Economic impacts of climate change
In 2019, climate change contributed to extreme weather events causing at least $100 billion in damages.[1] By 2050, cumulative damages from climate change may reach $8 trillion, impoverishing the world as a whole by 3% of GDP and the poorest regions by more.[2] A 2017 survey of independent economists looking at the effects of climate change found that "estimates for future damages ... rang[e] from 2% to 10% or more of global GDP per year."[3] The Stern Review presented to the British Government also predicted that world gross domestic product would be reduced by several percent due to climate related costs; among the factors they considered were increased extreme weather events and stresses to low-lying areas due to sea level rise. Insofar as their calculations may omit ecological effects that are difficult to quantify economically (such as human deaths or loss of biodiversity) or whose economic consequences will manifest slowly, these estimates may be low.[4]
Distribution of impacts
Climate change impacts can be measured as an economic cost (Smith et al., 2001:936-941).[5] This is particularly well-suited to market impacts, that is impacts that are linked to market transactions and directly affect GDP. Monetary measures of non-market impacts, e.g., impacts on human health and ecosystems, are more difficult to calculate. Other difficulties with impact estimates are listed below:
- Knowledge gaps: Calculating distributional impacts requires detailed geographical knowledge, but these are a major source of uncertainty in climate models.
- Vulnerability: Compared with developed countries, there is a limited understanding of the potential market sector impacts of climate change in developing countries.
- Adaptation: The future level of adaptive capacity in human and natural systems to climate change will affect how society will be impacted by climate change. Assessments may under- or overestimate adaptive capacity, leading to under- or overestimates of positive or negative impacts.
- Socioeconomic trends: Future predictions of development affect estimates of future climate change impacts, and in some instances, different estimates of development trends lead to a reversal from a predicted positive, to a predicted negative, impact (and vice versa).
In a literature assessment, Smith et al. (2001:957-958) concluded, with medium confidence, that:
- climate change would increase income inequalities between and within countries.
- a small increase in global mean temperature (up to 2 °C, measured against 1990 levels) would result in net negative market sector in many developing countries and net positive market sector impacts in many developed countries.
With high confidence, it was predicted that with a medium (2-3 °C) to high level of warming (greater than 3 °C), negative impacts would be exacerbated, and net positive impacts would start to decline and eventually turn negative.
Non-market impacts
Smith et al. (2001:942) predicted that climate change would likely result in pronounced non-market impacts.[5] Most of impacts were predicted to be negative. The literature assessment by Smith et al. (2001) suggested that climate change would cause substantial negative health impacts in developing countries. Smith et al. (2001) noted that few of the studies they reviewed had adequately accounted for adaptation. In a literature assessment, Confalonieri et al. (2007:415) found that in the studies that had included health impacts, those impacts contributed substantially to the total costs of climate change.[6]
Market sector
In 2019 the International Labour Organization published a report titled: "Working on a warmer planet: The impact of heat stress on labour productivity and decent work", in which it claims that even if the rise in temperature will be limited to 1.5 degree, by the year 2030, Climate Change will cause losses in productivity reaching 2.2% of all the working hours, every year. This is equivalent to 80 million full time jobs, or 2,400 billion dollars. The sector expected to be most affected is agriculture, which is projected to account for 60% of this loss. The construction sector is also projected to be severely impacted and accounts for 19% of projected losses. Other sectors that are most at risk are environmental goods and services, refuse collection, emergency, repair work, transport, tourism, sports and some forms of industrial work[7][8].
In 2020 McKinsey & Company issued a report about the current and future impacts of climate change on the economy. The report says that trillions of dollars and hundreds of millions of lives are at risk. Climate change should strongly influence the decisions of the business and governmental leaders[9]. The report, for example, found that socioeconomic impacts can increase by 2 - 20 times compare to today level by 2050[10].
Climate change driven migration possibly helped to trigger Brexit - the exit of Britain from European Union[11][12]. The uncertainty about Brexit has shrunk the British economy in 2019[13], and may cause it to contract further in the future Brexit can make it shrink it much more.
