Geography of Mayotte
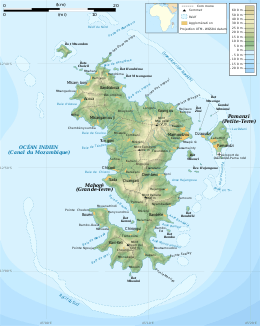
Mayotte is an island of volcanic origin in the northernmost Mozambique Channel, about one-half of the way from northern Madagascar to northern Mozambique. Mayotte is part of the Comoro Islands, and like them is the result of a former hot spot, the oldest of the Comoros archipelago, formed about 7.7 mya.[1] Mayotte has an area of 374 square kilometres, and a coastline of length 185.2 km. Its maritime claims are an exclusive economic zone of 200 nautical miles, and a territorial sea of 12 nm.
| Native name: Mahoré Nickname: Grande-Terre | |
|---|---|
 Map of Mayotte | |
 | |
| Geography | |
| Location | Mozambique Channel |
| Coordinates | 12°50′S 45°10′E |
| Archipelago | Comoro Islands |
| Area | 374 km2 (144 sq mi) |
| Length | 39 km (24.2 mi) |
| Width | 22 km (13.7 mi) |
| Coastline | 185.2 km (115.08 mi) |
| Highest elevation | 660 m (2,170 ft) |
| Highest point | Benara |
| Administration | |
France | |
| Overseas Department | Mayotte |
| Largest settlement | Mamoudzou (pop. 57,281) |
| Demographics | |
| Population | 256,518 (2017) |
| Pop. density | 690/km2 (1,790/sq mi) |
| Ethnic groups | Mahoran |
Terrain
The terrain of the island is undulating, with deep ravines and ancient volcanic peaks. The lowest point is the Indian Ocean, and the highest is Benara, at 660 m. The Baie de Bouéni is a large bay in the south-west of the island. Geologically, it is located within the Somali plate.
Climate
The climate of Mayotte is a tropical, marine climate. Between November and May, there is a hot, humid and rainy season, during the northeastern monsoon. At this time of the year, a hazard is posed by cyclones. Between May and November, there is a cooler, dry season.
See also
Notes
- Thomas Schlüter, Martin H. Trauth, Geological Atlas of Africa, s.v. "The Comoros", 2008:74.