Hexahydroxybenzene triscarbonate
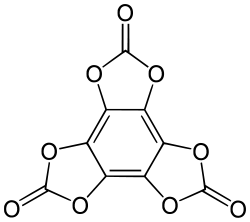
Hexahydroxybenzene triscarbonate is a chemical compound, an oxide of carbon with formula C
9O
9. Its molecular structure consists of a benzene core with the six hydrogen atoms replaced by three carbonate groups. It can be seen as a sixfold ester of hexahydroxybenzene (benzenehexol) and carbonic acid.
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Hexahydroxybenzene triscarbonate | |
| Systematic IUPAC name
3,5,8,10,13,15-Hexaoxatetracyclo[10.3.0.02,6.07,11]pentadeca-1(12),2(6),7(11)-triene-4,9,14-trione | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C9O9 | |
| Molar mass | 252.09 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
The compound was obtained by C. Nallaiah in 1984, as a tetrahydrofuran solvate.[1]
See also
References
- C. Nallaiah (1984), Synthesis of tetrahydroxy-1,4-benzoquinone biscarbonate and hexahydroxybenzene triscarbonate - new organic carbon oxidesTetrahedron, Volume 40, Issue 23, 1984, Pages 4897-4900 doi:10.1016/S0040-4020(01)91324-9
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.