Caribbean Terrane
The Caribbean Terrane (Spanish: Terreno del Caribe, TC) is one of the geological provinces (terranes) of Colombia. The terrane, dating to the Late Cretaceous, is situated on the North Andes Plate and borders the La Guajira, Chibcha and underlying Tahamí Terrane along the regional Bucaramanga-Santa Marta Fault.[1] The terrane overlies the Tahamí, Arquía and Quebradagrande Terranes along the Romeral Fault System.[2][3]
| Caribbean Terrane Stratigraphic range: Late Cretaceous (emplaced) ~100–65 Ma | |
|---|---|
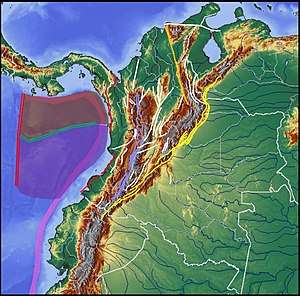 The Caribbean Terrane is enclosed by the Bucaramanga-Santa Marta Fault (orange), Romeral Fault System (violet) and plate boundaries with Coiba (red) and Malpelo Plates (purple) | |
| Type | Terrane |
| Unit of | North Andes Plate |
| Sub-units | Subunits |
| Overlies | Arquía, Tahamí & Quebradagrande Terranes |
| Lithology | |
| Primary | Complexes, basins |
| Other | Volcanoes |
| Location | |
| Coordinates | 6°28′00″N 77°00′00″W |
| Region | Caribbean, Pacific/Chocó |
| Country | |
| Extent | Central, Western, Darién, Baudó, Montes de María |
| Type section | |
| Named for | Caribbean |
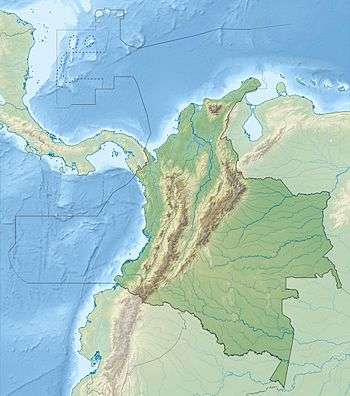 Caribbean Terrane (Colombia) 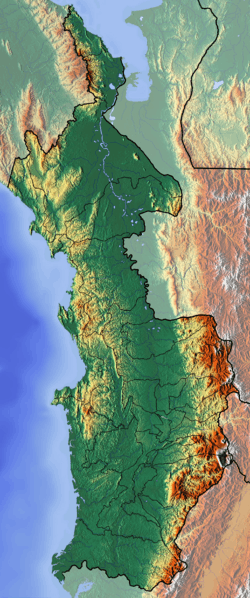 Caribbean Terrane (Chocó Department) | |
Reinterpretation
A study performed by Mora Bohórquez et al. in 2017 showed no basement variation between the Chibcha Terrane San Lucas basement underlying the Lower Magdalena Valley (VIM) and the SNSM basement to the east of the Santa Marta Fault. The authors redefined the contacts between the different terranes, using the names Calima Terrane for the coastal portion of the Caribbean Terrane (San Jacinto and Sinú foldbelts) and Tahamí-Panzenú Terrane for the Tahamí Terrane.[4]
Subdivision
Complexes
- Alto Condoto
- Santa Cecilia-La Equis
- Uré
- Cajamarca
- Puquí
- Bolo Azul
- Cañasgordas
- Mistrató[7]
- Mistrató Tonalite - Paleogene (46 ± 7 Ma)[8]
- Buriticá[7]
- Anserma - Late Cretaceous (71 ± 2.1 Ma)[7][9]
- Batholiths
- Puqui
- Río Tarazá
- Carauta
- Nudillales
- Cerro Plateado
- Farallones
- Comitá
- San José de Urama
- La Clara-Río Calle
Volcanoes
Ranges
Basins
- Cauca-Patía
- Chocó
- Sinú-San Jacinto
- Tumaco
- Urabá
Faults
Gallery
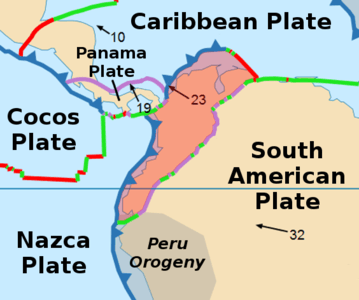 North Andes Plate
North Andes Plate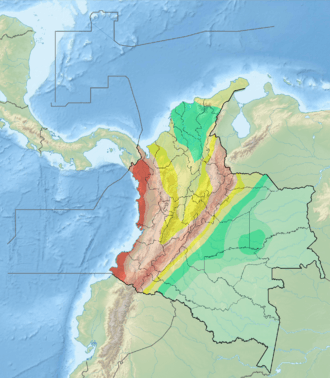 Seismic activity map
Seismic activity map_-_Carta_XVII_-_Geolog%C3%ADa_de_Colombia%2C_Venezuela_y_Ecuador.jpg) Geologic map (Codazzi, 1890)
Geologic map (Codazzi, 1890) Paleogeography of the Late Cretaceous (Blakey)
Paleogeography of the Late Cretaceous (Blakey)
See also
References
- Paris et al., 2000, p.10
- Paris et al., 2000, pp.20–26
- Gómez Tapias et al., 2015, p.209
- Mora Bohórquez et al., 2017, p.20
- Fuck et al., 2008, p.112
- Guiral Vega et al., 2015, p.42
- Vallejo Hincapié et al., 2011, p.48
- Vallejo Hincapié et al., 2011, p.56
- Vallejo Hincapié et al., 2011, p.55
- Paris et al., 2000, p.18
- Paris et al., 2000, p.51
- Paris et al., 2000, p.17
- Paris et al., 2000, p.52
- Paris et al., 2000, p.14
- Paris et al., 2000, p.12
- Paris et al., 2000, p.54
- Paris et al., 2000, p.55
- Paris et al., 2000, p.26
- Paris et al., 2000, p.53
- Paris et al., 2000, p.13
- Paris et al., 2000, p.15
Bibliography
Terranes
- Gómez Tapias, Jorge; Nohora E. Montes Ramírez; María F. Almanza Meléndez; Fernando A. Alcárcel Gutiérrez; César A. Madrid Montoya, and Hans Diederix. 2015. Geological Map of Colombia, 1–212. Servicio Geológico Colombiano. Accessed 2019-10-29.
