de Havilland Hercules
The de Havilland DH.66 Hercules was a 1920s British seven-passenger, three-engined airliner built by de Havilland Aircraft Company at Stag Lane Aerodrome. As a more modern replacement for the D.H.10s used on the RAF's airmail service, Imperial Airways used the Hercules effectively to provide long-distance service to far-flung regions. Although the giant airliners were slow and cumbersome, they pointed the way for future airliners.[1]
| DH.66 Hercules | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Imperial Airways de Havilland Hercules | |
| Role | Airliner |
| National origin | United Kingdom |
| Manufacturer | de Havilland Aircraft Company |
| First flight | 30 September 1926 |
| Introduction | 1926 |
| Retired | 1942 |
| Primary users | Imperial Airways West Australian Airways South African Air Force |
| Number built | 11 |
Design and development
The Hercules was designed for Imperial Airways when it took over the Cairo–Baghdad air route from the Royal Air Force. The Hercules was a three-engined two-bay biplane with room for seven passengers and the ability to carry mail. In order to minimise the risk of forced landings over remote desert areas, the Hercules had three radial engines. De Havilland moved away from the traditional plywood covered fuselage to remove the risk of deterioration in tropical areas and the fuselage was constructed using tubular steel. The cabin and rear baggage compartment were made of plywood suspended inside the steel structure.[2] The two pilots were in an open cockpit above the nose. The cabin had room for a wireless operator and seven passengers.[2]
With a contract for five years to run the Cairo to Baghdad air mail service, and a requirement to start a service between Cairo and Karachi, Imperial Airways ordered five aircraft. In June 1926, while the prototype was still being built, the type name Hercules was chosen in a competition in the Meccano Magazine. The prototype, registered G-EBMW, first flew on 30 September 1926 at Stag Lane Aerodrome.[2]
Four aircraft were built in 1929 for West Australian Airways. They had modifications to suit Australian requirements including an enclosed cockpit and seating for 14-passengers as well as room for the mail.[2]
Two additional aircraft were built for Imperial Airways in 1929 and they had the enclosed cockpit modification used on the Australian aircraft. These were also retro-fitted to the earlier aircraft.[2]
Operational history

- Imperial Airways
Following a period of crew training the prototype left the United Kingdom for Cairo on 18 December 1926 to be based at Heliopolis. The second aircraft left Croydon for Cairo on 27 December 1926, carrying the Secretary of State for Air Samuel Hoare. It flew on to India and arrived in Delhi on 8 January 1927. The prototype, later to be named the City of Cairo by King Fuad, operated the first commercial service between Basra and Cairo on 7 January 1927. The service to Karachi did not start until two years later after permission was granted from the Persian Government.[2]
With the start of the service between Cairo and Delhi in 1929 a sixth Hercules, the City of Basra entered service.[2] With the fatal loss of the City of Jerusalem in September 1929 a seventh new aircraft was ordered and delivered in January 1930. With the aircraft now out of production when the City of Tehran forced landed and was destroyed, Imperial Airways bought an aircraft from West Australian Airways to replace it.[2]
In 1931 two experimental air mail services between Croydon, England and Melbourne, Australia were attempted. The City of Cairo was to fly the mail from Karachi to Australia but ran out of fuel and forced landed at Koepang on 19 April 1931.[lower-alpha 1] West Australian Airways was approached again and another aircraft was sold to Imperial Airways. On the delivery flight to Karachi it carried the first through Australia to England mail.[2]
