Coyote Creek (San Gabriel River tributary)
Coyote Creek is a principal tributary of the San Gabriel River[3] in northwest Orange County, southeast Los Angeles County, and southwest Riverside County, California. It drains a land area of roughly 41.3 square miles (107 km2) covering five major cities, including Brea, Buena Park, Fullerton, La Habra, and La Palma.[4] Some major tributaries of the creek in the highly urbanized[5] watershed include Brea Creek, Fullerton Creek, and Carbon Creek.[6] The mostly flat creek basin is separated by a series of low mountains,[6] and is bounded by several small mountain ranges, including the Chino Hills, Puente Hills and West Coyote Hills.[7]
| Coyote Creek | |
|---|---|
.jpg) North Fork of Coyote Creek in La Mirada | |
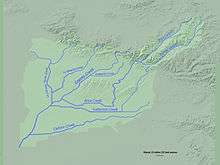 Map of the Coyote Creek watershed | |
| Etymology | Unknown |
| Location | |
| Country | United States |
| State | California |
| Counties | Orange County, Riverside County, Los Angeles, San Bernardino |
| Cities | Brea, Buena Park, Fullerton, La Habra, La Palma |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Source | |
| • location | Riverside County, Orange County, California |
| • coordinates | 33°56′49″N 117°57′31″W[1] |
| • elevation | 2,300 ft (700 m) |
| Mouth | San Gabriel River |
• coordinates | 33°47′41″N 118°05′24″W[1] |
• elevation | 0 ft (0 m) |
| Length | 13.7 mi (22.0 km) |
| Basin size | 41.3 sq mi (107 km2) |
| Discharge | |
| • location | Los Alamitos[2] |
| • average | 43.5 cu ft/s (1.23 m3/s)[2] |
| • minimum | 24 cu ft/s (0.68 m3/s) |
| • maximum | 14,300 cu ft/s (400 m3/s) |
| Basin features | |
| Tributaries | |
| • left | Brea Creek, Fullerton Creek, Carbon Creek |
| • right | La Canada Verde Creek |
Course
Coyote Creek is roughly 13.7 miles (22.0 km) long[8] and flows generally southwest, while its North Fork, shown on federal maps as La Canada Verde Creek, measures 9.1 miles (14.6 km). The longest single tributary is Carbon Creek, which flows 13.6 miles (21.9 km), followed closely by Fullerton Creek, which measures 13.0 miles (20.9 km).[8] Two major flood control reservoirs, Brea Reservoir and Fullerton Reservoir, are located in the watershed[7] and feed into Brea Creek and Fullerton Creek, respectively.[6] Brea Creek and Tonner Canyon form the uppermost reaches of the watershed. Coyote Creek joins the San Gabriel very near its mouth in Long Beach.
Beginning at the border of Los Angeles and Orange County, Coyote Creek rises in two forks in the northwesternmost corner of the latter county. Continuing south, it turns west and immediately receives a number of south-flowing tributaries on the right bank. The creek is soon joined by Imperial Creek as it begins to flow southwest through a series of flood control channels, alternatively earth and concrete lined. The somewhat haphazardly constructed channel is described as being either concrete lined, "composite", trapezoidal, or riprap. After having crossed the Los Angeles-Orange County border three times, Coyote Creek receives its first major tributary, 9.8-mile (15.8 km) Brea Creek, on the right bank.[6][7]
Brea Creek begins in the far northeastern corner of the watershed, at the border of Los Angeles and San Bernardino counties. The creek flows southwest, receiving numerous mountain tributaries on either bank. As it briefly turns north, it receives Tonner Canyon (spelled also Toner) on the left bank. Tonner Canyon begins in the vicinity of Brea Canyon, and flows south-southwest until it turns northwest and joins Brea. From the confluence downstream, the combined waters are called Brea Creek. The creek then proceeds to enter increasingly urbanized landscape, then flows into Brea Reservoir, which functions mainly for flood control. The creek then turns due west and flows into Coyote Creek on the left bank.[6][7]
After receiving the water of Brea Creek, Coyote Creek continues southwest, passing beneath Interstate 5, while bending south for a brief stretch before turning back north. Shortly downstream from the confluence, it is joined by its North Fork, or La Canada Verde Creek.[9] The 9.1-mile-long (14.6 km) North Fork begins in three forks, which merge and flow due south. The creek is joined by a small tributary on the left bank and then receives a larger tributary, La Mirada Creek, on the left bank. The creek then continues directly south through a flood control channel before meeting Coyote Creek. Soon after the confluence, the third major tributary, Fullerton Creek, joins Coyote on the left bank.[6][7]
Fullerton Creek begins several miles south of Tonner Canyon, and initially flows west-northwest. The creek then sharply bends south and flows into Fullerton Reservoir, which, like Brea, also serves a flood-control function. The creek then flows southwest and south, before flowing nearly at a right angle into another unnamed tributary. The creek sharply turns due west, and continues winding through predominantly residential suburbs, before flowing into Coyote on the left bank. The combined waters then continue southwest and soon flow beneath California State Route 91.[6][7]
Several miles after State Route 91, a smaller tributary, Moody Creek, joins Coyote Creek on the left bank. Moody Creek begins parallel to SR 91, and flows only about 3.7 miles (6.0 km) before it joins Coyote Creek.
