications in order to transact business with the LTO relative to Motor Vehicles or its components.[10] It also issues the Certificate of Stock Reported (CSR) which certifies that a motor vehicle or its component has already been reported by its manufacturer, assembler, or importer to MAIDRS.[11] The LTO also requires sales reports that inform the LTO that the reported stock is already sold to the end-user. Sales reports include regular sales transactions and stock transfers.[12] It also reports the issuance of a single CSR, of Motor Vehicles (MVs) formed out of combining components (new, used, or previously registered) MV/MC that are undocumented in a procedure called special reporting.[13] The LTO also maintains the processes that facilitate requests for the approval of the MAID office with LTO related transactions. Such transactions include the issuance of a conduction sticker, a public bidding of a motor vehicle, and the stamping of chassis identification number.[14]
Organizational structure
In 1987, under section 11 of Executive Order No. 125, the Regional Offices of the Land Transportation Commission were abolished and their functions were transferred to the Regional Offices for Land Transportation. The newly renamed Department of Transportation and Communication was placed under the authority of the Secretary of Transportation and Communication. As with the Land Transportation Commission before it, the Land Transportation Office is an office under the Department of Transportation and is headed by the Assistant Secretary for Land Transportation, who is appointed by the President upon the recommendation of the Secretary.
The current LTO Board is listed below:[15]
| Name of Agency | Head of Agency |
|---|---|
| OFFICE OF THE ASSISTANT SECRETARY | |
| OFFICE OF THE EXECUTIVE DIRECTOR | |
| Internal Compliance Enforcement Division | |
| ADMINISTRATIVE DIVISION | |
| Medical Unit | |
| General Services Section | |
| LTO Trunkline (PABX/Information) | |
| Ground & Building Maintenance Unit | |
| Records and Production Unit | |
| Motor Pool Unit | |
| HRM Section | |
| Property Section | |
| Equipment | |
| Plate Unit | |
| Supply Unit | |
| FINANCE AND MANAGEMENT DIVISION | |
| Accounting Section | |
| Budget Section | |
| Treasury Section | |
| MANAGEMENT DIVISION | |
| LAW ENFORCEMENT SERVICE | |
| Clearance and Custodial Section Data Control Unit | |
| Field Enforcement Division | |
| Intelligence and Investigation Division | |
| Traffic Safety Division | |
| Traffic Safety Management & Community Relations Section | |
| Road Safety Program Development Advocacy Section | |
| MANAGEMENT INFORMATION DIVISION | |
| Computer Section | |
| Records Section | |
| Statistics Section | |
| OPERATIONS DIVISION | |
| License Section | |
| Registration Section | |
| TRAFFIC ADJUDICATION SERVICE | |
| COMMISSION ON AUDIT | |
| RESIDENT OMBUDSMAN |
Branches
To service the entirety of the country, the LTO has established many branches in the different regions of the Philippines:
- Region I – Aguila Road, Brgy. Sevilla, San Fernando City, La Union
- Region II – San Gabriel, Tuguegarao, Cagayan
- Region III – Government Center, Brgy. Maimpis, City of San Fernando, Pampanga
- Region IVA – J. C. Abadilla Memorial Bldg., Old City Hall Compound, B. Morada Ave., Lipa City Batangas
- Region IVB – MIMAROPA – LTO Compd., East Avenue, QC.
- Region V – Regional Govt. Center Site, Rawis, Legaspi City
- Region VI – Tabuc-Suba, Jaro, Iloilo City
- Region VII – Natalio Bacalso Avenue, Cebu City
- Region VIII – Old Army Road, Tacloban City
- Region IX – Veterans Ave., Zamboanga City/Balangasan St., Pagadian
- Region X – MVIS Compound, Zone 7, Bulua, Cagayan de Oro City
- Region XI – Quimpo Blvd., Davao City
- Region XII – ARMM Compound, Cotabato City/No. 79 G. Del Pilar St., Koronadal City, South Cotabato
- National Capital Region (NCR) – #20 G. Araneta Avenue, Brgy. Sto Domingo, Q.C.
- Cordillera Administrative Region (CAR) – Engineer’s Hill, Baguio City/2nd Flr., Post Office Loop, Session Road, Baguio City
- CARAGA – J. Rosales Avenue, Butuan City
For more detailed information, please visit the LTO Directory.
Projects
The Land Transportation Office is in charge of various projects which aims to improve its functions and mandates.[4]
Land Transportation Office Infrastructure and Information System (LTO-IIS) Project
In 2012, the Department of Transportation and Communication and the Land Transportation Office introduced a project entitled the Land Transportation Office Infrastructure and Information System (LTO-IIS) which aims to utilize information and communication technology to enhance the functional efficiency of the LTO in the delivery of its front line services to the public and the performance of its mandate. LTO-IIS involves building an IT network for the LTO which can host and support its Front and Back Office Applications in order to computerize and automate its processes and services, develop its database information system, and provide interconnection between and among LTO offices nationwide.[16] In short, the LTO-IIS serves as an efficient means to process motor vehicle registrations, renewal and application of drivers’ licenses and permits, back-end transactions, apprehensions, and such ancillary transactions or processes.[17] This new LTO-IT system aimed to make accessing relevant vehicle information easier for authorities especially for tracing stolen vehicles while addressing issues including the involvement of third-party providers with key data such as vehicle registration. The IT system overhaul was estimated to cost P8.2-billion.[18]
5-year Validity of Drivers’ Licenses
August 29, 2017 marked the beginning of the five-year validity of drivers' licenses cards issued by the LTO. Applications were accepted beginning October 2016 for driver's licenses as well as renewals with five-year validity, however, issues with the printers' contracts stalled the card printing for almost one year resulting in a backlog of 3.6 million driver's licenses which only began to be processed September 2017.
