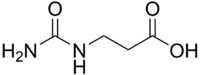
3-Ureidopropionic acid
3-Ureidopropionic acid, also called N-carbamoyl-beta-alanine, is an intermediate in the metabolism of uracil. It is a urea derivative of beta-alanine.
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
3-(Carbamoylamino)propanoic acid | |
| Other names
3-Ureidopropanoic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| 3DMet | |
| 1705263 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.255.338 |
| 675230 | |
| KEGG | |
| MeSH | N-carbamoyl-beta-alanine |
PubChem CID |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C4H8N2O3 | |
| Molar mass | 132.119 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White crystals |
| log P | −1.23 |
| Acidity (pKa) | 4.408 |
| Basicity (pKb) | 9.589 |
| Hazards | |
| S-phrases (outdated) | S22, S24/25 |
| Related compounds | |
Related alkanoic acids |
|
Related compounds |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
References
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.