Agriculture
Depending on underlying assumptions, studies of the economic impacts of a doubling in atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO2) from pre-industrial levels conclude that this would have a slightly negative to moderately positive aggregate effect (i.e., total impacts across all regions) on the agricultural sector (Smith et al., 2001:938).[5] This aggregate effect hides substantial regional differences, with benefits mostly predicted in the developed world and strongly negative impacts for populations poorly connected to regional and global trading systems. Poorer countries are more exposed to the weather because of the important role of agriculture and water resources in the economy.[14]
Other sectors
A number of other sectors will be affected by climate change, including the livestock, forestry, and fisheries industries. Other sectors sensitive to climate change include the energy, insurance, tourism and recreation industries. The aggregate impact of climate change on most of these sectors is highly uncertain (Schneider et al., 2007:790).[15]
Regions
- Africa: In Africa, coastal facilities are economically significant. In a literature assessment, Desanker et al. (2001:490) concluded that climate change would result in sea-level rise, coastal erosion, saltwater intrusion, and flooding. Desanker et al. (2001) predicted that these changes would have a significant impact on African communities and economies.[16]
- Coasts and low-lying areas: In literature assessment, Nicholls et al. (2007:338-339) concluded that the socio-economic impacts of climate change on coastal and low-lying areas would be overwhelmingly adverse.[17] Some benefits, however, were noted, e.g., the opening of new ocean routes due to reduced sea ice. Compared with developed countries, the protection costs associated with projected sea level rise were found to be relatively higher for developing countries.
- Polar regions: Anisimov et al. (2001:804) reviewed the literature on climate change impacts in polar regions.[18] With very high confidence, they concluded that the impact of climate change on infrastructure would increase economic costs. New opportunities for trading and shipping across the Arctic ocean, lower operational costs for the oil and gas industry, lower heating costs, and easier access for ship-based tourism, were expected to bring economic benefits.
- Small islands: In a literature assessment, Mimura et al. (2007:689) concluded, with high confidence, that on small islands, tourism would, for the most part, be negatively affected by climate change.[19] On many small islands, tourism is a major contributor to GDP and employment.
Other systems and sectors
- Freshwater resources: In this sector, costs and benefits of climate change may take several forms, including monetary costs and benefits, and ecosystem and human impacts, e.g., loss of aquatic species and household flooding. In a literature assessment, Kundzewicz et al. (2007:191) found that few of these costs had been estimated in monetary terms.[20] In respect to the water supply, they predicted that costs would very likely exceed benefits. Predicted costs included the potential need for infrastructure investments to protect against floods and droughts.
- Industry, settlements and society:
- In a literature assessment, Wilbanks et al. (2007:377) concluded, with high confidence, that the economic costs of extreme weather events, at large national or large regional scale, would be unlikely to exceed more than a few percent of the total economy in the year of the event, except for possible abrupt changes.[21] In smaller locations, particularly developing countries, it was estimated with high confidence that, in the year of the extreme event, short-run damages could amount to more than 25% GDP.
- Infrastructure: According to Tol (2008), roads, airport runways, railway lines and pipelines, (including oil pipelines, sewers, water mains etc.) may require increased maintenance and renewal as they become subject to greater temperature variation and are exposed to weather that they were not designed for.[22]
Aggregate impacts
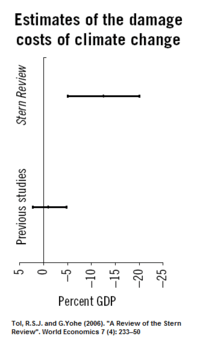
Aggregating impacts adds up the total impact of climate change across sectors and/or regions (IPCC, 2007a:76).[23] In producing aggregate impacts, there are a number of difficulties, such as predicting the ability of societies to adapt climate change, and estimating how future economic and social development will progress (Smith et al., 2001:941).[5] It is also necessary for the researcher to make subjective value judgements over the importance of impacts occurring in different economic sectors, in different regions, and at different times.
In 2020 the World Economic Forum ranked climate change as the biggest risk to economy and society[24].
