Ikoma clan
The Ikoma clan (生駒氏, Ikoma-shi) was a Japanese samurai clan that claimed descent from Fujiwara no Fusasaki of the "Northern House" of the Fujiwara clan (Fujiwara Hokke, 藤原北家). During the Sengoku period they supported the Unification of Japan as retainers of Oda Nobunaga, Toyotomi Hideyoshi and Tokugawa Ieyasu. In the Edo period the clan were daimyō and a hatamoto family for the Tokugawa shogunate.
| Ikoma clan 生駒 | |
|---|---|
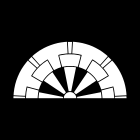 Ikoma clan mon | |
| Home province | Yamato Owari |
| Parent house | |
| Founder | Ikoma Iehiro (生駒家広) |
| Founding year | 15th century |
| Cadet branches | Sanuki-Ikoma clan (讃岐生駒氏) Takamatsu-Ikoma clan (高松藩主家) Yashima-Ikoma clan (矢島藩主家) |
The main line was the Owari-Ikoma clan (尾張生駒氏) and the supporting branch was the Sanuki-Ikoma clan (讃岐生駒氏). Even though the two lines were divided in opinion during the Azuchi–Momoyama period they had close and frequent exchange during the Edo period.
There is a story about the family crest ("mon") of the Ikoma clan. It is said that the crest was once a full circle but during Hideyoshi's Invasion of Korea, the crest painted on the side of the ship was submerged in the waves and only the top half showed above water. They won the subsequent battle and decided to change the crest to a half circle.[1]
Origins
During the Heian period, descendants of Fujiwara no Fusasaki moved to Ikoma District (生駒郡), Yamato Province (now part of Heguri District (平群郡), Nara Prefecture) from which the clan took its name.
The founder of the clan, Ikoma Iehiro (生駒家広), who lived during the Muromachi period moved to Niwa District (丹羽郡), Owari Province to escape the Ōnin War. He was a samurai merchant who lived at Ko-ori Castle (小折城) and accumulated wealth by storing ashes and oils for dyes and used bashaku to transport his goods.
The Ikoma clan genealogy records Ikoma Iehiro as a descendant of Fujiwara no Tameyoshi (藤原為義) but the names of the generations in between are missing. Fujiwara no Tameyoshi was a great-grandson of Fujiwara no Tokihira and a ninth generation descendant of Fujiwara no Fusasaki who founded the "Northern House" of the Fujiwara clan (Fujiwara Hokke, 藤原北家).
Another theory is that the brother of Tameyoshi, Fujiwara no Nobuyoshi (藤原信義), became Ikoma Shōji (生駒庄司) and began using the name Ikoma. In any case, the ancestors are the same.
| Fujiwara no Fusasaki (藤原房前, 681–737), founder of the Hokke branch of the Fujiwara | |||||
| Fujiwara no Matate (藤原真楯, 715–766) | |||||
| Fujiwara no Uchimaro (藤原内麻呂, 756–812) | |||||
| Fujiwara no Fuyutsugu (藤原冬嗣, 775–826) | |||||
| Fujiwara no Nagara (藤原長良, 802–856) | |||||
| Fujiwara no Mototsune (藤原基経, 836–891) | |||||
| Fujiwara no Tokihira (藤原時平, 871–909) | |||||
| Fujiwara no Akitada (藤原顕忠, 898–965) | |||||
| Fujiwara no Motosuke (藤原元輔, 916–975) | |||||
| Fujiwara no Tameyoshi (藤原為義, c.950–?), his brother Fujiwara no Nobuyoshi (藤原信義) was known as Ikoma Shōji (生駒庄司). | |||||
| Ikoma Iehiro (生駒家広, 15th century) moved to Niwa District (丹羽郡), Owari Province | |||||
Sengoku period

During the time of Ikoma Iemune (生駒家宗), the third head of the clan, Inuyama Castle (犬山城) in Owari Province belonged in to Oda Nobuyasu (織田信康). Nobuyasu's nephew Oda Nobunaga (織田信長) began visiting the Ikoma family mansion and approached them for their financial strength and knowledge of the surrounding area. Due to the Battle of Okehazama in 1560 the Ikoma had a brief respite from Nobunaga and were able to conduct business freely in the territory.[2]