In December 1931 the former West Australian Airways, City of Cape Town operated a survey flight to Cape Town pending the extension of the Empire Air Route to South Africa. The City of Cape Town was briefly used in South Africa from October 1932 until 1933 by Sir Alan Cobham for his itinerant air pageant. The City of Jodhpur was used in an aerial ant-locust campaign in Rhodesia in 1934 and the following year it crashed into a swamp near Lake Salisbury in Uganda and was destroyed. Imperial withdrew the Hercules from service between 1934 and 1935; three were sold to the South African Air Force.[2]
- South Africa Air Force
The South African Air Force bought three Hercules from Imperial Airways in 1935.[lower-alpha 2]. At the start of the Second World War they were used as military transport aircraft supporting South African forces around Africa. One was broken up for spares in 1939 and the other two were withdrawn from service and scrapped in 1943.[2]
- Stephens Aviation
Two former West Australian Airways aircraft, the City of Perth and the City of Adelaide were operated on the ferry service in New Guinea between Lae and Wau from 1936. The City of Perth crashed in February 1941 and the City of Adelaide was destroyed by enemy action in 1942.[2]
- West Australian Airways
West Australian Airways ordered four Hercules aircraft for a new passenger and mail service between Perth and Adelaide. Following acceptance testing in England the four aircraft were shipped to Perth, Australia and re-assembled. The first eastbound service was flown by two aircraft, the City of Adelaide and the City of Perth. They arrived in Perth on 29 May 1929 after flying the 1450 miles in 14 hours. Two aircraft were later sold to Imperial Airways and the remaining two were sold to Stephens Aviation when the airline was taken over by Australian National Airways.[2]
Accidents and incidents
- On 6 September 1929 an Imperial Airways DH.66 Hercules, registration G-EBMZ, crashed on landing at Jask, Iran, due to pilot error, killing three of five on board.[4]
- On 14 February 1930 an Imperial Airways DH.66 Hercules, registration G-EBNA, was damaged beyond repair during a forced landing in Gaza, Egypt.[5]
Specifications (DH.66A)
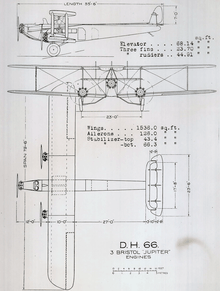
Data from de Havilland aircraft since 1909[2]
General characteristics
- Crew: 3
- Capacity: 7 passenger and up to 465 cu ft (13.2 m3) of mail
- Length: 55 ft 6 in (16.92 m)
- Wingspan: 79 ft 6 in (24.23 m)
- Height: 18 ft 3 in (5.56 m)
- Wing area: 1,547 sq ft (143.7 m2)
- Empty weight: 9,060 lb (4,110 kg)
- Gross weight: 15,660 lb (7,103 kg)
- Powerplant: 3 × Bristol Jupiter VI 9-cylinder air-cooled radial piston engine, 420 hp (310 kW) each
- Propellers: 2-bladed fixed-pitch propellers
Performance
- Maximum speed: 128 mph (206 km/h, 111 kn)
- Cruise speed: 110 mph (180 km/h, 96 kn)
- Service ceiling: 13,000 ft (4,000 m)
- Rate of climb: 765 ft/min (3.89 m/s)
See also
Related development
Related lists
Notes
- The mail was later collected and delivered to Darwin, Australia by Charles Kingsford Smith in the Southern Cross
- For £775 each
References
Notes
- "Western Australian Aviation History". Archived from the original on 20 July 2008.
- Jackson, A.J.; Jackson, R.T. (1988). de Havilland aircraft since 1909 (Rev. and updated ed.). Annapolis MD: Naval Institute Press. pp. 269–274. ISBN 0870218964.
- Unknown (3 April 1936). "Hercules Airliner for New Guinea". The Courier Mail, Brisbane (810). p. 24.
- Accident description for G-EBMZ at the Aviation Safety Network. Retrieved on 18 January 2013.
- Accident description for G-EBNA at the Aviation Safety Network. Retrieved on 21 December 2017.
Bibliography
- The Illustrated Encyclopedia of Aircraft (Part Work 1982–1985). London: Orbis Publishing, 1985.
- Jackson, A.J. British Civil Aircraft since 1919, Volume 2. London: Putnam, 1974. ISBN 0-370-10010-7.
- Jackson, A.J. De Havilland Aircraft since 1909. London: Putnam, 1987. ISBN 0-85177-802-X
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to de Havilland DH.66 Hercules. |
- De Havilland Hercules – British Aircraft Directory
- Imperial Airways History
