Inflorescence
An inflorescence is a group or cluster of flowers arranged on a stem that is composed of a main branch or a complicated arrangement of branches. Morphologically, it is the modified part of the shoot of seed plants where flowers are formed. The modifications can involve the length and the nature of the internodes and the phyllotaxis, as well as variations in the proportions, compressions, swellings, adnations, connations and reduction of main and secondary axes. One can also define an inflorescence as the reproductive portion of a plant that bears a cluster of flowers in a specific pattern.
| Look up inflorescence in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
The stem holding the whole inflorescence is called a peduncle and the major axis (incorrectly referred to as the main stem) holding the flowers or more branches within the inflorescence is called the rachis. The stalk of each single flower is called a pedicel. A flower that is not part of an inflorescence is called a solitary flower and its stalk is also referred to as a peduncle. Any flower in an inflorescence may be referred to as a floret, especially when the individual flowers are particularly small and borne in a tight cluster, such as in a pseudanthium. The fruiting stage of an inflorescence is known as an infructescence. Inflorescences may be simple (single) or complex (panicle). The rachis may be one of several types, including single, composite, umbel, spike or raceme.
General characteristics
Inflorescences are described by many different characteristics including how the flowers are arranged on the peduncle, the blooming order of the flowers and how different clusters of flowers are grouped within it. These terms are general representations as plants in nature can have a combination of types.
Bracts
Inflorescences usually have modified shoots foliage different from the vegetative part of the plant. Considering the broadest meaning of the term, any leaf associated with an inflorescence is called a bract. A bract is usually located at the node where the main stem of the inflorescence forms, joined to the main stem of the plant, but other bracts can exist within the inflorescence itself. They serve a variety of functions which include attracting pollinators and protecting young flowers. According to the presence or absence of bracts and their characteristics we can distinguish:
- Ebracteate inflorescences: No bracts in the inflorescence.
- Bracteate inflorescences: The bracts in the inflorescence are very specialised, sometimes reduced to small scales, divided or dissected.
- Leafy inflorescences: Though often reduced in size, the bracts are unspecialised and look like the typical leaves of the plant, so that the term flowering stem is usually applied instead of inflorescence. This use is not technically correct, as, despite their 'normal' appearance, these leaves are considered, in fact, bracts, so that 'leafy inflorescence' is preferable.
- Leafy-bracted inflorescences: Intermediate between bracteate and leafy inflorescence.
If many bracts are present and they are strictly connected to the stem, like in the family Asteraceae, the bracts might collectively be called an involucre. If the inflorescence has a second unit of bracts further up the stem, they might be called an involucel.
.svg.png) Ebracteate inflorescence.
Ebracteate inflorescence. Ebracteate inflorescence of Wisteria sinensis
Ebracteate inflorescence of Wisteria sinensis.svg.png) Bracteate inflorescence.
Bracteate inflorescence. Bracteate inflorescence of Pedicularis verticillata.
Bracteate inflorescence of Pedicularis verticillata..svg.png) Leafy-bracted inflorescence.
Leafy-bracted inflorescence. Leafy-bracted inflorescence of Rhinanthus angustifolius.
Leafy-bracted inflorescence of Rhinanthus angustifolius..svg.png) Leafy inflorescence.
Leafy inflorescence. Leafy inflorescence of Aristolochia clematitis.
Leafy inflorescence of Aristolochia clematitis.
Terminal flower
Plant organs can grow according to two different schemes, namely monopodial or racemose and sympodial or cymose. In inflorescences these two different growth patterns are called indeterminate and determinate respectively, and indicate whether a terminal flower is formed and where flowering starts within the inflorescence.
- Indeterminate inflorescence: Monopodial (racemose) growth. The terminal bud keeps growing and forming lateral flowers. A terminal flower is never formed.
- Determinate inflorescence: Sympodial (cymose) growth. The terminal bud forms a terminal flower and then dies out. Other flowers then grow from lateral buds.
Indeterminate and determinate inflorescences are sometimes referred to as open and closed inflorescences respectively. The indeterminate patterning of flowers is derived from determinate flowers. It is suggested that indeterminate flowers have a common mechanism that prevents terminal flower growth. Based on phylogenetic analyses, this mechanism arose independently multiple times in different species.[1]
In an indeterminate inflorescence there is no true terminal flower and the stem usually has a rudimentary end. In many cases the last true flower formed by the terminal bud (subterminal flower) straightens up, appearing to be a terminal flower. Often a vestige of the terminal bud may be noticed higher on the stem.