A United States government report in November 2018 raised the possibility of US GDP going down 10% as a result of the warming climate, including huge shifts in geography, demographics and technology.[25]
Smith et al. (2001) assessed the literature on the aggregate impacts of climate change. With medium confidence, they concluded that a small increase in global average temperature (up to 2 °C, measured against 1990 levels) would result in an aggregate market sector impact of plus or minus a few percent of world GDP. Smith et al. (2001) found that for a small to medium (2-3 °C) global average temperature increase, some studies predicted small net positive market impacts. Most studies they assessed predicted net damages beyond a medium temperature increase, with further damages for greater (more than 3 °C) temperature rises.
With low confidence, Smith et al. (2001) concluded that the non-market impacts of climate change would be negative. Smith et al. (2001:942) decided that studies might have understated the true costs of climate change, e.g., by not correctly estimating the impact of extreme weather events. It was thought possible that some of the positive impacts of climate change had been overlooked, and that adaptive capacity had possibly been underestimated.
Some of the studies assessed by Schneider et al. (2007:790) predicted that gross world product could increase for 1-3 °C warming (relative to temperatures over the 1990-2000 period), largely because of aggregate benefits in the agricultural sector.[15] In the view of Schneider et al. (2007), these estimates carried low confidence. Stern (2007) assessed climate change impacts using the basic economics of risk premiums (Yohe et al., 2007:821).[26] He found that unmitigated climate change could result in a reduction in welfare equivalent to a persistent average fall in global per-capita consumption of at least 5%. The study by Stern (2007) has received both criticism and support from other economists (see Stern Review for more information). IPCC (2007a) concluded that "Aggregate estimates of costs mask significant differences in impacts across sectors, regions and populations and very likely underestimate damage costs because they cannot include many non-quantifiable impacts."[23]
Richard S Tol has twice revised his figure incorporated as fig 10-1 in IPCC reports from his "The Economic Effects of Climate Change". In the second revision he says "The IPCC discussion of this figure offers some useful cautions about interpretation:" and quotes that as saying:
"Estimates agree on the size of the impact (small relative to economic growth), and 17 of the 20 impact estimates shown in Figure 10-1 are negative. Losses accelerate with greater warming, and estimates diverge. The new estimates have slightly widened the uncertainty about the economic impacts of climate. Welfare impacts have been estimated with different methods, ranging from expert elicitation to econometric studies and simulation models. Different studies include different aspects of the impacts of climate change, but no estimate is complete; most experts speculate that excluded impacts are on balance negative. Estimates across the studies reflect different assumptions about inter-sectoral, inter-regional, and inter-temporal interactions, about adaptation, and about the monetary values of impacts. Aggregate estimates of costs mask significant differences in impacts across sectors, regions, countries, and populations. Relative to their income, economic impacts are higher for poorer people."[27]
Marginal impacts
The social cost of carbon (SCC) is an aggregate measure of the impacts of climate change. It is defined as the incremental (or marginal) social cost of emitting one more tonne of carbon (as carbon dioxide) into the atmosphere at any point in time (Yohe et al., 2007:821).[26] Different GHGs have different social costs. For example, due to their greater physical capacity to trap infrared radiation, HFCs have a considerably higher social cost per tonne of emission than carbon dioxide. Another physical property that affects the social cost is the atmospheric lifetime of the GHG.
Estimates of the SCC are highly uncertain and cover a wide range (Klein et al., 2007:756).[28] The discrepancies in estimates can be broken down into normative and empirical parameters (Fisher et al., 2007:232).[29] Key normative parameters include the aggregation of impacts across time and regions. The other parameters relate to the empirical validity of SCC estimates. This reflects the poor quality of data on which estimates are based, and the difficulty in predicting how society will react to future climate change. In a literature assessment, Klein et al. (2007:757) placed low confidence in SCC estimates.
Sensitivity analysis
Sensitivity analysis allows assumptions to be changed in aggregate analysis to see what effect it has on results (Smith et al., 2001:943):[5]
- Shape of the damage function: This relates impacts to the change in atmospheric greenhouse gas (GHG) concentrations. There is little information on what the correct shape (e.g., linear or cubic) of this function is. Compared with a linear function, a cubic function shows relatively small damages for small increases in temperature, but more sharply increasing damages at greater temperatures.
- Rate of climate change: This is believed to be an important determinant of impacts, often because it affects the time available for adaptation.
