Celiac plexus
The celiac plexus or coeliac plexus, also known as the solar plexus because of its radiating nerve fibers,[1] is a complex network of nerves (a nerve plexus) located in the abdomen, near where the celiac trunk, superior mesenteric artery, and renal arteries branch from the abdominal aorta. It is behind the stomach and the omental bursa, and in front of the crura of the diaphragm, on the level of the first lumbar vertebra.
| Celiac plexus | |
|---|---|
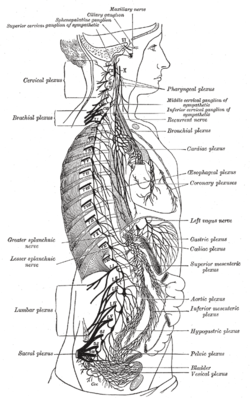 The right sympathetic trunk and its connections with the thoracic, abdominal, and pelvic plexuses. (Celiac plexus labelled at center right.) | |
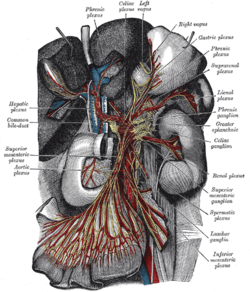 The celiac ganglia with the sympathetic plexuses of the abdominal viscera radiating from the ganglia. (Label for celiac plexus at top center.) | |
| Details | |
| From | celiac branches of vagus nerve |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | plexus coeliacus |
| MeSH | D002447 |
| TA | A14.3.03.021 |
| FMA | 6630 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
The plexus is formed in part by the greater and lesser splanchnic nerves of both sides, and fibers from the anterior and posterior vagal trunks.
The celiac plexus proper consists of the celiac ganglia with a network of interconnecting fibers. The aorticorenal ganglia are often considered to be part of the celiac ganglia, and thus, part of the plexus.
Structure
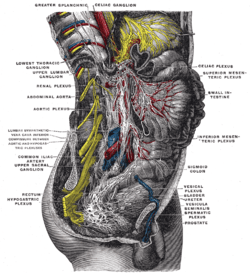
The celiac plexus includes a number of smaller plexuses:
- Hepatic plexus
- Splenic plexus
- Gastric plexus
- Pancreatic plexus
- Suprarenal plexus
Other plexuses that are derived from the celiac plexus:
- Renal plexus
- Testicular plexus / ovarian plexus
- Superior mesenteric plexus
Clinical significance
The celiac plexus is often popularly referred to as the solar plexus, generally in the context of a blow to the stomach. In many of these cases, it is not the celiac plexus itself being referred to, but rather the region around it. A blow to the stomach can upset this region. This can cause the diaphragm to spasm, resulting in difficulty in breathing—a sensation commonly known as "getting the wind knocked out of you". A blow to this region can also affect the celiac plexus itself, possibly interfering with the functioning of the viscera, as well as causing great pain.
A celiac plexus block by means of fluoroscopically guided injection is sometimes used to treat intractable pain from cancers[2] such as pancreatic cancer. Frequently, celiac plexus block is performed by pain management specialists and radiologists, with CT scans for guidance. Intractable pain related to chronic pancreatitis is an important indication for celiac plexus ablation.
References
- "Definition of SOLAR PLEXUS". www.merriam-webster.com.
- Garcia-Eroles X, Mayoral V, Montero A, Serra J, Porta J (2007). "Celiac plexus block: a new technique using the left lateral approach". The Clinical Journal of Pain. 23 (7): 635–7. doi:10.1097/AJP.0b013e31812e6aa8. PMID 17710015.
External links
- Anatomy photo:40:10-0101 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center - "Posterior Abdominal Wall: The Celiac Plexus"
- figures/chapter_32/32-6.HTM: Basic Human Anatomy at Dartmouth Medical School
- The Solar Plexus: Abdominal Brain By Theron Q. Dumont