Globotriaosylceramide
Globotriaosylceramide is a globoside.[1] It is also known as CD77, Gb3, GL3, and ceramide trihexoside.[2] It is one of the few clusters of differentiation that is not a protein.
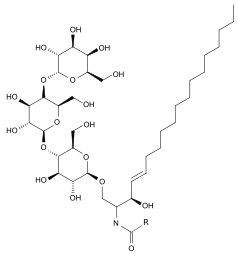
It is formed by the alpha linkage of galactose to lactosylceramide catalyzed by A4GALT.
It is metabolized by alpha-galactosidase, which hydrolyzes the terminal alpha linkage.
Clinical significance
Defects in the enzyme alpha-galactosidase lead to the buildup of globotriaosylceramide, causing Fabry's disease.[3] The pharmaceutical drug migalastat enhances the function of alpha-galactosidase and is used to treat Fabry's.
Globotriaosylceramide is also one of the targets of Shiga toxin, which is responsible for pathogenicity of enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli (EHEC).
The bacterial Shiga toxin can be used for targeted therapy of gastric cancer, because this tumor entity expresses the receptor of the Shiga toxin. For this purpose an unspecific chemotherapeutical is conjugated to the B-subunit to make it specific. In this way only the tumor cells, but not healthy cells should be destroyed during therapy.[4]
References
- globotriaosylceramide at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
- Bekri S, Lidove O, Jaussaud R, Knebelmann B, Barbey F (October 2006). "The role of ceramide trihexoside (globotriaosylceramide) in the diagnosis and follow-up of the efficacy of treatment of Fabry disease: a review of the literature". Cardiovasc Hematol Agents Med Chem. 4 (4): 289–97. doi:10.2174/187152506778520718. PMID 17073606. Archived from the original on 2013-04-14.
- Desnick RJ, Ioannou YA, Eng CM. a-Galactosidase A deficiency: Fabry disease. In: Scriver CR, Beaudet AL, Sly WS, Valle D, eds. The metabolic & molecular bases of inherited disease. 8th ed. Vol. 3. New York: McGraw-Hill, 2001:3733-74.
- Gastric adenocarcinomas express the glycosphingolipid Gb3/CD77: Targeting of gastric cancer cells with Shiga toxin B-subunit. https://doi.org/10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-15-0633