.svg.png) Indeterminate inflorescence with a perfect acropetal maturation.
Indeterminate inflorescence with a perfect acropetal maturation._m_K.svg.png) Indeterminate inflorescence with an acropetal maturation and lateral flower buds.
Indeterminate inflorescence with an acropetal maturation and lateral flower buds..svg.png) Indeterminate inflorescence with the subterminal flower to simulate the terminal one (vestige present)
Indeterminate inflorescence with the subterminal flower to simulate the terminal one (vestige present)
In determinate inflorescences the terminal flower is usually the first to mature (precursive development), while the others tend to mature starting from the bottom of the stem. This pattern is called acropetal maturation. When flowers start to mature from the top of the stem, maturation is basipetal, while when the central mature first, divergent.
.svg.png) Determinate inflorescence with acropetal maturation
Determinate inflorescence with acropetal maturation.svg.png) Determinate inflorescence with basipetal maturation
Determinate inflorescence with basipetal maturation.svg.png) Determinate inflorescence with divergent maturation
Determinate inflorescence with divergent maturation
Phyllotaxis
As with leaves, flowers can be arranged on the stem according to many different patterns. See 'Phyllotaxis' for in-depth descriptions
 Alternate flowers
Alternate flowers.svg.png) Opposite flowers
Opposite flowers
Similarly arrangement of leaf in bud is called Ptyxis.
When a single or a cluster of flower(s) is located at the axil of a bract, the location of the bract in relation to the stem holding the flower(s) is indicated by the use of different terms and may be a useful diagnostic indicator.
Typical placement of bracts include:
- Some plants have bracts that subtend the inflorescence, where the flowers are on branched stalks; the bracts are not connected to the stalks holding the flowers, but are adnate or attached to the main stem (Adnate describes the fusing together of different unrelated parts. When the parts fused together are the same, they are connately joined.)
- Other plants have the bracts subtend the pedicel or peduncle of single flowers.
Metatopic placement of bracts include:
- When the bract is attached to the stem holding the flower (the pedicel or peduncle), it is said to be recaulescent; sometimes these bracts or bracteoles are highly modified and appear to be appendages of the flower calyx. Recaulescences is the fusion of the subtending leaf with the stem holding the bud or the bud itself,[2] thus the leaf or bract is adnate to the stem of flower.
- When the formation of the bud is shifted up the stem distinctly above the subtending leaf, it is described as concaulescent.
.svg.png) Flower and subtending bract
Flower and subtending bract Lilium martagon (flower and subtending bract)
Lilium martagon (flower and subtending bract).svg.png) Concaulescence
Concaulescence Solanum lycopersicum (concaulescence)
Solanum lycopersicum (concaulescence).svg.png) Recaulescence
Recaulescence Tilia cordata (recaulescence)
Tilia cordata (recaulescence)
Organization
There is no general consensus in defining the different inflorescences. The following is based on Focko Weberling's Morphologie der Blüten und der Blütenstände (Stuttgart, 1981). The main groups of inflorescences are distinguished by branching. Within these groups, the most important characteristics are the intersection of the axes and different variations of the model. They may contain many flowers (pluriflor) or a few (pauciflor). Inflorescences can be simple or compound.
Simple inflorescences

Indeterminate or racemose
Indeterminate simple inflorescences are generally called racemose /ˈræsɪmoʊs/. The main kind of racemose inflorescence is the raceme (/ˈræsiːm/, from classical Latin racemus, cluster of grapes).[3] The other kind of racemose inflorescences can all be derived from this one by dilation, compression, swelling or reduction of the different axes. Some passage forms between the obvious ones are commonly admitted.
- A raceme is an unbranched, indeterminate inflorescence with pedicellate (having short floral stalks) flowers along the axis.
- A spike is a type of raceme with flowers that do not have a pedicel.
- A racemose corymb is an unbranched, indeterminate inflorescence that is flat-topped or convex due to their outer pedicels which are progressively longer than inner ones.
