International Radio and Television Organisation
The International Radio and Television Organisation (official name in French: Organisation Internationale de Radiodiffusion et de Télévision or OIRT (before 1960 International Broadcasting Organization (IBO), official name in French: Organisation Internationale de Radiodiffusion (OIR)) was an East European network of radio and television broadcasters with the primary purpose of establishing ties and securing an interchange of information between those various organizations responsible for broadcasting services, promoting the interests of broadcasting, seeking by international cooperation a solution to any matter relating to broadcasting, and studying and working out all measures having as their aim the development of broadcasting.
Organisation Internationale de Radiodiffusion et de Télévision | |
 The OIRT logo | |
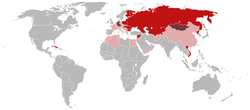 Members at the date of dissolution Members who participated at various times before dissolution Associate members | |
| Merged into | European Broadcasting Union |
|---|---|
| Established | 28 June 1946 |
| Dissolved | 1 January 1993 |
| Type | Union of broadcasting organisations |
| Headquarters | Brussels, Belgium (1946–1950) Prague, Czechoslovakia (1950–1993) |
History
Without British participation, 26 members founded the OIR on 28 June 1946. The next day, at the General Assembly of the International Broadcasting Union (IBU), an attempt was made to dissolve this body, but the motion failed to obtain the required majority. However, 18 of the 28 existing members left the IBU and become co-founders of the new OIR.[1]
In 1946, the newly created OIR installed itself in the IBU building in Brussels. Technical activity was taken up again under the authority of two directors, one delegated by the Soviet Union and the other by France. However, the political situation gradually degraded into the Cold War and this created an uneasy situation of distrust within the staff of the Technical Centre.[1]
In 1950 some members (mostly western European) left the organization to form the new European Broadcasting Union (EBU), among them Belgium, Egypt, France, Italy, Lebanon, Luxembourg, Monaco, Morocco, Netherlands, Tunisia and Yugoslavia.[1]
Broadcasting organizations from the following countries remained members: Albania, Bulgaria, Czechoslovakia, Finland (also a member of EBU), East Germany, Hungary, Poland, Romania, Syria and the Soviet Union.
As a consequence, the OIR headquarters and its Technical Centre was relocated from Brussels to Prague in 1950.[2][3] Staff members from Belgium and other Western countries, some of whom had already been active before the war, stayed on in Brussels and the centre became the technical centre of the new EBU.
Unlike the EBU, the OIRT was not limited to European and Mediterranean countries and has been operating since its inception as a global organization. Members of the organization included countries aligned with the Eastern bloc, such as Cuba, Vietnam, the People's Republic of China and North Korea (although the latter's membership was temporarily inactive after their break with the USSR), as well as the allies of the USSR temporarily led by communist parties, such as Nicaragua and the Democratic Republic of Afghanistan, and the African and Middle Eastern states having been temporarily associated or supported by the socialist camp.
On January 1, 1993, about a year after the dissolution of the Soviet Union, the OIRT merged with the European Broadcasting Union.[3][4]
Intervision

The television network of OIRT was established in 1960 and was called Intervision[5] (Russian Интервидение, Bulgarian Интервизия, Polish Interwizja, Czech Intervize, Slovak Intervízia, Hungarian Intervízió, Romanian Interviziune, Finnish Intervisio).
Between 1977 and 1980 the OIRT organised four Intervision Song Contests in Sopot, Poland, in an attempt to imitate the Eurovision Song Contest.
Active members
Associated members
| Country | Organism | Abbreviation | Date of joining | Date of withdraw |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| West Germany | Arbeitsgemeinschaft der öffentlich-rechtlichen Rundfunkanstalten der Bundesrepublik Deutschland | ARD | 1988 | 1992 |
| Zweites Deutsches Fernsehen | ZDF | 1988 | 1992 | |
| Mongolia | Mongolian National Broadcaster | MNB | 1967 | 1992 |
References
- "EBU 50th Anniversary" (PDF). Difussion EBU. Geneva: European Broadcasting Union. 2000. Retrieved July 24, 2017.
- Lewis, David (January 20, 2012). "The Situation of Public Broadcasting in Europe" (PDF). Geneva: European Broadcasting Union. Retrieved July 24, 2017.
The EBU was founded in 1950 and initially drew its membership largely from western Europe, while a rival sister organization based in Prague, the OIRT, served the state broadcasters under Soviet domination the other side of the Iron Curtain.
- Central and Eastern Europe: Audiovisual landscape and copyright legislation. Audiovisual Eureka and European Audiovisual Observatory. 1994. ISBN 978-9-0621-5459-3. Retrieved July 24, 2017.
- "50 years of Eurovision" (PDF). EBU Dossiers. Geneva: European Broadcasting Union. January 2004. Retrieved July 24, 2017.
- Paulu, Burton (1967). "Programs: information". Radio and Television Broadcasting on the European Continent. Minneapolis: University of Minnesota Press. p. 141. OCLC 321366. Retrieved July 24, 2017.