Integral monotopic protein
Integral monotopic proteins, are permanently attached to the membrane from one side.[1]
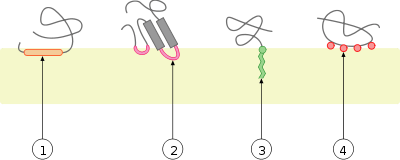
Schematic representation of the different types of interaction between monotopic membrane proteins and the cell membrane:
1. interaction by an amphipathic α-helix parallel to the membrane plane (in-plane membrane helix)
2. interaction by a hydrophobic loop
3. interaction by a covalently bound membrane lipid (lipidation)
4. electrostatic or ionic interactions with membrane lipids (e.g. through a calcium ion)
Three-dimensional structures of the following integral monotopic proteins have been determined:
- prostaglandin H2 syntheses 1 and 2 (cyclooxygenases)
- lanosterol synthase and squalene-hopene cyclase
- microsomal prostaglandin E synthase
- carnitine O-palmitoyltransferase 2
There are also structures of integral monotopic domains of transmembrane proteins:
- monoamine oxidases A and B
- fatty acid amide hydrolase
- mammalian cytochrome P450 oxidases
- corticosteroid 11-beta-dehydrogenases
References
- Fowler, Philip W.; Coveney, Peter V. (July 2006). "A Computational Protocol for the Integration of the Monotopic Protein Prostaglandin H2 Synthase into a Phospholipid Bilayer". Biophysical Journal. 91 (2): 401–410. doi:10.1529/biophysj.105.077784. PMC 1483072. PMID 16632499.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.