- An umbel is a type of raceme with a short axis and multiple floral pedicels of equal length that appear to arise from a common point. It is characteristic of Umbelliferae.
- A spadix is a spike of flowers densely arranged around it, enclosed or accompanied by a highly specialised bract called a spathe. It is characteristic of the family Araceae.
- A flower head or capitulum is a very contracted raceme in which the single sessile flowers share are borne on an enlarged stem. It is characteristic of Dipsacaceae.
- A catkin or ament is a scaly, generally drooping spike or raceme. Cymose or other complex inflorescences that are superficially similar are also generally called thus.
.svg.png)
 Epilobium angustifolium
Epilobium angustifolium Spike
Spike- Plantago media (spike)
.svg.png) Racemose corymb
Racemose corymb Iberis umbellata (racemose corymb)
Iberis umbellata (racemose corymb)
 Astrantia minor (umbel)
Astrantia minor (umbel).svg.png)
 Arum maculatum (spadix)
Arum maculatum (spadix).svg.png) Head (round)
Head (round)- Dipsacus fullonum (head)
.svg.png) Catkin (racemose or spicate)
Catkin (racemose or spicate) Alnus incana (ament)
Alnus incana (ament)
Determinate or cymose
Determinate simple inflorescences are generally called cymose. The main kind of cymose inflorescence is the cyme (pronounced 'saim', from the Latin cyma in the sense ‘cabbage sprout’, from Greek kuma ‘anything swollen’[4]).[5] Cymes are further divided according to this scheme:
- Only one secondary axis: monochasium
- Secondary buds always develop on the same side of the stem: helicoid cyme or bostryx
- The successive pedicels are aligned on the same plane: drepanium
- Secondary buds develop alternately on the stem : scorpoid cyme
- The successive pedicels are arranged in a sort of spiral: cincinnus (characteristic of the Boraginaceae and Commelinaceae)
- The successive pedicels follow a zig-zag path on the same plane: rhipidium (many Iridaceae)
- Secondary buds always develop on the same side of the stem: helicoid cyme or bostryx
- Two secondary axes: dichasial cyme
- Secondary axis still dichasial: dichasium (characteristic of Caryophyllaceae)
- Secondary axis monochasia: double scorpioid cyme or double helicoid cyme
- More than two secondary axes: pleiochasium
.svg.png) Double cyme
Double cyme.svg.png) Double cyme
Double cyme.jpg) Bostryx (lateral and top view)
Bostryx (lateral and top view) Hypericum perforatum (bostryx)
Hypericum perforatum (bostryx).jpg) Drepanium (lateral and top view)
Drepanium (lateral and top view) Gladiolus imbricatus (drepanium)
Gladiolus imbricatus (drepanium) Cincinnus (lateral and top view)
Cincinnus (lateral and top view) Symphytum officinale (cincinnus)
Symphytum officinale (cincinnus).jpg) Rhipidium (lateral and top view)
Rhipidium (lateral and top view) Canna sp. (rhipidium)
Canna sp. (rhipidium).svg.png) Dichasium
Dichasium_(inflorescence).svg.png) Dichasium, top view
Dichasium, top view Silene dioica (dichasium)
Silene dioica (dichasium)
A cyme can also be so compressed that it looks like an umbel. Strictly speaking this kind of inflorescence could be called umbelliform cyme, although it is normally called simply 'umbel'.
Another kind of definite simple inflorescence is the raceme-like cyme or botryoid; that is as a raceme with a terminal flower and is usually improperly called 'raceme'.
 Umbelliform cyme
Umbelliform cyme- Pelargonium zonale (umbelliform cyme)
.svg.png) Botryoid
Botryoid Berberis vernae (botryoid)
Berberis vernae (botryoid)
A reduced raceme or cyme that grows in the axil of a bract is called a fascicle. A verticillaster is a fascicle with the structure of a dichasium; it is common among the Lamiaceae. Many verticillasters with reduced bracts can form a spicate (spike-like) inflorescence that is commonly called a spike.
- Gentiana lutea (fascicles)
 Lamium orvala (verticillaster)
Lamium orvala (verticillaster) Mentha longifolia ('spike')
Mentha longifolia ('spike')
Compound inflorescences
Simple inflorescences are the basis for compound inflorescences or synflorescences. The single flowers are there replaced by a simple inflorescence, which can be both a racemose or a cymose one. Compound inflorescences are composed of branched stems and can involve complicated arrangements that are difficult to trace back to the main branch.