- Discount rate and time horizon: Models used in aggregate studies suggest that the most severe impacts of climate change will occur in the future. Estimated impacts are therefore sensitive to the time horizon (how far a given study projects impacts into the future) and the discount rate (the value assigned to consumption in the future versus consumption today).
- Welfare criteria: Aggregate analysis is particularly sensitive to the weighting (i.e., relative importance) of impacts occurring in different regions and at different times. Studies by Fankhauser et al. (1997) and Azar (1999) found that greater concern over the distribution of impacts lead to more severe predictions of aggregate impacts.
- Uncertainty: Usually assessed through sensitivity analysis, but can also be viewed as a hedging problem. EMF (1997) found that deciding on how to hedge depends on society's aversion to climate change risks, and the potential costs of insuring against these risks.
Advantages and disadvantages
There are a number of benefits of using aggregated assessments to measure climate change impacts (Smith et al., 2001:954).[5] They allow impacts to be directly compared between different regions and times. Impacts can be compared with other environmental problems and also with the costs of avoiding those impacts. A problem of aggregated analyses is that they often reduce different types of impacts into a small number of indicators. It can be argued that some impacts are not well-suited to this, e.g., the monetization of mortality and loss of species diversity. On the other hand, Pearce (2003:364) argued that where there are monetary costs of avoiding impacts, it is not possible to avoid monetary valuation of those impacts.[30]
Incomplete estimates
As stated, economic estimates of climate change impacts are incomplete.[31] Analysts have used integrated assessment models to estimate the economic impacts of climate change. These models do include estimates of some impacts, for instance, the effects of climate change on agriculture.[31] In other areas, models exclude some impacts. An example is the possibility that climate change could lead to migration or conflict.[31]
Relative impacts
The effects of climate change can be compared to other effects on human society and the environment. Future socio-economic development may strongly affect climate change impacts.[32] For example, projections of the number of people at risk of hunger vary significantly according to assumptions over future socio-economic development.[33]
Some ecosystems are likely to be especially affected by climate change (e.g., coral reefs).[34] In the long-term (beyond 2050), climate change may become the major driver for biodiversity loss globally.[35]
The socio-economic impacts of climate change are likely to be greatest in communities that face other stresses.[36] For example, poor communities are vulnerable to extreme weather events, and are likely to be especially affected by climate change.[37] In general, however, other changes (e.g., demographic and technological)[38] are likely to have a greater effect on human society than climate change.[39] On the other hand, major ("non-marginal") impacts could occur with abrupt changes in natural and social systems.[37][40] Scientific understanding of abrupt changes is limited.[31][41]
Another consideration is how vulnerability to climate change varies with scale. At local scales, extreme weather events can have a significant impact, especially in vulnerable locations.[42] Another potentially significant impact is the long-term effect of sea-level rise on low-lying coastal areas.[37]
Comments on relative impacts
Bostrom (2009)[43] comments that:
Even the Stern Review on the Economics of Climate Change, a report prepared for the British Government which has been criticized by some as overly pessimistic, estimates that under the assumption of business-as-usual with regard to emissions, global warming will reduce welfare by an amount equivalent to a permanent reduction in per capita consumption of between 5 and 20%. In absolute terms, this would be a huge harm. Yet over the course of the twentieth century, world GDP grew by some 3,700%, and per capita world GDP rose by some 860%. It seems safe to say that (absent a radical overhaul of our best current scientific models of the Earth’s climate system) whatever negative economic effects global warming will have, they will be completely swamped by other factors that will influence economic growth rates in this century.
Other analysts have commented on the risks of climate change damages. The German Advisory Council on Global Change (WBGU, 2007)[44] comments that:
Although [the Stern Review's] figures tend to be at the upper end of the scale compared to other estimates currently circulating, even [its] quantitative estimates fail to include the economic upheavals that would arise as a consequence of climate-induced conflicts or might be triggered by climate-induced migration.
Several analysts have emphasized the importance of "catastrophic" risks due to climate change. WBGU (2007)[45] states that due to climate change, "significant impairment" of the global economy is a "distinct possibility". Weitzman (2012)[46] has commented:
Climate change potentially affects the whole worldwide portfolio of utility by threatening to drive all of planetary welfare to disastrously low levels in the most extreme scenarios. With global climate change, diversification [of risk] is limited because all eggs are inherently in one basket.
