Chromomycin A3
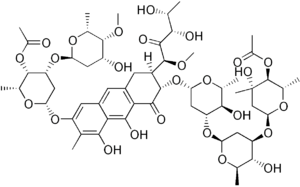
Chromomycin A3 (CMA3) or Toyomycin is an anthraquinone antibiotic glycoside produced by the fermentation of a certain strain of Streptomyces griseus (No. 7).[1]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(1S)-1-C-((2S,3S)-7-{[4-O-acetyl-2,6-dideoxy-3-O-(2,6-dideoxy-4-O-methyl-α-D-lyxo-hexopyranosyl)-β-D-lyxo-hexopyranosyl]oxy}-3-{[4-O-acetyl-2,6-dideoxy-3-C-methyl-α-L-arabino-hexopyranosyl-(1→3)-2,6-dideoxy-β-D-arabino-hexopyranosyl-(1→3)-2,6-dideoxy-β-D-arabino-hexopyranosyl]oxy}-5,10-dihydroxy-6-methyl-4-oxo-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroanthracen-2-yl)-5-deoxy-1-O-methyl-D-xylulose | |
| Other names
Toyomycin | |
| Identifiers | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.027.589 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| Properties | |
| C57H82O26 | |
| Molar mass | 1183.257 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Fluorescence properties
In the presence of Mg2+ ions, Chromomycin A3 binds reversibly to DNA, preferentially to contiguous G/C base pairs.[2][3]
When bound to DNA, Chromomycin A3 has a maximum excitation wavelength of 445 nm (blue), and a maximum emission wavelength of 575 nm (yellow).[4]
Uses
- in-vitro membrane-impermeant G/C-specific fluorescent DNA-binding dye.[3]
- in-vitro antibiotic of gram-positive bacteria, through inhibition of the incorporation of Pi in the RNA.[1]
- in-vitro anticancer drug that inhibits RNA synthesis.[5]
- Evaluation of male fertility: Chromomycin A3 and protamines compete for the same binding sites in the DNA, so CMA3 positivity in spermatozoa reflects protamine deficiency (affecting sperm morphology and decreasing fertility).[6][7]
- Kamiyama, M.; Kaziro, Y. (January 1966). "Mechanism of action of chromomycin A3. 1. Inhibition of nucleic acid metabolism in Bacillus subtilis cells". Journal of Biochemistry. 59 (1): 49–56. doi:10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a128257. ISSN 0021-924X. PMID 4957278.
- Kamiyama, M. (May 1968). "Mechanism of action of chromomycin A3. 3. On the binding of chromomycin A3 with DNA and physiochemical properties of the complex". Journal of Biochemistry. 63 (5): 566–572. doi:10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a128814. ISSN 0021-924X. PMID 4972707.
- Van Dyke, M. W.; Dervan, P. B. (1983-05-10). "Chromomycin, mithramycin, and olivomycin binding sites on heterogeneous deoxyribonucleic acid. Footprinting with (methidiumpropyl-EDTA)iron(II)". Biochemistry. 22 (10): 2373–2377. doi:10.1021/bi00279a011. ISSN 0006-2960. PMID 6222762.
- https://www.caymanchem.com/pdfs/11315.pdf
- Kajiro, Y.; Kamiyama, M. (October 1967). "Mechanism of action of chromomycin A3. II. Inhibition of RNA polymerase reaction". Journal of Biochemistry. 62 (4): 424–429. doi:10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a128685. ISSN 0021-924X. PMID 5587590.
- Iranpour, Farhad Golshan; Nasr-Esfahani, Mohammad Hosein; Valojerdi, Mojtaba Rezazadeh; Al-Taraihi, Taki Mohammad Taki (2000-01-01). "Chromomycin A3 Staining as a Useful Tool for Evaluation of Male Fertility". Journal of Assisted Reproduction and Genetics. 17 (1): 60–66. doi:10.1023/a:1009406231811. ISSN 1058-0468. PMC 3455193. PMID 10754785.
- Nijs, Martine; Creemers, Eva; Cox, Annemie; Franssen, Kim; Janssen, Mia; Vanheusden, Elke; Jonge, Christopher De; Ombelet, Willem (November 2009). "Chromomycin A3 staining, sperm chromatin structure assay and hyaluronic acid binding assay as predictors for assisted reproductive outcome". Reproductive BioMedicine Online. 19 (5): 671–684. doi:10.1016/j.rbmo.2009.07.002.
gollark: Or must you?
gollark: You may see something odd but it's called a feature.
gollark: Seriously. No bugs at all.
gollark: PotatOS doesn't have bugs. Use that.
gollark: Cactusactus
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.