The clan became relatives of Oda Nobunaga when Ikoma Iemune's daughter, Ikoma Kitsuno (生駒吉乃) became a concubine of Nobunaga. She had previously been married to Yaheji Dota who died in the Battle of Akechi. After the loss of her husband, Kitsuno returned to her family's home, Ikoma mansion and it was there that she met Nobunaga. It was believed that Oda Nobunaga was charmed by Kitsuno's beauty at first sight, and immediately took her as his concubine. Nobunaga was officially married to Lady Nō, the daughter of Saitō Dōsan, but it was believed that theirs was not a happy marriage, especially since Nōhime could not conceive. It is often thought that Kitsuno was Nobunaga's most beloved concubine and that she probably had a higher position than Nōhime. In 1557 Kitsuno gave birth to Nobutada and later Nobukatsu and Tokuhime (Lady Toku). In 1564, Kitsuno moved to Kori Castle (in present-day Kōnan, Aichi). She suffered due to the difficulty of her childbirths, and in 1566 she died at the age of 29. Even though Nobunaga is often regarded as a callous and bellicose figure, it is said that Nobunaga mourned her throughout the night and had her buried within view of his castle. Her body was cremated and buried in the cemetery at Kyusho temple (the Ikoma family temple), in Tashiro town. Nobunaga gave his son Nobukatsu the area in which Kyusho temple lies in order to protect it and Kitsuno's tomb, out of respect for his treasured concubine. Her brother, Ikoma Ienaga became Nobunaga's stable master (umamawari, 馬廻).[3]
At Ikoma mansion (Ko-ori Castle, 小折城) there was a well known episode when Nobunaga's sandle-bearer, Kinoshita Tōkichirō (木下 藤吉郎), who was later known as Toyotomi Hideyoshi asked Kitsuno to mediate to help him become an officer. He also heated up straw sandles on his bossom and gave them to Nobunaga. There was a strong geographical and blood relation with the Hachisuka clan (蜂須賀氏) of Kawanami-shū (川並衆).[4]
Both Ikoma Ienaga, the fourth clan head and his son Ikoma Toshitoyo, the fifth clan head, served Oda Nobunaga with 1900 koku annual stipend. After the Honnō-ji incident when Nobunaga was assassinated, they served his second son Oda Nobukatsu (織田信雄). After Nobukatsu was forced to become a monk the Ikoma clan became rōnin and so became retainers of Toyotomi Hideyoshi.
At the Battle of Sekigahara they joined the forces of Fukushima Masanori. Ikoma Chikamasa was part of Ishida Mitsunari's force while his son, Ikoma Kazumasa was part of Tokugawa Ieyasu's force. Chikamasa remained at Sanuki and sent his retainers in his stead to attack Tanabe castle in Tango Province. He chose this strategy to preserve the Ikoma clan regardless of which side prevailed. Because Kazumasa fought in Ieyasu's force, Ieyasu allowed Chikamasa to rule his existing domain after the battle, but Chikamasa took responsibility for fighting on the losing side by transferring the headship of the family to Kazumasa. He became a priest and withdrew to Mount Kōya. He was soon permitted to return to Sanuki Province. In 1603, he died in Takamatsu castle.[5]
Edo period

After the war the main line of the Ikoma clan were asked by Tokugawa Ieyasu to be the bannermen for Matsudaira Tadayoshi when he entered Owari Province but after the death of Tadayoshi they became retainers of Tokugawa Yoshinao as samurai of the Owari Domain.
The fifth clan head was Ikoma Toshitoyo (生駒利豊). His older brother, Ikoma Yoshinaga (生駒善長), created a new branch of the family known as the Awa-Ikoma family (阿波生駒家). His sister Jikouin (慈光院) became wife of the lords of the Tokushima Domain (徳島藩)
After the sixth clan head, Ikoma Toshikatsu (生駒利勝), the clan received an annual stipend of 4,000 koku in the Owari Domain and in the aftermath of the Meiji Restoration they became consultants for the Owari-Tokugawa family.
Family Heads
Owari-Ikoma clan (尾張生駒氏)
- Ikoma Iehiro (生駒家広, 15th century) - lord of Ko-ori Castle (小折城).
- Ikoma Toyomasa (生駒豊政, ?–?) - lord of Ko-ori Castle (小折城).
- Ikoma Iemune (生駒家宗, ?–1556) - father of Ikoma Kitsuno, concubine of Oda Nobunaga, mother of Nobutada, Nobukatsu and Tokuhime (Lady Toku).
- Ikoma Ienaga (生駒家長, ?–1607) - retainer of Oda clan, lord of Ko-ori Castle (小折城).
- Ikoma Toshitoyo (生駒利豊, 1575–1670) - retainer of Oda clan, lord of Ko-ori Castle (小折城).
- Ikoma Toshikatsu (生駒利勝, 1629–1694) - son of Toshitoyo's daughter and Hida Tadashige (肥田忠重).
- Ikoma Munekatsu (生駒宗勝, ?–1701)
- Ikoma Munenaga (生駒致長, 1679–1741)
- Ikoma Muneshige (生駒致稠, ?–?)
- Ikoma Chikafusa (生駒周房, 1714–1780)
- Ikoma Chikakuni (生駒周邑, ?–?)
- Ikoma Chikajun (生駒周詢, ?–?)
- Ikoma Chikatake (生駒周武, ?–?)
- Ikoma Chikaakira (生駒周晃, ?–?)
- Ikoma Chikayuki (生駒周行, ?–?)
- Ikoma Shō (生駒鍾, ?–?)
- Ikoma Akihiko (生駒秋彦, ?–?)