Further reading
- Maximilian Auffhammer. 2018. "Quantifying Economic Damages from Climate Change." Journal of Economic Perspectives—Volume 32, Number 4—Fall 2018—Pages 33–52.
- Solomon Hsiang and Robert E. Kopp. 2018. "An Economist’s Guide to Climate Change Science." Journal of Economic Perspectives—Volume 32, Number 4—Fall 2018—Pages 3–32
See also
- Consequences of global warming
- Ecoflation
- Economics of global warming
- Effects of global warming
- Environmental Security and Peace
Notes
- "Counting the cost 2019: a year of climate breakdown" (PDF). December 2019. Retrieved 31 May 2020.
- "Global economy will be 3 percent smaller by 2050 due to lack of climate resilience". 20 November 2019. Retrieved 31 May 2020.
- Harris, Roach, Codur, Jonathan M., Brian, Anne-Marie (2017). "The Economics of Global Climate Change". Cite journal requires
|journal=(help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Harris, Roach, Codur, Jonathan M., Brian, Anne-Marie (2015). "The Economics of Global Climate Change" (PDF). Global Development and Environment Institute, Tufts University – via www.sciencetheearth.com.CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
- Smith, J.B.; et al. (2001). "Vulnerability to Climate Change and Reasons for Concern: A Synthesis. In: Climate Change 2001: Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability. Contribution of Working Group II to the Third Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change [J.J. McCarthy et al. Eds.]". Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK, and New York, N.Y., U.S.A. Retrieved 2010-01-10.
- Confalonieri, U.; et al. (2007). "Human health. In: Climate Change 2007: Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability. Contribution of Working Group II to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change [M.L. Parry et al., Eds.]". Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK, and New York, N.Y., U.S.A. Retrieved 2009-05-20.
- Working on a warmer planet The impact of heat stress on labour productivity and decent work (PDF). International Labour Organization. 2019. Retrieved 7 July 2019.
- "International Labour Organization Warns of Heat-Related Job Losses". United Nations Climate Change. Retrieved 7 July 2019.
- Stevens, Pippa (16 January 2020). "'Urgent' need for businesses to adapt to growing threat from climate change, McKinsey says". CNBS. Retrieved 29 March 2020.
- Woetzel, Jonathan; Pinner, Dickon; Samandari, Hamid; Engel, Hauke; Boland, Brodie; Powis, Carter; Krishnan, Mekala (January 2020). Climate risk and response Physical hazards and socioeconomic impacts. Mckinsey. p. 7. Retrieved 29 March 2020.
- SMITH, OLI (March 25, 2017). "Is CO2 behind Brexit?! Al Gore says GLOBAL WARMING led to shock Leave victory". Express. Retrieved 13 August 2019.
- Ahmed, Nafeez. "Brexit was Triggered by Climate-Driven Collapse in the Middle East". Resilience. Retrieved 13 August 2019.
- Horowitz, Julia (August 9, 2019). "UK economy shrinks for first time since 2012. Brexit could tip it into recession". CNN. Retrieved 13 August 2019.
- Tol, Richard S. J. (2018-02-01). "The Economic Impacts of Climate Change". Review of Environmental Economics and Policy. 12 (1): 4–25. doi:10.1093/reep/rex027. ISSN 1750-6816.
- Schneider, S. H.; et al. (2007). "Assessing key vulnerabilities and the risk from climate change. In: Climate Change 2007: Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability. Contribution of Working Group II to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change [M.L. Parry et al., Eds.]". Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK, and New York, N.Y., U.S.A. Retrieved 2009-05-20.
- Desanker, P.; et al. (2001). "Africa. In: Climate Change 2001: Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability. Contribution of Working Group II to the Third Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change [J.J. McCarthy et al. Eds.]". Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK, and New York, N.Y., U.S.A. Retrieved 2010-01-10.
- Nicholls, R.J.; et al. (2007). "Coastal systems and low-lying areas. In: Climate Change 2007: Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability. Contribution of Working Group II to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change [M.L. Parry et al., Eds.]". Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK, and New York, N.Y., U.S.A. pp. 315–356. Retrieved 2009-05-20.
