Hydnora
Hydnora is a group of parasitic plants described as a genus in 1775.[2][3] It is native to Africa, Madagascar, and the Arabian Peninsula.[1][4][5]
| Hydnora | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Hydnora africana | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Magnoliids |
| Order: | Piperales |
| Family: | Aristolochiaceae |
| Subfamily: | Hydnoroideae |
| Genus: | Hydnora Thunb. |
| Synonyms[1] | |
|
Aphyteia Ach. | |
Taxonomy
The following species are listed within the genus Hydnora:[1]
- Hydnora abyssinica A.Br. - Oman, Yemen, Saudi Arabia; S + C + SE + E Africa from Eritrea + Sudan to Namibia + KwaZulu-Natal
- Hydnora africana Thunb. - Angola, Namibia, Cape Province
- Hydnora arabica [6]Bolin & Musselman - Oman & Yemen
- Hydnora esculenta Jum. & H.Perrier - Madagascar
- Hydnora sinandevu Beentje & Q.Luke - Kenya, Tanzania
- Hydnora triceps Drège & E.Mey. - Northern Cape Province, Namibia
- Hydnora visseri Bolin, E.Maass, & Musselman - Northern Cape Province, Namibia
Etymology
The genus name Hydnora derives from the ancient greek ὕδνον, 'truffle',[7][8] because of the somatic structure of this root parasite.[9]
Genomics
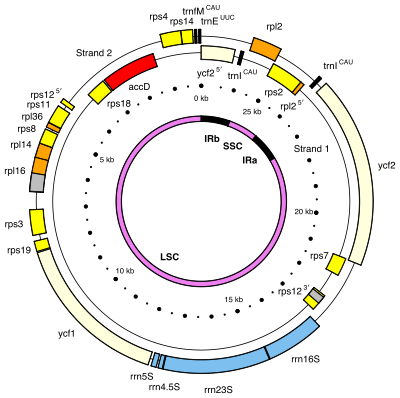
The highly reduced plastid genome map of a species of Hydnora (H. visseri).[10]
One of the smallest plastid genomes among flowering plants has been found in the genus Hydnora.[11] As compared to the chloroplast genome of its closest photosynthetic relatives, the plastome of Hydnora visseri shows extreme reduction in both size (ca. 27 kilo base pairs) and gene content (24 genes appear to be functional).[10]
gollark: Oh, that? We replaced your blood for this, obviously.
gollark: You unthink wrongly.
gollark: <@!330678593904443393> You are in group 1.
gollark: <@356107472269869058> You are in group "", a new group.
gollark: <@!402456897812168705> You are in group one.
References
- Kew World Checklist of Selected Plant Families
- Thunberg, Carl Peter. 1775. Kongliga Vetenskaps Academiens Handlingar 36: 69, .
- Tropicos, Hydnora Thunb.
- Beentje, H. & Luke, Q. (2002). Hydnoraceae. Flora of Tropical East Africa: 1-8.
- Germishuizen, G. & Meyer, N.L. (eds.) (2003). Plants of Southern Africa: an annotated checklist. Strelitzia 14.: i-vi, 1-1231. National Botanical Institute, Pretoria.
- BOLIN, JAY F.; LUPTON, DARACH; MUSSELMAN, LYTTON JOHN (2018-02-09). "Hydnora arabica (Aristolochiaceae), a new species from the Arabian Peninsula and a key to Hydnora". Phytotaxa. 338 (1). doi:10.11646/phytotaxa.338.1.8. ISSN 1179-3163.
- Bailly, Anatole (1981-01-01). Abrégé du dictionnaire grec français. Paris: Hachette. ISBN 2010035283. OCLC 461974285.
- Bailly, Anatole. "Greek-french dictionary online". www.tabularium.be. Retrieved 2017-01-24.
- Gledhill, David (2008-03-06). The Names of Plants. Cambridge University Press. p. 206. ISBN 9780521866453.
- Naumann, Julia; Der, Joshua P.; Wafula, Eric K.; Jones, Samuel S.; Wagner, Sarah T.; Honaas, Loren A.; Ralph, Paula E.; Bolin, Jay F.; Maass, Erika; Neinhuis, Christoph; Wanke, Stefan; dePamphilis, Claude W. (2016-02-01). "Detecting and Characterizing the Highly Divergent Plastid Genome of the Nonphotosynthetic Parasitic Plant Hydnora visseri (Hydnoraceae)". Genome Biology and Evolution. 8 (2): 345–363. doi:10.1093/gbe/evv256. ISSN 1759-6653. PMC 4779604. PMID 26739167.
- List of sequenced plastomes: Flowering plants
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.