A kind of compound inflorescence is the double inflorescence, in which the basic structure is repeated in the place of single florets. For example, a double raceme is a raceme in which the single flowers are replaced by other simple racemes; the same structure can be repeated to form triple or more complex structures.
Compound raceme inflorescences can either end with a final raceme (homoeothetic), or not (heterothetic). A compound raceme is often called a panicle. Note that this definition is very different from that given by Weberling.
Compound umbels are umbels in which the single flowers are replaced by many smaller umbels called umbellets. The stem attaching the side umbellets to the main stem is called a ray.
.svg.png) Homeothetic compound raceme
Homeothetic compound raceme Melilotus officinalis (homoeothetic compound raceme)
Melilotus officinalis (homoeothetic compound raceme).svg.png) Heterothetic compound raceme
Heterothetic compound raceme Hebe albicans (heterothetic compound raceme)
Hebe albicans (heterothetic compound raceme)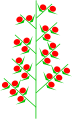 Compound spike
Compound spike Lolium temulentum (compound spike)
Lolium temulentum (compound spike).svg.png) Compound capitulum
Compound capitulum Echinops ritro (compound capitulum)
Echinops ritro (compound capitulum)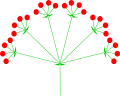 Compound (double) umbel
Compound (double) umbel Laserpicium latifolium (double umbel)
Laserpicium latifolium (double umbel).svg.png) Compound (triple) umbel
Compound (triple) umbel
The most common kind of definite compound inflorescence is the panicle (of Webeling, or 'panicle-like cyme'). A panicle is a definite inflorescence that is increasingly more strongly and irregularly branched from the top to the bottom and where each branching has a terminal flower.
The so-called cymose corymb is similar to a racemose corymb but has a panicle-like structure. Another type of panicle is the anthela. An anthela is a cymose corymb with the lateral flowers higher than the central ones.
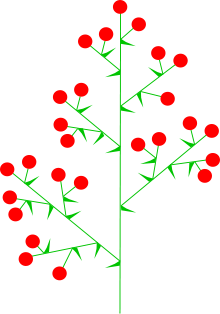
 Vitis vinifera (panicle)
Vitis vinifera (panicle).svg.png) Cymose corymb
Cymose corymb Sambucus nigra (cymose corymb)
Sambucus nigra (cymose corymb).svg.png) Anthela
Anthela Juncus inflexus (anthela)
Juncus inflexus (anthela)
A raceme in which the single flowers are replaced by cymes is called a (indefinite) thyrse. The secondary cymes can be of any of the different types of dichasia and monochasia. A botryoid in which the single flowers are replaced by cymes is a definite thyrse or thyrsoid. Thyrses are often confusingly called panicles.
.svg.png) Thyrse
Thyrse
.svg.png) Thyrsoid
Thyrsoid
Other combinations are possible. For example, heads or umbels may be arranged in a corymb or a panicle.
- Achillea sp. (heads in a corymb)
 Hedera helix (umbels in a panicle)
Hedera helix (umbels in a panicle)
Other
The family Asteraceae is characterised by a highly specialised head technically called a calathid (but usually referred to as 'capitulum' or 'head'). The family Poaceae has a peculiar inflorescence of small spikes (spikelets) organised in panicles or spikes that are usually simply and improperly referred to as spike and panicle. The genus Ficus (Moraceae) has an inflorescence called syconium and the genus Euphorbia has cyathia (sing. cyathium), usually organised in umbels.
 Matricaria chamomilla (calathid)
Matricaria chamomilla (calathid)- Triticum aestivum (compound spikes, "spikes")
 Oryza sativa (spikes in a panicle, "panicle")
Oryza sativa (spikes in a panicle, "panicle") Ficus carica (syconium)
Ficus carica (syconium) Euphorbia tridentata (cyathium)
Euphorbia tridentata (cyathium) Euphorbia cyparissias (cyathia in an umbel)
Euphorbia cyparissias (cyathia in an umbel)- (Coleus-false spike)
Development and patterning
Development
Genetic basis
Genes that shape inflorescence development have been studied at great length in Arabidopsis. LEAFY (LFY) is a gene that promotes floral meristem identity, regulating inflorescence development in Arabidopsis.[6] Any alterations in timing of LFY expression can cause formation of different inflorescences in the plant.[7] Genes similar in function to LFY include APETALA1 (AP1). Mutations in LFY, AP1, and similar promoting genes can cause conversion of flowers into shoots.[6] In contrast to LEAFY, genes like terminal flower (TFL) support the activity of an inhibitor that prevents flowers from growing on the inflorescence apex (flower primordium initiation), maintaining inflorescence meristem identity.[8] Both types of genes help shape flower development in accordance with the ABC model of flower development. Studies have been recently conducted or are ongoing for homologs of these genes in other flower species.
