Canton of Nidwalden
The canton of Nidwalden, also canton of Nidwald (German: Kanton Nidwalden, [ˈnidˌvaldən] (![]()
Kanton Nidwalden | |
|---|---|
 Coat of arms | |
Location in Switzerland
Map of Nidwalden 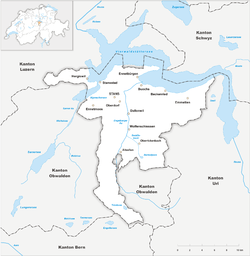 | |
| Coordinates: 46°56′N 8°4′E | |
| Capital | Stans |
| Subdivisions | 11 municipalities |
| Government | |
| • Executive | Regierungsrat (7) |
| • Legislative | Landrat (60) |
| Area | |
| • Total | 275.84 km2 (106.50 sq mi) |
| Population (December 2018)[2] | |
| • Total | 43,223 |
| • Density | 160/km2 (410/sq mi) |
| ISO 3166 code | CH-NW |
| Highest point | 2,901 m (9,518 ft): Rotstöckli |
| Lowest point | 434 m (1,424 ft): Lake Lucerne |
| Joined | 1291 |
| Languages | German |
| Website | www |
History
The earliest traces of human settlement date to the Neolithic with sites found near Stansstad that are from 4000–3100 BC.[4] The same sites, near Stansstad, also contain Late Bronze Age (1400–1100 BC) artifacts, with additional Bronze Age sites near Hergiswil and Ennetmoos. A La Tène (500–100 BC) grave for a 10-year-old girl has been found in Stans. Based on these finds, it appears that the Nidwalden region has been settled since the 1st millennium BC.[4]
During the Roman Empire Ob and Nidwalden were inhabited by a Gallo-Roman or Celtic population. While there are few artifacts from the population, many names of the towns, rivers and mountains have either Celtic or Gallo-Roman roots.[4] By the 8th century the Alemanni entered the valleys of present-day Nidwalden and intermingled. At this time a Roman Catholic church was built in Stans, most likely founded by an Alemanni noble family. The church in Stans would remain until the 10th century when it was replaced by a church in Buochs.[4]
Initially the land was owned by a number of noble families and abbeys. But by the late 13th century the major powers in Nidwalden had shrunk to three: the Habsburgs, Murbach Abbey and Engelberg Abbey. In 1291 Rudolph of Habsburg bought Obwalden from Murbach Abbey. In response the people of Nidwalden (Obwalden joined shortly before the document was signed, the two halves forming Unterwalden) [5] joined Uri and Schwyz to form an alliance which is considered the foundation of the Old Swiss Confederacy.
At the time there was no state, but towards the end of the 14th century early forms of government were established. This included institutionalized assemblies and courts. In the 14th and 15th century the people of Nidwalden joined the people of Obwalden to discuss important matters, but the two cantons were never really one. For example, Obwalden did not participate in the annexation of Bellinzona, Riviera and Blenio areas (today located in the canton of Ticino).
Under the Helvetic Republic imposed in 1798 by French Revolutionary troops, Switzerland became a united country. The ideas of the French Revolution were not popular in some parts of the Swiss nation including Nidwalden. The cantons were accustomed to self-government and many resented the limits on the freedom of worship in particular. When rebel forces threatened the Republic, Nidwalden was attacked by French troops on 9 September 1798. The canton's infrastructure was badly damaged and at least 400 people were killed.
After the end of Napoleonic rule in 1814, most of the changes were reverted. Only in 1877 did Nidwalden introduce a new constitution. The open assembly (Landsgemeinde) was abolished in 1997.
Geography
Nidwalden is located in the centre of Switzerland. To the north it is bounded by the Lake Lucerne (Vierwaldstättersee), to all other directions by mountain chains (Urner Alps). The area of the canton is 276.1 square kilometers (106.6 sq mi) of which about 40% is inhabited or used for farming.[6] Forests occupy about one third of the canton with about one quarter being considered unproductive (mountains or glaciers).[6]
Politics
Federal election results
| Percentage of the total vote per party in the canton in the Federal Elections 1971-2015[7] | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Party | Ideology | 1971 | 1975 | 1979 | 1983 | 1987 | 1991 | 1995 | 1999 | 2003 | 2007 | 2011 | 2015 | |
| FDP.The Liberalsa | Classical liberalism | * b | * | 39.0 | * | * | * | 48.1 | 90.4 | 88.5 | c | 35.2 | * | |
| CVP/PDC/PPD/PCD | Christian democracy | 97.2 | 97.6 | 49.5 | 97.2 | 96.9 | 97.7 | 32.1 | * | * | c | * | * | |
| SP/PS | Social democracy | * | * | 10.6 | * | * | * | * | * | * | c | * | * | |
| SVP/UDC | Swiss nationalism | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | c | 45.2 | 82.8 | |
| GPS/PES | Green politics | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | c | 19.6 | * | |
| SD/DS | National conservatism | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | 8.0 | 10.2 | c | * | * | |
| Other | 2.8 | 2.4 | 0.9 | 2.8 | 3.1 | 2.3 | 19.8 | 1.6 | 1.2 | c | * | 17.2 | ||
| Voter participation % | 51.3 | 38.9 | 59.7 | 29.5 | 23.4 | 23.6 | 58.9 | 46.0 | 39.4 | c | 60.9 | 58.3 | ||
Cantonal election
The cantonal executive (Regierungsrat) is composed of seven members. The local parliament has 60 seats. Nidwalden sends only one deputy to the Swiss Council of States.
