Carian Trail
The Carian Trail (Turkish: Karia Yolu) is an 820 km long-distance footpath exploring the South Western corner of Turkey through the modern provinces of Muğla and Aydın.[1] The trail is officially opened in 2013 and winds through some of the lesser known regions of Turkey.
| Carian Trail | |
|---|---|
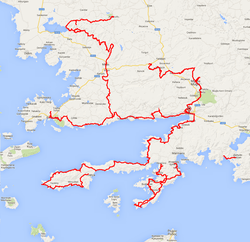 Map of the Carian Trail | |
| Length | c. 820 km (510 mi) |
| Location | Aydın and Muğla, Turkey |
| Established | 2013 |
| Trailheads | İçmeler, Marmaris |
| Use | Hiking and cycling |
| Hiking details | |
| Months | Spring, autumn and winter months |
| Waymark | Red and white stripes |
| Hazards | Severe weather, dehydration, wildlife |
The trail is named after the Carian civilization, indigenous people of Asia Minor. It passes through an area with many ancient ruins.[2] Stone paved caravan roads and mule paths connect villages from the coast to a mountainous hinterland. There are pine forest covered mountain slopes, olive terraces and almond groves which are an important part of the region's economy.
The trail is signed and waymarked with red and white stripes (Grande Randonnee convention) allowing both independent and group travelers from inside and outside of Turkey to hike and enjoy the scenic beauty and cultural treasures of Caria.[3][4][5]
History

Even though it's known that local hikers have used the trail for outdoor sports before the establishment of the Carian trail,[6] foundation of a continuous trail can be attributed to the premise expedition trips of Yunus Özdemir, Altay Özcan, Volkan Demir and Dean Livesley starting in 2009, which lasted 4 winters.[7] The idea behind the expedition was to establish a long-distance hiking trail around the historical Carian regions.[8] After the initial expeditions a route made of historic roads, village paths, ridgeways and forest alleys was established.[8]
Under the leadership of Muğla Chamber of Commerce and Industry (Muğla Ticaret ve Sanayi Odası) the Carian Trail project has been launched. In 2012 South Aegean Development Agency (Güney Ege Kalkınma Ajansı) also started to support the it with additional monetary backing.[8] The Carian Trail has officially opened in February 2013.[9][10]
Route
820 km long trail has 4 main sections, Bozburun, Datça Peninsula, Gulf of Gökova and Carian Hinterland, with an additional section that encompass Muğla and surrounding regions.[11] All of the trail has been divided into 46 stages.[8] It also includes a smaller 11 km long section called Dalyan, which is isolated from other sections. Some sections and stages can be cycled.
Bozburun Peninsula
Bozburun Peninsula section is 141.2 km long and is the official starting point of the trail.[12] It starts from İçmeler and follows Turunç, Kumlubük, Bayır, Taşlıca, Söğüt, Bozburun, Selimiye, Orhaniye, and ends in Hisarönü.
Datça Peninsula
Datça Peninsula is 240.7 km of length. The section starts from Old town of Datça, 3 km before Datça, and follows Hızırşah, Domuzçukuru, Mesudiye, Palamutbükü, Knidos, Karaköy, Kızlan, Emecik, Balıkaşıran, Akçapınar, and ends in Akyaka. The part from Balıkaşıran to Akyaka can also be biked.
Gulf of Gökova
Ceramic Gulf (Gulf of Gökova) is a section with 139.2 km of trail. The section starts from Akyaka and heads west following Turnalı, Sarnıç, Akbük, Alatepe, Ören (Ceramos), Türkevleri, Bozalan, Mazı, Çiftlik, Kızılağaç and arrives in Bodrum (Halicarnassos) finishing in ancient city of Pedasa.
Carian Hinterland
Carian Hinterland section is 174.2 km long and starts from Bozalan heading North and follows Fesleğen, Karacahisar, Milas (Mylasa), Kargıcak, Labraunda, Sarıkaya, Çomakdağ, Kayabükü, Sakarkaya and arrives at the shores of Lake Bafa. Heading up the Latmos (Menteşe mountains) the trail continues to the summit (1350 m), Bağarcık, Kullar, Yahşiler, Tekeler and finishes in Karpuzlu (Alinda) which is the official finish of the Carian Trail.
Muğla Environs
Muğla Environs section consists of 108.5 km of trail. Heading north to Akyaka, the section passes through Kuyucak, Karabağlar, Muğla, Değirmendere Kanyonu, Ekizce, Bayır, Belen Kahvesi and finishes in the ancient city of Stratonikeia. It is possible to bike most of this section.
Ancient sites
The route passes through many ancient cities like;[13]

See also
References
- Lonely Planet; James Bainbridge; Brett Atkinson; Stuart Butler; Steve Fallon; Will Gourlay; Jessica Lee; Virginia Maxwell (1 March 2015). Lonely Planet Turkey. Lonely Planet Publications. pp. 571–. ISBN 978-1-74360-531-8.
- "The top 10 activity holidays in Turkey". The Telegraph.
- Yedig, Serhan. "Karya Yolu'nda baharla kucaklaşma". www.hurriyet.com.tr (in Turkish). Retrieved 2019-09-24.
- http://www.anadolujet.com/aj-en/anadolujet-magazin/2013/july/articles/a-brand-new-culture-route-carian-trail.aspx
- "Turkey on two feet". New Zealand Herald, By Aaron Millar Sep 1, 2014
- "ANTİK KARYA YÜRÜYÜŞ YOLU (05.02.2013)" (in Turkish). Retrieved 2019-09-22.
- "Walking holidays in Turkey: the ancient stones of the new Carian Trail". The Telegaph, By Nigel Richardson 11 Aug 2014
- "Karia Yolu Tarihçesi". Retrieved 2019-09-22.
- Millar, Aaron "The Carian Trail: Turkey on two feet ". The Independent, 30 August 2014.
- Fodor's (27 May 2014). Fodor's Turkey. Fodor's Travel Publications. pp. 450–. ISBN 978-0-8041-4192-5.
- "Bölümler | Karia Yolu". Retrieved 2019-09-22.
- Richardson, Nigel. "Walking holidays in Turkey: the ancient stones of the new Carian Trail". The Telegraph, 11 August 2014
- "Historical trails in Turkey bound by nature and beauty". Daily Sabah, SENA ALKAN, ISTANBUL July 3, 2015