The fourth major tributary, 13.6-mile (21.9 km) Carbon Creek, then joins on the left bank. Carbon Creek is a mostly channelized course, beginning almost 10 miles (16 km) south of Brea and Tonner Canyons. The creek flows west and south into several small flood-control basins, before resuming its west-southwest course and receiving several small tributaries on either bank. The creek flows into Coyote Creek very near its mouth at the San Gabriel River, on the left bank.[6][7]
Streamflow
The United States Geological Survey (USGS) operated two stream gauges on Coyote Creek. From 1965 to 1978, the USGS recorded flows at Los Alamitos, California, which is at its confluence with the San Gabriel River. The highest flow recorded there was 14,300 cubic feet per second (400 m3/s), and with three other high flows exceeding ten thousand second-feet.[2]
For Brea Creek streamflow data see Brea Creek#Streamflow.
For Fullerton Creek, the USGS operated two stream gauges from 1936 to 1964. The highest flow during that period (mouth, at Fullerton) was 1,600 cubic feet per second (45 m3/s) on 14 March 1941. In that time period, no other flow passed 1,000 second-feet, although it did come close to on 2 March 1938 (the peak of the Los Angeles Flood of 1938).[10]
For Carbon Creek, only one streamflow gauge was operated by the USGS, downstream of Carbon Canyon Dam, from 1962 to 2008. The highest recorded flow during that period was 741 cubic feet (21.0 m3) per second, on 19 February 2005.[11]
Watershed
Geography and geology
Coyote Creek drains a roughly diamond-shaped watershed between the drainage basins of the San Gabriel and Santa Ana rivers, bounded on the north by the small mountain ranges Chino Hills, Puente Hills and West Coyote Hills. The watershed, with the exception of these hills, a small partial divide inside the watershed, and several recreational areas, such as Chino Hills State Park, is almost entirely developed, and is in sharp contrast to the San Gabriel River watershed viewed as a whole, which in total has only twenty-six percent of its area developed.[12]
Biology
Although channelized in many areas along its course, Coyote Creek and its tributaries provide some rich habitat for riparian and other species, including salt marsh instream, as well as coastal sage scrub, live oak, grassland and sand dunes. Native wildlife is common in the areas described, especially in the far upper reaches of the watershed, which include Brea and Tonner canyons. Aside from the native wildlife, a number of invasive species, both plant and animal, also inhabit the watershed.[7]
History
The Army Corps of Engineers expanded the channel and lined the creek with concrete beginning in the early 1960s. A young boy drowned in 1963, while playing on a makeshift raft, on the water behind a temporary dam built for the project.
See also
References
- "Coyote Creek". Geographic Names Information System. United States Geological Survey. Retrieved 29 May 2009.
- "USGS 11090700 Coyote Creek at Los Alamitos CA: Monthly Statistics". United States Geological Survey. nwis.waterdata.usgs.gov. Retrieved 29 May 2009.
- "The San Gabriel River Watershed". Know Your Watershed. The River Project. Archived from the original on 9 February 2009. Retrieved 30 May 2009.
- "Introduction to Coyote Creek Watershed". Watershed and Coastal Resources Division of Orange County. ocwatersheds.com. Archived from the original on 9 October 2007. Retrieved 29 May 2009.
- "Coyote Creek Watershed – Land Use". Watershed and Coastal Resources Division of Orange County. ocwatersheds.com. Archived from the original on 16 May 2008. Retrieved 29 May 2009. Note: The Orange County California Watershed Site notes that "Orange County, California is a rapid developing area. Land Use is constantly changing and this information may not reflect the current conditions of the land."
- "Coyote Creek Watershed and Elevation Ranges". Watershed and Coastal Resources Division of Orange County. ocwatersheds.com. Archived from the original on 16 May 2008. Retrieved 29 May 2009.
- "Summary of Existing Conditions Data: Coyote Creek Watershed Management Plan" (PDF). CH2M HILL. ocwatersheds.com. Archived from the original (PDF) on 30 October 2007. Retrieved 29 May 2009.
- U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline data. The National Map Archived 5 April 2012 at WebCite, accessed 16 March 2011
- U.S. Geological Survey Geographic Names Information System: La Canada Verde Creek
- "USGS 11090000: Fullerton Creek at Fullerton, CA". United States Geological Survey. nwis.waterdata.usgs.gov. Retrieved 29 May 2009.
- "USGS 11075720: Carbon Creek Below Carbon Canyon Dam CA". United States Geological Survey. nwis.waterdata.usgs.gov. Retrieved 30 May 2009.
- "San Gabriel River Watershed". Los Angeles Department of Public Works. lacounty.gov. Archived from the original on 5 August 2009. Retrieved 30 May 2009.