Environmental influences
Inflorescence-feeding insect herbivores shape inflorescences by reducing lifetime fitness (how much flowering occurs), seed production by the inflorescences, and plant density, among other traits.[9] In the absence of this herbivory, inflorescences usually produce more flower heads and seeds.[9] Temperature can also variably shape inflorescence development. High temperatures can impair the proper development of flower buds or delay bud development in certain species, while in others, an increase in temperature can hasten inflorescence development.[10][11][12]
Meristems and inflorescence architecture
The shift from the vegetative to reproductive phase of a flower involves the development of an inflorescence meristem that generates floral meristems.[13] Plant inflorescence architecture depends on which meristems becomes flowers and which become shoots.[14] Consequently, genes that regulate floral meristem identity play major roles in determining inflorescence architecture because their expression domain will direct where the plant's flowers are formed.[13]
On a larger scale, inflorescence architecture affects the quality and quantity of offspring from selfing and outcrossing, as the architecture can influence pollination success. For example, Asclepias inflorescences have been shown to have an upper size limit, shaped by self-pollination levels due to crosses between inflorescences on the same plant or between flowers on the same inflorescence.[15] In Aesculus sylvatica, it has been shown that the most common inflorescence sizes are correlated with the highest fruit production as well.[16]
Issues with inflorescence identification
Some species have flower and inflorescence intermediates. In these cases, some reproductive structures of certain flowers appear as transitional between inflorescences and flowers, making it difficult to accurately categorize and identify the structure as one or the other. For example, plants of the genus Potamogeton have inflorescences that appear to be single flowers.[17]
References
- Bradley, Desmond; Ratcliffe, Oliver; Vincent, Coral; Carpenter, Rosemary; Coen, Enrico (1997-01-03). "Inflorescence Commitment and Architecture in Arabidopsis". Science. 275 (5296): 80–83. doi:10.1126/science.275.5296.80. ISSN 0036-8075. PMID 8974397.
- Kubitzki, Klaus, and Clemens Bayer. 2002. Flowering plants, Dicotyledons: Malvales, Capparales, and non-betalain Caryophyllales. The Families and genera of vascular plants, 5. Berlin: Springer. p. 77
- Oxford English Dictionary. Raceme 2. Bot. A type of inflorescence in which the flowers are arranged on short, nearly equal, lateral pedicels, at equal distances along a single elongated axis
- Collins English Dictionary. 8th Edition first published in 2006
- Oxford English Dictionary. Cyme(1) Bot. A species of inflorescence wherein the primary axis bears a single terminal flower which develops first, the system being continued by axes of secondary and higher orders which develop successively in like manner; a centrifugal or definite inflorescence: opposed to Raceme. Applied esp. to compound inflorescences of this type forming a more or less flat head.
- Shannon, S.; Meeks-Wagner, D. R. (1993-06-01). "Genetic Interactions That Regulate Inflorescence Development in Arabidopsis". The Plant Cell. 5 (6): 639–655. doi:10.1105/tpc.5.6.639. ISSN 1040-4651. PMC 160302. PMID 12271079.
- Schultz, E. A.; Haughn, G. W. (1991-08-01). "LEAFY, a Homeotic Gene That Regulates Inflorescence Development in Arabidopsis". The Plant Cell. 3 (8): 771–781. doi:10.1105/tpc.3.8.771. ISSN 1040-4651. PMC 160044. PMID 12324613.
- Alvarez, John; Guli, Catherine L.; Yu, Xiang-Hua; Smyth, David R. (1992-01-01). "terminal flower: a gene affecting inflorescence development in Arabidopsis thaliana". The Plant Journal. 2 (1): 103–116. doi:10.1111/j.1365-313X.1992.00103.x. ISSN 1365-313X.