- Restrepo, Jorge Julián; Oswaldo Ordóñez Carmona; Uwe Martens, and Ana María Correa. 2009. Terrenos, complejos y provincias en la Cordillera Central de Colombia (Terrains, complexes and provinces in the central cordillera of Colombia). Ingeniería Investigación y Desarrollo 9. 49-56. Accessed 2019-10-31.
- Cordani, U.G.; A. Cardona; D.M. Jiménez; L. Dunyl, and A.P. Nutman. 2003. Geochronology of Proterozoic basement from the Colombian Andes: Tectonic history of remnants from a fragmented Grenville Belt, 1-10. 10o Congreso Geológico Chileno.
- Restrepo, Jorge Julian, and Jean F. Toussaint. 1988. Terranes and continental accretion in the Colombian Andes. Episodes 11. 189-193. Accessed 2019-10-31.
Caribbean Terrane
- Mora Bohórquez, Josué Alejandro; Mauricio Ibánez Mejía; Onno Oncken; Mario de Freitas; Vickye Vélez; Andrés Mesa, and Lina Serna. 2017. Structure and age of the Lower Magdalena Valley basin basement, northern Colombia: New reflection-seismic and U-Pb-Hf insights into the termination of the central andes against the Caribbean basin. Journal of South American Earth Sciences 74. 1-26. Accessed 2019-10-29.
- Vallejo Hincapié, Diego Felipe; Andrés Felipe Salazar Ríos, and Luz Mary Toro Toro. 2011. Petrografía y geoquímica de las rocas intrusivas aflorantes entre los municipios de Mistrató y Belén de Umbría (Departamento de Risaralda, Cordillera Occidental Colombiana). Boletín de Geología 33. 47-57. Accessed 2019-10-29.
- Fuck, Reinhardt A.; Benjamim Bley Brito Neves, and Carlos Schobbenhaus. 2008. Rodinia descendants in South America. Precambrian Research 160. 108–126. Accessed 2019-10-29.
- Paris, Gabriel; Michael N. Machette; Richard L. Dart, and Kathleen M. Haller. 2000. Map and Database of Quaternary Faults and Folds in Colombia and its Offshore Regions, 1–66. USGS. Accessed 2017-06-20.
- Paris, Gabriel; Michael N. Machette; Richard L. Dart, and Kathleen M. Haller. 2000b. Map of Quaternary Faults and Folds of Colombia and Its Offshore Regions, 1. USGS. Accessed 2017-09-18.
Reports
- González, Humberto. 2001. Mapa Geológico del Departamento de Antioquia - 1:400,000 - Memoria explicativa, 1–120. INGEOMINAS.
- Royero Gutiérrez, Jose María, and Jairo Clavijo Torres. 2000. Mapa geológico generalizado del Departamento de Bolívar - 1:400,000 - Memoria explicativa, 1–99. INGEOMINAS. Accessed 2017-08-31.
Maps
- Rodríguez, Gabriel; Gilberto Zapata; María I. Sierra; Juan R. Peláez, and Tomás Correa. 2010. Plancha 58 - Sapzurro - 1:100,000, 1. INGEOMINAS. Accessed 2017-06-06.
- Zapata, Gilberto, and Cossio Ubaldo. 1999. Plancha 93 - Cáceres - 1:100,000, 1. INGEOMINAS. Accessed 2017-06-06.
- Álvarez A., Jairo; Héctor Rico H.; Hernán Vásquez; Robert B. Hall, and Lawrence V. Blade. 1975. Plancha 104 - Ituango - 1:100,000, 1. INGEOMINAS. Accessed 2018-06-01.
- Rodríguez, Gabriel; Gilberto Zapata, and Juán Felipe Gómez. 2013. Plancha 114 - Dabeiba - 1:100,000, 1. Servicio Geológico Colombiano. Accessed 2018-06-01.
- Cossio, Ubaldo, and Gilberto Zapata. 2002. Plancha 128 - Murrí - 1:100,000, 1. INGEOMINAS. Accessed 2017-06-06.
- Calle, B., and . Salinas. 2005. Plancha 165 - Carmen de Atrato - 1:100,000, 1. INGEOMINAS. Accessed 2018-06-01.
- Zapata, Gilberto, and Ubaldo Cossio. 1994. Plancha 204 - Pueblo Rico - 1:100,000, 1. INGEOMINAS. Accessed 2017-06-06.
- McCourt, William J., and Germán Verdugo. 1985. Plancha 300 - Cali - 1:100,000, 1. INGEOMINAS. Accessed 2017-06-06.