Gustaf Dalén
Nils Gustaf Dalén (Swedish pronunciation: [ˈɡɵ̂sːtav daˈleːn] (![]()
Gustaf Dalén | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Born | 30 November 1869 |
| Died | 9 December 1937 (aged 68) |
| Nationality | Swedish |
| Alma mater | Chalmers University of Technology, Polytechnikum, Zürich |
| Known for | Sun valve and other lighthouse regulators |
| Awards | Nobel Prize in Physics (1912) |
| Scientific career | |
| Fields | Physics, mechanical engineering |
| Institutions | AGA |
Early years
Dalén was born in Stenstorp, a small village in Falköping Municipality, Västra Götaland County. He managed the family farm, which he expanded to include a market garden, a seed merchants and a dairy. In 1892 he invented a milk-fat tester to check milk quality of the milk delivered and went to Stockholm to show his new invention for Gustaf de Laval. de Laval was impressed by the self-taught Dalén and the invention and encouraged him to get a basic technical education. He was admitted to the Chalmers University of Technology where he earned his Master's degree and a Doctorate on leaving in 1896. Dalén was much the same type of inventor as Gustaf de Laval, not afraid of testing "impossible" ideas, but Dalén was much more careful with the company economy. The products should have a solid market place before he introduced a new product.
Career with AGA
In 1906 Dalén became chief engineer at the Gas Accumulator Company (manufacturer and distributor of acetylene) and in 1909 when AGA was founded, he was appointed the managing director for the company. During his life, AGA was one of the most innovative companies in Sweden and produced a large variety of products that grew every year. Finally in the early 1970s AGA was forced to reduce the number of markets it was involved in and concentrate on the production of gases for industrial use.
In 1909 he ascended to the position of Managing Director of the renamed company Svenska Aktiebolaget Gasaccumulator (AGA). AGA developed lighthouses using Dalén's products. In 1910 the company bought a large real estate in Lidingö and built a production plant that was completed around 1912, when they moved out from the facilities in Stockholm.
Dalen light

Initially Dalén worked with acetylene (IUPAC: ethyne), a flammable and sometimes explosive hydrocarbon gas. Dalén invented Agamassan (Aga), a substrate used to absorb the gas allowing safe storage and hence commercial exploitation.
Acetylene produced an ultra-bright white light which superseded the less bright LPG as the fuel of choice for lighthouse illumination.
Dalén exploited the new fuel, developing the Dalén light which incorporated another invention, the sun valve. This device allowed the light to operate only at night, conserving fuel, and extending their service life to over a year.
The 'Dalen Flasher' was a device that, except for a small pilot light, only consumed gas during the flash stage. This reduced gas consumption by more than 90%. The AGA lighthouse equipment worked without any type of electric supply and was thus extremely reliable.
To a rugged coastal area like Scandinavia, his mass-produced, robust, minimal maintenance buoys were a significant boon to safety and livelihood. AGA Lighthouses covered the entire Panama Canal.
AGA cooker
In 1922 he patented his invention of the AGA cooker. Most of the testing for the cooker was made in his private kitchen in his Villa Ekbacken that was built when AGA moved to Lidingö in 1912 but that he never actually had a chance to see with his own eyes. His family helped him with the development work, checking temperatures, airflow etc., as the development work proceeded.
Personal life
His parents were Anders and Lovisa Dalén. He married Elma Persson in 1901. They had four children, two daughters and two sons:
- Maja, married Silfverstolpe (1904–1995)
- Gunnar (1905–1970)
- Anders (1907–1994)
- Inga-Lisa, married Keen (1910–2006)
The accident in 1912
Early in 1912, Dalén was blinded in an acetylene explosion during a test of maximum pressure for the accumulators. Later the same year he was awarded the Nobel Prize for physics for his work on lighthouse technology. Too ill to attend the presentation, Dalén had his brother, ophthalmologist Professor Albin Dalén of the Caroline Institute, stand in his place.
The presentation speech praised the quality of sacrificing personal safety in scientific experimentation, a compliment that compared Dalén with Nobel himself. Despite his blindness, Dalén controlled AGA until his death in 1937. He received over 100 patents during his lifetime.
Honours and awards
- Nobel Prize for Physics 1912
- Member of the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences
- Member of the Academy of Science and Engineering
Image gallery
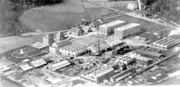 The AGA production and development center around 1920.
The AGA production and development center around 1920. Some of the remaining AGA-buildings, today working as a center for small companies. The AGA head office with about 150 employees is still in some of the buildings. Photo: October 2009.
Some of the remaining AGA-buildings, today working as a center for small companies. The AGA head office with about 150 employees is still in some of the buildings. Photo: October 2009. Gustaf Dalén, 1926 at the peak of his career as the managing director for AGA industry.
Gustaf Dalén, 1926 at the peak of his career as the managing director for AGA industry. Villa Ekbacken, the private residence for the Dalén family, built in 1912 close to AGA production plant. Today the residence for Canada's ambassador in Sweden.
Villa Ekbacken, the private residence for the Dalén family, built in 1912 close to AGA production plant. Today the residence for Canada's ambassador in Sweden. Gustaf Dalén and his wife Elma, outside Villa Ekbacken, 1937.
Gustaf Dalén and his wife Elma, outside Villa Ekbacken, 1937.
References
Further reading
- Clark, R. N. (2003). "Nils Gustaf Dalén (1869–1937): Inventor, experimenter, engineer, and nobel laureate". IEEE Control Systems Magazine. 23 (4): 68–70. doi:10.1109/MCS.2003.1213605.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Gustaf Dalén. |
- Gustaf Dalén biography from the AGA corporation
- (in Swedish) The Dalén Museum, a museum in Stenstorp celebrating Dalén
Gustaf Dalén on Nobelprize.org
