Nioghalvfjerdsbrae
Nioghalvfjerdsbrae (79°00′N 025°00′W), sometimes referred to as "79 N Glacier", is a large glacier located in King Frederick VIII Land, northeastern Greenland. It drains an area of 103,314 km2 (39,890 sq mi) of the Greenland Ice Sheet with a flux (quantity of ice moved from the land to the sea) of 14.3 km3 (3.4 cu mi) per year, as measured for 1996.[1]
| Nioghalvfjerdsbrae | |
|---|---|
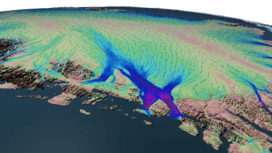 Velocity flow over the Nioghalvfjerdsbrae. | |
 Location within Greenland | |
| Location | Greenland |
| Coordinates | 79°0′N 25°0′W |
| Area | 103,314 km2 (39,890 sq mi) |
| Length | 89 km |
| Width | 20 km |
| Terminus | Nioghalvfjerd Fjord, Greenland Sea |
History
This glacier was named by the ill-fated Denmark expedition 1906-1908 because it lies at a latitude of 79°. The name had been meant to be temporary, but it acquired a new significance when it was deemed to be the place where expedition leader Ludvig Mylius-Erichsen, as well as cartographer Niels Peter Høeg Hagen, had died according to Jørgen Brønlund's diary.[2]
Since 1990 Greenland's longest persistent supraglacial stream runs on the glacier, 73 km long in 2011, 71 km in 2017. The width of the stream remains relatively constant over most of the length ranging from 20-35 m.[3]
In August 1997 the southern calving front retreated by 5 km with no significant upstream thinning.[4]
Geography
The terminus of the glacier is in the Nioghalvfjerd Fjord, south of the Dijmphna Sound. The fjord and the glacier form the southern limit of Crown Prince Christian Land.[2] The glacier has had an 80 km long and 20 km wide floating tongue, widening toward its terminus north of Lambert Land.[5] There are two calving fronts where the glacier meets the ocean, separated by Hovgaard Island.[6]
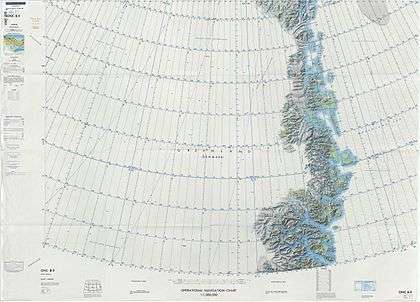 Map of Northeastern Greenland. |
 View of the terminus of the Nioghalvfjerdsbrae glacier with the southwestern end of Hovgaard Island and Cape Adolf Jensen. |
References
- Rignot E., Kanagaratnam P. (2006). "Changes in the velocity structure of the Greenland Ice Sheet". Science. 311 (5763): 986–990. doi:10.1126/science.1121381. PMID 16484490.
- Place names, NE Greenland
- Mauri Pelto (27 June 2018). "Nioghalvfjerdsbræ 70 km+ Long Supraglacial stream, Greenland's Longest?".
- Sustained mass loss of the northeast Greenland ice sheet triggered by regional warming
- "Nioghalvfjerdsfjorden". Mapcarta. Retrieved 16 June 2016.
- Wilson N. J. (2015). "Water exchange between the continental shelf and the cavity beneath Nioghalvfjerdsbrae (79 North Glacier)". Geophysical Research Letters. 42 (18): 7648–7654. doi:10.1002/2015GL064944. hdl:1912/7641.