Engine-indicating and crew-alerting system
An engine-indicating and crew-alerting system (EICAS)[1] is an integrated system used in modern aircraft to provide aircraft flight crew with instrumentation and crew annunciations for aircraft engines and other systems. On EICAS equipped aircraft the "recommended remedial action" is called a checklist.
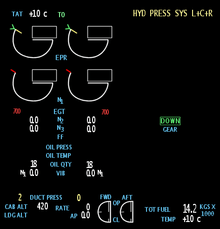
Components
EICAS typically includes instrumentation of various engine parameters, including for example speed of rotation, temperature values, fuel flow and quantity, oil pressure etc. Other aircraft systems typically monitored by EICAS are for example hydraulic, pneumatic, electrical, deicing, environmental and control surface systems. EICAS has high connectivity & provides data acquisition and routing.
EICAS is a key function of a glass cockpit system, which replaces all analog gauges with software-driven electronic displays. Most of the display area is used for navigation and orientation displays, but one display or a section of a display is set aside specifically for EICAS.
The crew-alerting system (CAS) is used in place of the annunciator panel on older systems. Rather than signaling a system failure by turning on a light behind a translucent button, failures are shown as a list of messages in a small window near the other EICAS indications.
See also
- Electronic centralised aircraft monitor, a similar system by Airbus
References
- Alexander T. Wells and Clarence C. Rodrigues (2004). Commercial aviation safety (4th ed.). McGraw-Hill Professional. p. 245. ISBN 978-0-07-141742-6.
External links
- Astronautics Corporation of America EICAS displays