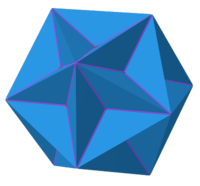
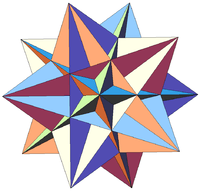
Excavated dodecahedron
In geometry, the excavated dodecahedron is a star polyhedron that looks like a dodecahedron with concave pentagonal pyramids in place of its faces. Its exterior surface represents the Ef1g1 stellation of the icosahedron. It appears in Magnus Wenninger's book Polyhedron Models as model 28, the third stellation of icosahedron.
| Excavated dodecahedron | |
|---|---|
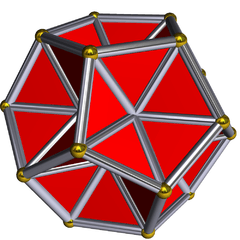 | |
| Type | Stellation |
| Index | W28, 26/59 |
| Elements (As a star polyhedron) | F = 20, E = 60 V = 20 (χ = −20) |
| Faces | 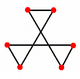 Star hexagon |
| Vertex figure |  Concave hexagon |
| Stellation diagram |  |
| Symmetry group | icosahedral (Ih) |
| Dual polyhedron | self |
| Properties | noble polyhedron, vertex transitive, self-dual polyhedron |
Description
All 20 vertices and 30 of its 60 edges belong to its dodecahedral hull. The 30 other internal edges are longer and belong to a great stellated dodecahedron. (Each contains one of the 30 edges of the icosahedral core.) There are 20 faces corresponding to the 20 vertices. Each face is a self-intersecting hexagon with alternating long and short edges and 60° angles. The equilateral triangles touching a short edge are part of the face. (The smaller one between the long edges is a face of the icosahedral core.)
| Core | Long edges | Faces | Hull | Cut |
|---|---|---|---|---|
 Icosahedron |
 G. s. dodecahedron |
 |
 Dodecahedron |
 one hexagonal face in blue |
Faceting of the dodecahedron
It has the same external form as a certain facetting of the dodecahedron having 20 self-intersecting hexagons as faces. The non-convex hexagon face can be broken up into four equilateral triangles, three of which are the same size. A true excavated dodecahedron has the three congruent equilateral triangles as true faces of the polyhedron, while the interior equilateral triangle is not present.
The 20 vertices of the convex hull match the vertex arrangement of the dodecahedron.
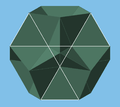 One of the star hexagon faces highlighted.
One of the star hexagon faces highlighted.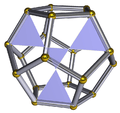 Its face as a facet of the dodecahedron.
Its face as a facet of the dodecahedron.
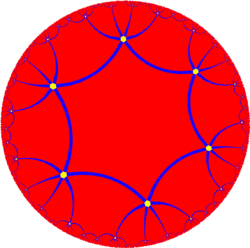
The faceting is a noble polyhedron. With six six-sided faces around each vertex, it is topologically equivalent to a quotient space of the hyperbolic order-6 hexagonal tiling, {6,6} and is an abstract type {6,6}6. It is one of ten abstract regular polyhedra of index two with vertices on one orbit.[1][2]
Related polyhedra
 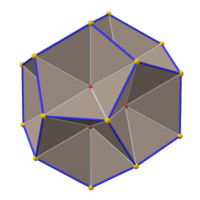 A pentakis dodecahedron (left) with inverted pyramids (right) has the same surface. |
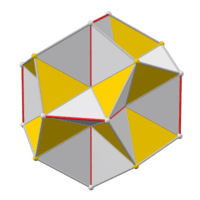 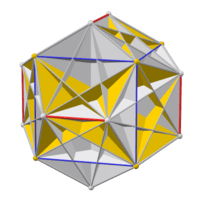 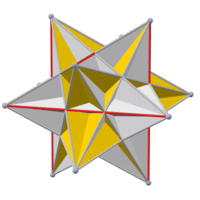 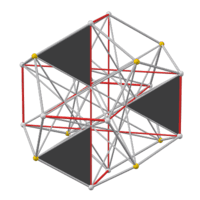 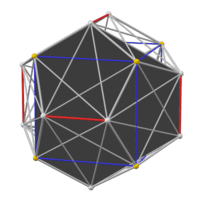 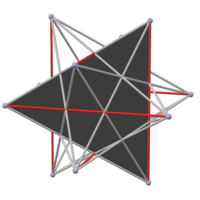 The faces of the e. d. (left) are part of the faces of the great icosahedron (right). Extending the short edges of a hexagon until they meet gives the triangle that contains it. Replacing each self-intersecting hexagon with a convex one gives a figure containing the edges of the compound of five cubes (middle). But this is not really a polyhedron, because each of these edges belongs to only one face. |
  The great dodecahedron (left) is an excavated icosahedron. It also has 60 visible triangles. But unlike the e. d. (right) it has convex faces and thus no inner edges. |
References
- Regular Polyhedra of Index Two, I Anthony M. Cutler, Egon Schulte, 2010
- Regular Polyhedra of Index Two, II Beitrage zur Algebra und Geometrie 52(2):357-387 · November 2010, Table 3, p.27
- H.S.M. Coxeter, Regular Polytopes, (3rd edition, 1973), Dover edition, ISBN 0-486-61480-8, 3.6 6.2 Stellating the Platonic solids, pp.96-104
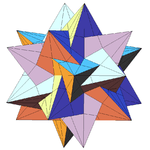
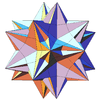
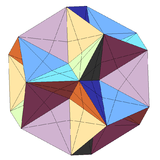
| Notable stellations of the icosahedron | |||||||||
| Regular | Uniform duals | Regular compounds | Regular star | Others | |||||
| (Convex) icosahedron | Small triambic icosahedron | Medial triambic icosahedron | Great triambic icosahedron | Compound of five octahedra | Compound of five tetrahedra | Compound of ten tetrahedra | Great icosahedron | Excavated dodecahedron | Final stellation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
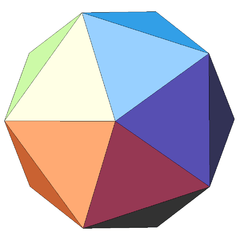 |
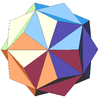 |
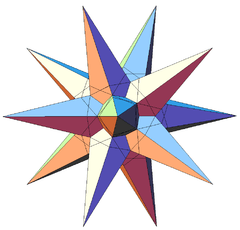 |
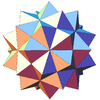 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
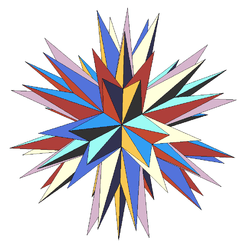 | |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 | |
| The stellation process on the icosahedron creates a number of related polyhedra and compounds with icosahedral symmetry. | |||||||||