- Anisimov, O.; et al. (2001). "Polar Regions (Arctic and Antarctic). In: Climate Change 2001: Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability. Contribution of Working Group II to the Third Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change [J.J. McCarthy et al. Eds.]". Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK, and New York, N.Y., U.S.A. Retrieved 2010-01-10.
- Mimura, N.; et al. (2007). "Small islands. In: Climate Change 2007: Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability. Contribution of Working Group II to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change [M.L. Parry et al., Eds.]". Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK, and New York, N.Y., U.S.A. pp. 687–716. Retrieved 2009-05-20.
- Kundzewicz, Z.W.; et al. (2007). "Freshwater resources and their management. In: Climate Change 2007: Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability. Contribution of Working Group II to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change [M.L. Parry et al. Eds.]". Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK, and New York, N.Y., U.S.A. pp. 173–210. Retrieved 2009-05-20.
- Wilbanks, T.J.; et al. (2007). "Industry, settlement and society. In: Climate Change 2007: Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability. Contribution of Working Group II to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change [M.L. Parry et al., Eds.]". Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK, and New York, N.Y., U.S.A. pp. 357–390. Retrieved 2009-05-20.
- Tol, R.S.J. (2008). "Why Worry about Climate Change? A Research Agenda" (PDF). Environmental Values. 17 (4): 437–470. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.175.5947. doi:10.3197/096327108X368485. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2011-07-19. Retrieved 2010-01-13.
- IPCC (2007a). "Climate Change 2007: Synthesis Report. Contribution of Working Groups I, II and III to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change [Core Writing Team, Pachauri, R.K and Reisinger, A. (eds.)]". IPCC, Geneva, Switzerland. p. 104. Retrieved 2009-05-20.
- Hessler, Uwe (15 January 2020). "Climate Change Named Biggest Global Threat in New WEF Risks Report". Deutch Welle. Ecowatch. Retrieved 17 January 2020.
- Irwin, Neil (2019-01-17). "Climate Change's Giant Impact on the Economy: 4 Key Issues". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved 2019-01-22.
- Yohe, G.W.; et al. (2007). "Perspectives on climate change and sustainability. In: Climate Change 2007: Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability. Contribution of Working Group II to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change [M.L. Parry et al., Eds.]". Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK, and New York, N.Y., U.S.A. Retrieved 2009-05-20.
- Tol Correction
- Klein, R.J.T.; et al. (2007). "Inter-relationships between adaptation and mitigation. In: Climate Change 2007: Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability. Contribution of Working Group II to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change [M.L. Parry et al. Eds.]". Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK, and New York, N.Y., U.S.A. pp. 745–777. Retrieved 2009-05-20.
- Fisher, B.S.; et al. (2007). "Issues related to mitigation in the long term context. In: Climate Change 2007: Mitigation. Contribution of Working Group III to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change [B. Metz et al. Eds.]". Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK, and New York, N.Y., U.S.A. Retrieved 2009-05-20.
- Pearce, D. (November 2003). "The Social Cost of Carbon and its Policy Implications" (PDF). Oxford Review of Economic Policy. 19 (3): 362–384. doi:10.1093/oxrep/19.3.362. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2009-02-19. Retrieved 2009-01-10.
-
- Sec 3.1, in: Ch 3: Understanding the social cost of carbon, in Downing & others 2005, pp. 12–13 (pp.20-21 of PDF).