- Louda, Svata M.; Potvin, Martha A. (1995-01-01). "Effect of Inflorescence-Feeding Insects on the Demography and Lifetime of a Native Plant". Ecology. 76 (1): 229–245. doi:10.2307/1940645. ISSN 1939-9170. JSTOR 1940645.
- Moss, G (27 November 2015). "Influence of Temperature and Photoperiod on Flower Induction and Inflorescence Development in Sweet Orange (Citrus Sinensis L. Osbeck)". Journal of Horticultural Sciences. 44 (4): 311–320. doi:10.1080/00221589.1969.11514314.
- Bjorkman, T.; Pearson, K. J. (1998-01-01). "High temperature arrest of inflorescence development in broccoli (Brassica oleracea var. italica L.)". Journal of Experimental Botany. 49 (318): 101–106. doi:10.1093/jxb/49.318.101. ISSN 0022-0957.
- BREWSTER, J. L. (1983-04-01). "Effects of Photoperiod, Nitrogen Nutrition and Temperature on Inflorescence Initiation and Development in Onion (Allium cepa L.)". Annals of Botany. 51 (4): 429–440. doi:10.1093/oxfordjournals.aob.a086487. ISSN 0305-7364.
- Souer, E.; Krol, A. van der; Kloos, D.; Spelt, C.; Bliek, M.; Mol, J.; Koes, R. (1998-02-15). "Genetic control of branching pattern and floral identity during Petunia inflorescence development". Development. 125 (4): 733–742. ISSN 0950-1991. PMID 9435293.
- Benlloch, R.; Berbel, A.; Serrano-Mislata, A.; Madueno, F. (2007-09-01). "Floral Initiation and Inflorescence Architecture: A Comparative View". Annals of Botany. 100 (3): 659–676. doi:10.1093/aob/mcm146. ISSN 0305-7364. PMC 2759223. PMID 17679690.
- WYATT, ROBERT (1980-05-01). "The Reproductive Biology of Asclepias Tuberosa: I. Flower Number, Arrangement, and Fruit-Set". New Phytologist. 85 (1): 119–131. doi:10.1111/j.1469-8137.1980.tb04453.x. ISSN 1469-8137.
- Wyatt, Robert (1982-04-01). "Inflorescence Architecture: How Flower Number, Arrangement, and Phenology Affect Pollination and Fruit-Set". American Journal of Botany. 69 (4): 585–594. doi:10.1002/j.1537-2197.1982.tb13295.x. ISSN 1537-2197. JSTOR 2443068.
- Tucker, Shirley C.; Grimes, James (1999-10-01). "The inflorescence: Introduction". The Botanical Review. 65 (4): 303–316. doi:10.1007/BF02857752. ISSN 0006-8101.
Bibliography
- Focko Weberling: Morphologie der Blüten und der Blütenstände; Zweiter Teil. Verlag Eugen Ulmer, Stuttgart 1981
- Wilhelm Troll: Die Infloreszenzen; Erster Band. Gustav Fischer Verlag, Stuttgart 1964
- Wilhelm Troll: Die Infloreszenzen; Zweiter Band, Erster Teil. Gustav Fischer Verlag, Stuttgart 1969
- Wilhelm Troll: Praktische Einführung in die Pflanzenmorphologie. Gustav Fischer Verlag, Jena 1957
- Bernhard Kausmann: Pflanzenanatomie. Gustav Fischer Verlag, Jena 1963
- Walter S. Judd, Christopher S. Campbell, Elizabeth A. Kellogg, Peter F. Stevens, Michael J. Donoghue: Plant Systematics: A Phylogenetic Approach, Sinauer Associates Inc. 2007
- Stevens, P. F. (2001 onwards). Angiosperm Phylogeny Website. Version 7, May 2006 [and more or less continuously updated since].
- Strasburger, Noll, Schenck, Schimper: Lehrbuch der Botanik für Hochschulen. 4. Auflage, Gustav Fischer, Jena 1900, p. 459
- R J Ferry. Inflorescences and Their Names. The McAllen International Orchid Society Journal.Vol. 12(6), pp. 4-11 June 2011
External links
