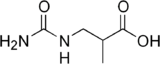
beta-Ureidoisobutyric acid
β-Ureidoisobutyric acid is an intermediate in the catabolism of thymine.
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
2-Methyl-3-ureidopropanoic acid | |
| Systematic IUPAC name
3-(Carbamoylamino)-2-methylpropanoic acid[1] | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| 3DMet | |
| 1768736 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.236.960 |
| KEGG | |
| MeSH | beta-ureidoisobutyric+acid |
PubChem CID |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C5H10N2O3 | |
| Molar mass | 146.146 g·mol−1 |
| Related compounds | |
Related alkanoic acids |
|
Related compounds |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
References
- "beta-ureidoisobutyric acid - Compound Summary". PubChem Compound. USA: National Center for Biotechnology Information. 16 September 2004. Identification. Retrieved 28 June 2012.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.