George Allen Mansfield
George Allen Mansfield was a prominent Australian architect of the nineteenth century who designed many iconic buildings in Sydney, New South Wales, Australia.
George Allen Mansfield | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Born | 1834 |
| Died | 1908 (aged 73–74) |
| Nationality | Australian |
| Occupation | Architect |
| Spouse(s) | Mary Emma Allen |
| Children | Seven |
| Practice | John Fredrick Hilly |
Life
Born in 1834 in Sydney, his father, the Reverend Ralph Mansfield, had been a Methodist missionary.[1] He was educated at the privately run school of Mr. W. T. Cape and then articled with the architect John Fredrick Hilly.
He married Mary Emma Allen, third daughter of prominent politician and solicitor George Allen, and had seven children. The family lived in Tranby, Glebe, which was designed by Mansfield.[2] They then lived at Oakwood in Bridge Road From 1864 to 1869, and Lynedoch in Glebe Road from 1870 to 1879.[3]
Mansfield was a lieutenant in the Glebe branch of the New South Wales Militia, a commissioner for Peace and an alderman for Glebe Council. Mansfield was also a member of the Royal Institute of British Architects,[1] and the founder and first president of the Institute of Architecture NSW (now Australian Institute of Architects).
He died in 1908[1] and he is remembered in the name of Mansfield Street, Glebe.[2][4]
Works
His many prominent colonial buildings including and ten listed on the NSW State Heritage Register,[2] include:
Schools

- Castle Hill Public School, Sydney
- Cleveland Street Public School[6]
- Crown Street Public School[7][8]
- The Old School, Darlington[2]
- Mudgee Public School (part)
- Newcastle East Public School
- North Sydney Technical High School (1876–1877)[9]
- Pyrmont Public School[1]
- Redfern Public School (now demolished)[6]
- Rosebank College
- Sussex Street Primary School, Sydney[1]
Houses
- Toxteth Park for his inlaws
- Carthona, Darling Point
- 'The Warren' at Marrickville
- Coombing Park at Carcoar for the founders of Cobb and Co
Commercial buildings

- Australia Hotel (now demolished for the MLC Centre)
- several bank buildings for the Commercial Bank of Australia, now Westpac[10]
- AMP offices in Pitt Street, Sydney
- Much of commercial building stock of O’Connell Street
- The Darling Harbour facilities of AGL Energy (now Demolished)[1]
- Mansfield House in Maitland
Other
- Royal Prince Alfred Hospital, Admission Block and Victoria & Albert Pavilions (1904)[11]
- History House, Macquarie Street offices for the Royal Australian Historical Society[12]
- Macleay Museum, (University of Sydney)[2]
Gallery
former_public_school.jpg) Former public school
Former public school Tranby House, Glebe
Tranby House, Glebe Additions to St Scholastica's, formerly known as Toxteth Park
Additions to St Scholastica's, formerly known as Toxteth Park Carthona, Darling Point, circa 1870 before the 1880s extensions at the back were made
Carthona, Darling Point, circa 1870 before the 1880s extensions at the back were made Royal Prince Alfred Hospital - Administration Building
Royal Prince Alfred Hospital - Administration Building- History House
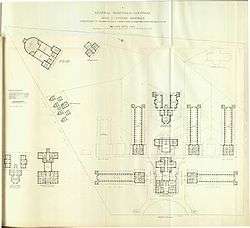 Mansfield's 1893 floor plan of RPA.
Mansfield's 1893 floor plan of RPA.
See also
- List of George Allen Mansfield buildings
References
- "DEATH OF MR. G. A. MANSFIELD". The Sydney Morning Herald. 21 January 1908. p. 6 – via Trove, National Library of Australia.
- Glebe Walks.
- George Allen Mansfield Retrieved 8 May 2017.
- NSW chapter of the Australian Institute of Architects Webpage
- "Uniting Church and Pipe Organ". New South Wales State Heritage Register. Office of Environment and Heritage. H00747. Retrieved 13 October 2018.
- Planning department report for Red Fern Public School Archived 3 August 2008 at the Wayback Machine.
- "Crown Street Public School". New South Wales State Heritage Register. Office of Environment and Heritage. H00562. Retrieved 13 October 2018.
- Dictionary of Sydney
- "North Sydney Technical High School (former)". New South Wales State Heritage Register. Office of Environment and Heritage. H00517. Retrieved 2 June 2018.
- CBC officers Club Website Archived 25 April 2013 at the Wayback Machine.
- Glebe Walks Webpage.
- Royal Australian Historical Society Website.
External links
- Portrait at Institute of Architecture