General somatic efferent fibers
The general (spinal) somatic efferent neurons (GSE, 'somatomotor, or somatic motor fibers), arise from motor neuron cell bodies in the ventral horns of the gray matter within the spinal cord. They exit the spinal cord through the ventral roots, carrying motor impulses to skeletal muscle through a neuromuscular junction.[1]
| General somatic efferent fibers | |
|---|---|
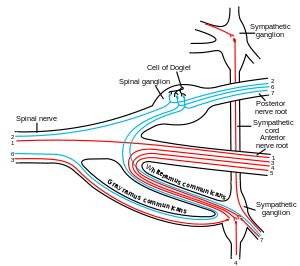 Scheme showing structure of a typical spinal nerve. 1. Somatic efferent. 2. Somatic afferent. 3,4,5. Sympathetic efferent. 6,7. Sympathetic afferent. | |
| Anatomical terminology |
Of the somatic efferent neurons, there exist subtypes.
- Alpha motor neurons (α) target extrafusal muscle fibers.
- Gamma motor neurons (γ) target intrafusal muscle fibres
Cranial nerves also supply their own somatic efferent neurons to the extraocular muscles and some of the muscles of the tongue.
See also
- Nerve fiber
- Efferent nerve
References
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 849 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
- Ross, Muriel D. (April 1969). "The general visceral efferent component of the eighth cranial nerve" (PDF). Journal of Comparative Neurology. 135 (4): 453–477. doi:10.1002/cne.901350405.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.