Coeroeni
Coeroeni is a resort in Suriname, located in the Sipaliwini District. Its population at the 2012 census was 1,046. The resort is mainly inhabited by indigenous people[1] of the Tiriyó tribe.[2] Kwamalasamutu is the main village of the resort and home to the granman (paramount chief) Asongo Alalaparu.[3]
Coeroeni | |
|---|---|
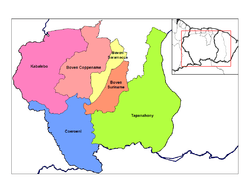 Map showing the resorts of Sipaliwini District.
Coeroeni | |
| Country | |
| District | Sipaliwini District |
| Area | |
| • Total | 33,133 km2 (12,793 sq mi) |
| Population (2012)[1] | |
| • Total | 1,046 |
| • Density | 0.032/km2 (0.082/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC-3 (AST) |
The resort was created in 1983 out of Nickerie as a tribal area.[4] The disputed area of south-west Suriname known as Tigri Area belongs to the Coeroeni resort.[5]
Villages
- Alalapadu
- Amatopo
- Kasuela (disputed)
- Kuruni
- Kwamalasamutu
- Sakuru (disputed)
- Sipaliwini
- Vier Gebroeders
The resort is also home to villages which are only inhabited part of the time.[6]
Kamani
Kamani is a border village. It was founded in 2008 by people from Kwamalasamutu.[7] The population as of 2009 was 6 people.[8] The location is 2°34′5″N 57°0′30″W.
Nature
_Edit.jpg)
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Sipaliwini Savanna. |
The Sipaliwini Savanna is a 100,000 hectare nature reserve. It has been a protected area since 1972. The majority of the reserve consists of a savannah which in turn is a continuation of the Brazilian Tumucumaque Mountains National Park. The reserve is in pristine condition with almost no human habitation.[9] This reserve is one of the last frontiers in the tropics, however relatively little is known about the region.[10] The savannah consists of large grasslands with wetter islands of trees. The bird life is abundant,[11] and the park is where the blue poison dart frog was discovered in 1969.[12] In 2005, six new birds had been discovered. It includes a new species of Sun parakeet, and a new Rufous-sided pygmy tyrant.[13]
The area was first explored in October 1935 by A.J.H. van Lynden who was surprised to discover an immense savannah behind the dense rain forests.[14] In 1962, a study was started whether the savannah could be used for animal husbandry, however the transport costs via airplane would make the enterprise unprofitable.[15] A detailed study into the plant and animal life commenced in 1968.[16]
Archaeology
The Werehpai archaeological site, which consists of caves containing petroglyphs of pre-Columbian origin, is located about 10 kilometres from Kwamalasamutu.[17] On the Sipaliwini Savanna relics were discovered of human habitation dating from about 6,000 BC.[18]
Notes
- "Resorts in Suriname Census 2012" (PDF). Retrieved 18 May 2020.
- "DORPSPLAN KWAMALASAMUTU 2011–2014" (PDF). Institute for Graduate Studies and Research (IGSR) (in Dutch). Retrieved 27 May 2020.
- Heemskerk & Delvoye 2007, p. 100.
- "Districtenindeling Suriname - herstel oude grenzen district Nickerie". nickerie.net (in Dutch). Retrieved 17 June 2020.
- "Suriname, Guyana in Dispute Over Mineral-Rich Land". Atlanta Black Star. Retrieved 25 May 2020.
- "Planning Office Suriname - Districts" (PDF). Planning Office Suriname (in Dutch). Retrieved 23 May 2020.
- "Amotopoan trails : a recent archaeology of Trio movements - Page 5". University of Leiden. Retrieved 15 June 2020.
- Carlin, Eithne B.; Van Goethem, Diederik (2009). In the Shadow of the Tiger: The Amerindians of Suriname. Amsterdam: KIT Publishers. ISBN 978-9460220-265.
- "Natuurreservaten Suriname". Reisgraag (in Dutch). Retrieved 16 June 2020.
- Burton Kim & Thomas E. Lee Jr (2018). "Community Ecology and Phylogeography of Bats in the Guianan Savannas of Northern South America" (PDF). MDPI. Retrieved 17 June 2020.
- "Geography The Sipaliwini Savanna". Retrieved 16 June 2020.
- "Zoology". Sipaliwini Savanna. Retrieved 16 June 2020.
- B.J. O’Shea (2005). "NOTES ON BIRDS OF THE SIPALIWINI SAVANNA AND OTHER LOCALITIES IN SOUTHERN SURINAME, WITH SIX NEW SPECIES FOR THE COUNTRY" (PDF). University of Minnesota. Retrieved 16 June 2020.
- "Op zoek naar de Zuidgrens" (PDF). Sipaliwini Savanna. 1938. Retrieved 27 May 2020.
- "Verslag van een Bodemverkenning op de Sipaliwini Savanne 19-30 Juli 1962, Paramaribo". Wageningen University and Research (in Dutch). 1962. Retrieved 17 June 2020.
- "Welcome to the Plants of the Sipaliwini Savanna". Sipaliwini Savanna (in Dutch). Retrieved 17 June 2020.
- "A Survey of the Large Mammal Fauna of the Kwamalasamutu Region, Suriname". Bioone.org (in Dutch). Retrieved 16 June 2020.
- "My Beloved Nickerie". Nickerie.com. Retrieved 17 June 2020.
References
- Heemskerk, Marieke; Delvoye, Katia (2007). Trio Baseline Study: A sustainable livelihoods perspective on the Trio Indigenous Peoples of South Suriname (PDF). Paramaribo: Stichting Amazon Conservation Team-Suriname.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)