- Ikoma Mutsuhiko (生駒陸彦, ?–?)
Branches
Tsuchida-Ikoma clan (土田生駒氏)
- Ikoma Chikashige (生駒親重, ?–1570) - son of a daughter of the clan founder, Ikoma Iehiro, who married Tsuchida Hidehisa (土田秀久).
- Ikoma Chikamasa (生駒親正 1526–1603) - daimyō of Takamatsu Domain.
- Ikoma Kazumasa (生駒一正, 1555–1610) - daimyō of Takamatsu Domain.
- Ikoma Masatoshi (生駒正俊, 1586–1621) - daimyō of Takamatsu Domain.
- Ikoma Takatoshi (生駒高俊, 1611–1659) - daimyō of Takamatsu Domain.
- Ikoma Takakiyo (生駒高清, 1643–1694) - daimyō of Yashima Domain.
- Ikoma Chikaoki (生駒親興, 1655–1702) - daimyō of Yashima Domain.
- Ikoma Masachika (生駒正親, 1678–1706) - daimyō of Yashima Domain.
- Ikoma Chikanao (生駒親猶, 1691–1753) - daimyō of Yashima Domain.
- Ikoma Chikakata (生駒親賢, 1715–1786) - daimyō of Yashima Domain.
- Ikoma Chikakata (生駒親賢, 1715–1786) - daimyō of Yashima Domain.
- Ikoma Chikanobu (生駒親信, ?–?) - daimyō of Yashima Domain.
- Ikoma Chikakira (生駒親章, 1773–1817) - daimyō of Yashima Domain.
- Ikoma Chikanori (生駒親孝, 1790–1836) - daimyō of Yashima Domain.
- Ikoma Chikayoshi (生駒親愛, 1818–1839) - daimyō of Yashima Domain.
- Ikoma Chikamichi (生駒親道, 1827–1855) - daimyō of Yashima Domain.
- Ikoma Chikayuki (生駒親敬, 1849–1880) - daimyō of Yashima Domain.
- Ikoma Chikatsugu (生駒親承, 1868–1886) - daimyō of Yashima Domain.
- Ikoma Chikatada (生駒親忠, ?–?) - daimyō of Yashima Domain.
- Ikoma Keio (生駒慶男, 1715–1786)
- Ikoma Mitsuo (生駒光男, 1715–1786)
- Ikoma Michinori (生駒道孝, 1715–1786)
- Ikoma Michiyuki (生駒道敬, 1715–1786)
- Ikoma Kazuyuki (生駒一敬, 1715–1786)
Awa-Ikoma family (阿波生駒家)
- Ikoma Yoshinaga (生駒善長, ?–1642) - elder brother of Ikoma Toshitoyo who inherited the main line.
- Ikoma Kotokei (生駒言慶, ?–?)
Yagari-Ikoma clan (矢柄生駒氏)
- Ikoma Masayuki (生駒正幸, ?–?) - son of a daughter of Ikoma Kazumasa who married Inokuma Noritoshi (猪熊教利).
- Ikoma Toshiyuki (生駒俊幸, ?–?)
- Ikoma Masanami (生駒正並, ?–?)
Mihara-Ikoma clan (三原生駒氏)
- Ikoma Sukeuemon Masanari (生駒助右衛門正也, ?–?)
- Ikoma Sukeuemon Naomasa (生駒助右衛門直正, ?–?)
- Ikoma Sukeuemon Naoyuki (生駒助右衛門直行, ?–?)
Significant Members
- Ikoma Kitsuno (生駒吉乃, 1528?–1566), concubine of Oda Nobunaga, mother of Nobutada, Nobukatsu and Tokuhime (Lady Toku).
- Ikoma Chikamasa (生駒親正 1526–1603), appointed one of the three chūrō (arbiters) by Toyotomi Hideyoshi.
- Ikoma Kazumasa (生駒一正, 1555–1610), fought with distinction under Oda Nobunaga, and then in Korea with Toyotomi Hideyoshi's forces.
References
- http://www2.harimaya.com/sengoku/html/ikoma_k.html
- http://www.samurai-archives.com/dictionary/i.html
- Specific
- Turnbull, Stephen (2012). Samurai Heraldry. Bloomsbury Publishing. ISBN 1782000143.
- S., Yasuke (2013). Oda Clan: Oda Retainers, Oda Nobunaga, Toyotomi Hideyoshi, Oda Nobuhide, Nobunari Oda, Oichi, Maeda Toshiie, Gamo Ujisato, Akechi Mitsuhide. University-Press Org. ISBN 1230579931.
- Ōta, Gyūichi (2011). The Chronicle of Lord Nobunaga. BRILL. ISBN 9004201629.
- Berry, Mary Elizabeth (1989). Hideyoshi. Harvard Univ Asia Center. ISBN 0674390261.
- Deal, William E. (2005). Handbook to Life in Medieval and Early Modern Japan. Infobase Publishing. ISBN 0816074852.