- "More research, more uncertainty?", in Downing & Butterfield 2012, pp. 27–28
-
Parry, M.L.; et al., "Technical summary", TS.5.4 Perspectives on climate change and sustainability Missing or empty
|title=(help), in IPCC AR4 WG2 2007 -
Easterling, W.E.; et al., "Ch 5: Food, Fibre, and Forest Products", Sec 5.6.5 Food security and vulnerability Missing or empty
|title=(help), in IPCC AR4 WG2 2007 -
Parry, M.L.; et al., "Technical summary", TS.4.5 Especially affected systems, sectors and regions Missing or empty
|title=(help), in IPCC AR4 WG2 2007 -
Fischlin, A.; et al., "Ch. 4: Ecosystems, their properties, goods and services", Sec. 4.4.11 Global synthesis including impacts on biodiversity Missing or empty
|title=(help), in IPCC AR4 WG2 2007. -
Wilbanks, T.J.; et al., "Ch. 7: Industry, Settlement and Society", Sec 7.4.3 Key vulnerabilities Missing or empty
|title=(help), in IPCC AR4 WG2 2007 -
Wilbanks, T.J.; et al., "Ch. 7: Industry, Settlement and Society", Sec 7.3 Assumptions about future trends Missing or empty
|title=(help), in IPCC AR4 WG2 2007 -
Wilbanks, T.J.; et al., "Ch. 7: Industry, Settlement and Society", Sec 7.4 Key future impacts and vulnerabilities Missing or empty
|title=(help), in IPCC AR4 WG2 2007 -
Smith, J.B.; et al., "Chapter 19: Vulnerability to Climate Change and Reasons for Concern: A Synthesis", Sec. 19.6.1. The Irregular Face of Climate Change Missing or empty
|title=(help), in IPCC TAR WG2 2001. -
Smith, J.B.; et al., "Ch. 19: Vulnerability to Climate Change and Reasons for Concern: A Synthesis", Sec. 19.6.4. Climate Protection in an Irregular World Missing or empty
|title=(help), in IPCC TAR WG2 2001. -
Wilbanks, T.J.; et al., "Ch. 7: Industry, Settlement and Society", Sec 7.5 Costs and other socio-economic issues Missing or empty
|title=(help), in IPCC AR4 WG2 2007 - Bostrom, N. The Future of Humanity, in: New Waves in Philosophy of Technology, eds. Jan-Kyrre Berg Olsen, Evan Selinger & Soren Riis (Palgrave Macmillan, 2009) (PDF)
- Sec. 5.2.4.2: Climate change impacts on the global economy, in: Ch. 5: Impacts of climate change on the biosphere and human society, in WBGU 2007, p. 72
- Sec. 8.3.2: Risks for global economic development, in: Ch. 8: Climate change as a driver of social destabilization and threat to international security, in WBGU 2007, pp. 170–171
- Conclusion, in Weitzman 2012, p. 243
References
- Climate Change and Capable Development by Ananda Kumar Biswas
- Downing, T.E. & R.E. Butterfield (April 2012), Extreme Outcomes: Prospects for major tipping and socially contingent events and associated economic and social costs. Summary of cross-sectoral results from the ClimateCost project funded by the European Community's Seventh Framework Programme. Technical Policy Briefing Note 7 (PDF), Oxford: Stockholm Environment Institute, ISBN 978-91-86125-35-6. Report website.
- Downing, T.E.; et al. (August 2005), Social Cost of Carbon: A Closer Look at Uncertainty (final revision) (PDF), London: UK Government: Department for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs
- IPCC TAR WG2 (2001), McCarthy, J. J.; Canziani, O. F.; Leary, N. A.; Dokken, D. J.; White, K. S. (eds.), Climate Change 2001: Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability, Contribution of Working Group II to the Third Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, Cambridge University Press, ISBN 978-0-521-80768-5, retrieved 2019-08-02 (pb: 0-521-01500-6).
- IPCC AR4 WG2 (2007), Parry, M.L.; Canziani, O.F.; Palutikof, J.P.; van der Linden, P.J.; Hanson, C.E. (eds.), Climate Change 2007: Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability, Contribution of Working Group II to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, Cambridge University Press, ISBN 978-0-521-88010-7 (pb: 978-0-521-70597-4).
- WBGU (2007), Flagship Report 2007: World in Transition: Climate Change as a Security Risk. A report by the German Advisory Council on Global Change (WBGU) (PDF), Earthscan, ISBN 978-3-936191-20-2, archived from the original (PDF) on 2015-04-03, retrieved 2013-07-06. Report website.
- Weitzman, M. (2012), "GHG Targets as Insurance Against Catastrophic Climate Damages" (PDF), Journal of Public Economic Theory, 14 (2): 221–244, doi:10.1111/j.1467-9779.2011.01539.x.