Municipalities
There are eleven municipalities: Beckenried, Buochs, Dallenwil, Emmetten, Ennetbürgen, Ennetmoos, Hergiswil, Oberdorf, Stans, Stansstad and Wolfenschiessen. The capital is Stans.
Demographics
The population of the canton (as of 31 December 2018) is 43,223.[2] As of 2007, the population included 4,046 foreigners, or about 10% of the total population. By gender the canton is nearly evenly split with 50.9% male and 49.1% female.[3] In 2000, 75.6% of the population was Roman Catholic while 11.9% belong to the Swiss Reformed Church.[8] The population density in December 2005 was 144.3 persons per km2.[6] Most of the population (as of 2000) speaks German (92.5%) with a small minority speaking Italian (1.4%) or Serbo-Croatian (1.2%).[6]
Economy
Up to the 20th century Nidwalden was dominated by agriculture. Cattle and cheese were exported mainly to northern Italy. Around 1500, many people in Nidwalden worked as mercenary soldiers.
From the middle of the 19th century onwards, trade, industry and tourism gained momentum. Nevertheless, until the middle of the 20th century, agriculture dominated the canton. Today a great number of small and middle-sized businesses dominate the economy. The largest employer is the airplane constructor Pilatus. The small and middle-sized businesses work in a wide range of areas. Many specialize in machine construction, medical equipment, international trade, optics and electronics.
Traditional areas such as forestry and agriculture are still of importance. Agriculture is specialized in cattle and dairy farming. The farms are still run by individual families.
In recent years, Nidwalden is becoming an increasingly common place to live and work. This is caused by its low taxes, its central location between Zürich and Milan, and its natural environment.
Tourism

Because of its mountainous geography, tourism is important in Nidwalden. The lake and the mountains attract many tourists, both during the winter and the summer. Major resorts include Klewenalp, Stanserhorn (mountain), the region around Bannalp, and Bürgenstock.
Culture
Traditional culture in Nidwalden has been kept alive by many local organisations. There is traditional music, yodeling, dances, theaters and festivals. There are also a number of modern cultural events, such a concerts and galleries.
Notes and references
- Arealstatistik Land Cover - Kantone und Grossregionen nach 6 Hauptbereichen accessed 27 October 2017
- Swiss Federal Statistical Office - STAT-TAB, online database – Ständige und nichtständige Wohnbevölkerung nach institutionellen Gliederungen, Geburtsort und Staatsangehörigkeit (in German) accessed 23 September 2019
- Federal Department of Statistics (2008). "Ständige Wohnbevölkerung nach Staatsangehörigkeit, Geschlecht und Kantonen". Archived from the original (XLS) on 15 December 2008. Retrieved 5 November 2008.
- Ackermann, Hansjacob; Schleifer, Karin; Weber, Emil (March 2007). Geschichte Nidwaldens: Ein kurzer Überblick. Staatsarchive Nidwalden. Archived from /Publikation+-+Geschichte+NW+%DCberblick_2008_02.pdf the original Check
|url=value (help) (PDF) on 5 June 2011. Retrieved 1 December 2008. (in German) - . Encyclopædia Britannica. 26 (11th ed.). 1911.
- Federal Department of Statistics (2008). "Regional Statistics for Nidwalden". Retrieved 1 December 2008.
- Nationalratswahlen: Stärke der Parteien nach Kantonen (Schweiz = 100%) (Report). Swiss Federal Statistical Office. 2015. Archived from the original on 2 August 2016. Retrieved 3 August 2016.
- Federal Department of Statistics (2008). "Wohnbevölkerung nach Religion, nach Kantonen und Städten". Archived from the original (Microsoft Excel) on 24 September 2016. Retrieved 6 October 2008.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Canton of Nidwalden. |
- Official Site (in German)
- Official statistics
- Nidwalden Tourism
