Carminic acid
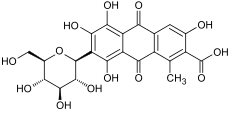
Carminic acid (C22H20O13) is a red glucosidal hydroxyanthrapurin that occurs naturally in some scale insects, such as the cochineal, Armenian cochineal, and Polish cochineal. The insects produce the acid as a deterrent to predators. An aluminum salt of carminic acid is the coloring agent in carmine, a pigment. Natives of Peru had been producing cochineal dyes for textiles since at least 700 CE.[3] Synonyms are C.I. 75470 and C.I. Natural Red 4.
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
7-(β-D-Glucopyranosyl)-3,5,6,8-tetrahydroxy-1-methyl-9,10-dioxo-9,10-dihydroanthracene-2-carboxylic acid | |
| Other names
Carminic acid C.I. Natural Red 4 C.I. 75470 CI 75470 | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.013.658 |
| EC Number |
|
| E number | E120 (colours) |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C22H20O13 | |
| Molar mass | 492.38 g/mol |
| Melting point | 120 °C (248 °F; 393 K) (decomposes) |
| Acidity (pKa) | 3.39, 5.78, 8.35, 10.27, 11.51[2] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
The chemical structure of carminic acid consists of a core anthraquinone structure linked to a glucose sugar unit. Carminic acid was first synthesized in the laboratory by organic chemists in 1991.[4][5]
It was previously thought that it contains α-D-glucopyranosyl residue,[1] which was later redetermined to be the β-D-glucopyranosyl anomer.[6]
References
- Merck Index, 11th Edition, 1989, 1850.
- Atabey, Hasan; Sari, Hayati; Al-Obaidi, Faisal N. (28 April 2012). "Protonation Equilibria of Carminic Acid and Stability Constants of Its Complexes with Some Divalent Metal Ions in Aqueous Solution". Journal of Solution Chemistry. 41 (5): 793–803. doi:10.1007/s10953-012-9830-7. S2CID 95406643.
- Jan Wouters, Noemi Rosario-Chirinos (1992). "Dye Analysis of Pre-Columbian Peruvian Textiles with High-Performance Liquid Chromatography and Diode-Array Detection". Journal of the American Institute for Conservation. The American Institute for Conservation of Historic &. 31 (2): 237–255. doi:10.2307/3179495. JSTOR 3179495.
- Allevi, P.; et al. (1991). "The First Total Synthesis of Carminic Acid". Journal of the Chemical Society, Chemical Communications. 18 (18): 1319–1320. doi:10.1039/C39910001319.
- Ishida, T.; Inoue, M.; Baba, K.; Kozawa, M.; Inoue, K.; Inouye, H. (1987). "Absolute configuration and structure of carminic acid existing as the potassium salt in Dactylopius cacti L". Acta Crystallographica Section C Crystal Structure Communications. 43 (8): 1541–1544. doi:10.1107/S0108270187091169.
- Fiecchi, Alberto; Galli, Mario Anastasia Giovanni; Gariboldi, Pierluigi (1981-03-01). "Assignment of the β configuration to the C-glycosyl bond in carminic acid". The Journal of Organic Chemistry. 46 (7): 1511. doi:10.1021/jo00320a061. ISSN 0022-3263.