Geography of French Polynesia
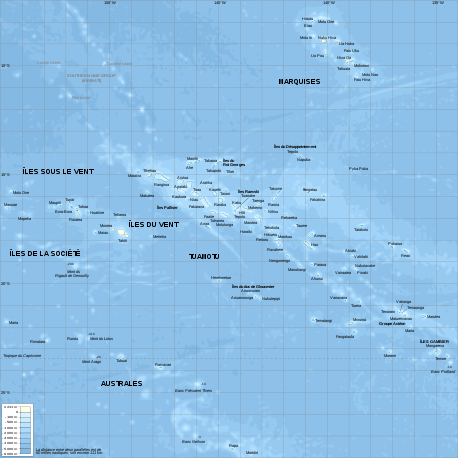
French Polynesia is located in Oceania. It is a group of six archipelagos in the South Pacific Ocean, about halfway between South America and Australia. Its area is about 4,167 km² (around 130 islands),[1] of which 3,827 km² is land and 340 km² is (inland) water. It has a coastline of 2,525 km but no land borders with other countries.
Physical geography
There are 118 islands in French Polynesia (and many more islets or motus around atolls). Four of the islands are volcanic and one island is coral. Makatea in French Polynesia is one of the three great phosphate rock islands in the Pacific Ocean – the others are Banaba (Ocean Island) in Kiribati and Nauru. The terrain consists of a mixture of rugged high islands and low islands with reefs.
It is made up of six archipelagos. The largest and most populated island is Tahiti, in the Society Islands.
The archipelagos are:
- Marquesas Islands – administratively making the Marquesas Islands subdivision (12 high islands and 1 atoll)
- Society Islands – administratively subdivided into the Windward Islands subdivision (5 high islands) and the Leeward Islands District (5 atolls)
- Tuamotu Archipelago – administratively part of the Tuamotu-Gambier subdivision (80 atolls, grouping over 3,100 islands or islets)
- Gambier Islands – administratively part of the Tuamotu-Gambier subdivision (2 atolls in genesis)
- Austral Islands – administratively part of the Austral Islands subdivision (5 atolls)
- Bass Islands – administratively part of the Austral Islands subdivision (2 atolls)
Aside from Tahiti, some other important atolls, islands, and island groups in French Polynesia are: Ahē, Bora Bora, Hiva 'Oa, Huahine, Mai'ao, Maupiti, Meheti'a, Mo'orea, Nuku Hiva, Raiatea, Taha'a, Tetiaroa, Tupua'i, and Tūpai. The country's highest point is Mont Orohena on Tahiti at 2,241 meters high.[2]
Climate
The country has a tropical, but moderate climate. Occasional cyclonic storms occur in January.
Statistics
- Maritime claims
- Territorial sea: 12 nautical miles
- Exclusive economic zone: 200 nautical miles
- Natural resources
- Timber, fish, cobalt, hydropower
.jpg) Hatiheu Bay on the island of Nuku Hiva
Hatiheu Bay on the island of Nuku Hiva - Land use
- Arable land: 0.68%
- Permanent crops: 6.28%
- Other: 93.03% (2012)
- Irrigated land
- 10 km2 (2003)
See also
References
- Kingfisher Geography Encyclopedia. ISBN 1-85613-582-9. Page 546
- "French Polynesia", Wikipedia, 2019-04-21, retrieved 2019-04-23
![]()