Republic Act (RA) No. 10930 effectively amended Section 23 of Republic Act No. 4136, otherwise known as the "Land Transportation (LTO) and Traffic Code" which was signed on August 2, 2017 by President Rodrigo Duterte to extend the validity of the driver's license from three years to five years. According to the law, "Except for student permits, all drivers' licenses shall be valid for five years reckoned from the birthdate of the licensee, unless sooner revoked or suspended."
This amendment also added that holders of nonprofessional and professional driver's licenses who do not commit violations in RA 4136 or any other traffic laws during the five-year period "shall be entitled to a renewal of such license of 10 years, subject to the restrictions as may be imposed by the LTO." [19]
Besides the amendments to the law, new improvements to the quality and security of the license cards were introduced. The old cards with three-year validity were made from PVC, thermally printed, and had limited security features. The new plastic license cards are laser engraved and made of polycarbonate material which are more durable. The new cards also includes several new security features.
The Transportation Secretary, Arthur Tugade, and LTO chief Assistant Secretary, Edgar Galvante, led the official rollout.[20]
Controversies
Fixers
The Land Transportation Office and their various constituent branches and offices are notorious for their corrupt employees who engage in the malpractice of hiring and colluding with ‘fixers’ to illicitly garner more income. Fixers litter the various branches of the LTO, offering faster and/or easier transaction and procurement of official LTO paraphernalia at a more expensive price than the standard fee. These fixers and their employers pocket the extra payment in exchange for placing a client higher up in the queuing system, falsifying official government documents, fabricating driving test and written test results, and many other illegal practices.
Section 11 of the Republic Act No. 9485 or the “Anti-Red Tape Act of 2007” lists fixing and/or collusion with fixers as a grave offense, with the penalty being dismissal and perpetual disqualification from public service. The fixers themselves can receive a penalty of imprisonment not exceeding six years or a fine not less than Twenty Thousand Pesos (P20,000.00) but not more than Two Hundred Thousand Pesos (P200,000.00) or both fine and imprisonment at the discretion of the court.[21]
References
- "Mandate and Functions". Land Transportation Office. Retrieved July 7, 2018.
- "Mission". Land Transportation Office. Retrieved July 7, 2018.
- "Vision". Land Transportation Office. Retrieved July 7, 2018.
- "Historical Background". lto.gov.ph. Land Transportation Office. Retrieved July 9, 2018.
- Transportation and Public Service Law. Phoenxi Bldg., 315 Quezon Blvd. Ext. Quezon City, Philippines: CENTRAL LAWBOOK PUBLISHING CO., INC. 1966. p. 166.CS1 maint: location (link)
- Passage of RA 4136 Archived July 4, 2009, at the Wayback Machine
- "Department of Transportation and Communications". Archived from the original on April 13, 2006. Retrieved February 22, 2020.
- "Everything you need to know about vehicle registered in the Philippines". September 18, 2019.
- Romero, Segundo, Danielle Guillen, Lorenzo Cordova, and Gina Gatarin. “Land-Based Transport Governance in the Philippines: Focus on Metro Manila.” Inclusive Mobility Project, Ateneo School of Government (2014).
- "Manufacturers, Assemblers, Importers, and Dealers Accreditation". Republic of the Philippines – Land Transportation Office – Department of Transportation. Retrieved July 9, 2018.
- "Stock Reporting". Republic of the Philippines – Land Transportation Office – Department of Transportation. Retrieved July 9, 2018.
- "Sales Reporting". Republic of the Philippines – Land Transportation Office – Department of Transportation. Retrieved July 9, 2018.
- "Special Reporting". Republic of the Philippines – Land Transportation Office – Department of Transportation. Archived from the original on July 6, 2018. Retrieved July 9, 2018.
- "Approvals". Republic of the Philippines – Land Transportation Office – Department of Transportation. Retrieved July 9, 2018.
- "LTO Directory". Republic of the Philippines – Land Transportation Office – Department of Transportation. Retrieved July 8, 2018.
- "Land Transportation Office Infrastructure and Information System (LTO-IIS) Project / DOTCLTO". gov.ph. Republic of the Philippines: National Government Portal. Retrieved July 9, 2018.
- "DOTC-LTO Infrastructure and Information Systems Project Request for Information" (PDF). Republic of the Philippines National Government Portal. Retrieved July 9, 2018.
- "LTO's P8.2-billion IT system overhaul to push through — DOTC". GMA News Online. GMA Network, Inc. October 3, 2012. Retrieved July 9, 2018.
- "LTO to start releasing driver's licenses with 5-year validity". CNN Philippines. August 29, 2017. Retrieved July 9, 2018.
- "DOTR-LTO Rolls Out Driver's License Card with 5-Y Year Validity". dotr.gov.ph. Republic of the Philippines: Department of Transportation. Retrieved July 9, 2018.
- "Republic Act No. 9485: Anti-Red Tape Act of 2007". Republic of the Philippines – Congress of the Philippines. Retrieved July 9, 2018.