King Frederick VIII Land
King Frederick VIII Land (Danish: Kong Frederik VIII Land) is a major geographic division of northeastern Greenland. It extends above the Arctic Circle from 76°N to 81°N in a N/S direction along the coast of the Greenland Sea.[1]
- Not to be confused with King Frederick VI Coast
King Frederick VIII Land Kong Frederick VIII Land | |
|---|---|
 Landscape of Danmarkshavn. | |
 Location of King Frederick VIII Land | |
| Country | Greenland |
| Elevation | 900 m (3,000 ft) |
History
This vast desolate region was still uncharted territory around 1900.[2] It was explored by the 1906–08 Danmark Expedition, the 1909–12 Alabama Expedition and by J.P. Koch's 1912–13 Danish Expedition to Queen Louise Land, when the ruling monarch was Frederik VIII (1843 – 1912)
The area between 79° and 81°30´N was first marked as 'King Frederick VIII Land', after King Frederick VIII of Denmark then the ruling monarch, by the 1906–08 Danmark Expedition in its maps of the region. Einar Storgaard used the name again in a 1927 map —he also proposed a division of the region into a northern and a southern part with a border along Nioghalvfjerd Fjord.[3] Finally the name came into general usage only after the publication of the 1931–34 Three-year Expedition to East Greenland (Treårsekspedition) reports.[1]
Geography
King Frederick VIII Land stretches between 76°N along the middle of the Bessel Fjord in the south and 81°N, the boundary running along the middle of the Independence Fjord and the Academy Glacier. It is bordered by King Christian X Land on the south, the Wandel Sea to the north, Peary Land to the northwest, and the Greenland Ice Sheet to the west. All its territory is included in the large Northeast Greenland National Park zone.[4]
King Frederick VIII Land includes mountain ranges, such as the Princess Caroline-Mathilde Alps, nunataks, such as Queen Louise Land, and vast glacier expanses, such as the Storstrommen, the Zachariae Isstrom and the Nioghalvfjerdsbrae of far northeastern Greenland. In the areas of the shore it also includes fjords, such as the Skaer Fjord, the Ingolf Fjord and the Borge Fjord in Dove Bay, as well as numerous coastal islands, such as Hovgaard Island in the shore of the Greenland Sea or Princess Thyra Island in the Wandel Sea. The Greenland ice sheet reaches the shore at Jokel Bay.
The area of King Frederick VIII Land is practically uninhabited. Currently the only two inhabited places are:
- Danmarkshavn weather station is on the southern shore of the Germania Land Peninsula.[5] It was named by the 1906–08 Danmark Expedition after 'Danmark', the ship of the expedition which wintered there.[1]
- Nord, a Danish military base/weather station located further north in the Crown Prince Christian Land Peninsula.
Limits of King Frederik VIII Land. |
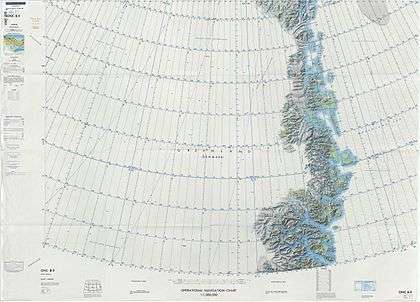 Map of Greenland section. |
 View of the strikingly-shaped Elephant Foot Glacier in Romer Lake, at the far northern limit of King Frederick VIII Land. |
References
- "Catalogue of place names in northern East Greenland". Geological Survey of Denmark. Retrieved 21 April 2016.
- Map of the Arctic regions, showing the limit of the treated area. by C. H. Ostenfeld in Flora Arctica (1902)
- "Nioghalvfjerdsfjorden". Mapcarta. Retrieved 21 April 2016.
- Greenland Map
- Danmarkshavn