Beaumont-de-Lomagne
Beaumont-de-Lomagne is a commune in the Tarn-et-Garonne department in the Occitanie region in southern France.
Beaumont-de-Lomagne | |
|---|---|
 Beaumont-de-Lomagne | |
.svg.png) Coat of arms | |
Location of Beaumont-de-Lomagne 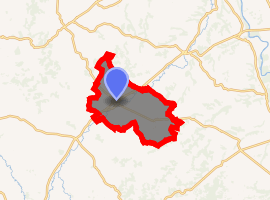
| |
 Beaumont-de-Lomagne  Beaumont-de-Lomagne | |
| Coordinates: 43°53′02″N 0°59′21″E | |
| Country | France |
| Region | Occitanie |
| Department | Tarn-et-Garonne |
| Arrondissement | Castelsarrasin |
| Canton | Beaumont-de-Lomagne |
| Government | |
| • Mayor | Jean-Luc Deprince |
| Area 1 | 46 km2 (18 sq mi) |
| Population (2017-01-01)[1] | 3,758 |
| • Density | 82/km2 (210/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+01:00 (CET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+02:00 (CEST) |
| INSEE/Postal code | 82013 /82500 |
| 1 French Land Register data, which excludes lakes, ponds, glaciers > 1 km2 (0.386 sq mi or 247 acres) and river estuaries. | |
Geography
The river Gimone runs through the town.
History
Beaumont-de-Lomagne, bastide, was founded in 1276 following the act of coregency between the abbey of Grandselve and King Philip III of France – the King was represented by his seneschal for the former County of Toulouse, Eustace de Beaumarchais. In 1278 the town was granted a very liberal charter of laws, by the standards of the period, defining the rights and duties of its inhabitants.
In 1280, work commenced on a large church; its flat apse shows the influence of Cîteaux. The bell-tower, was made in the fifteenth century and resembles that of Saint-Sernin in Toulouse. Construction finished around 1430 and the Bishop of Montauban, driven out of his city by the English, made it his episcopal seat until 1432.
The market hall, in the centre of the town square, was designed for the markets that took place every Saturday.
The fourteenth century marked the beginning of the Hundred Years' War. Taken by the English in 1345, Beaumont was recaptured in 1350 but continued to be plundered by "Great Companies" and experienced civil war due to the opposition of two military chiefs: Count of Foix and John I, Count of Armagnac. The century ended with an epidemic of the plague which killed 500 inhabitants.
By the sixteenth century, Beaumont, a catholic town, was surrounded by three protestant towns: Montauban, Mas-Grenier and Mauvezin. In 1577, Henri III sold Beaumont to Henri III of Navarre (future Henri IV), leader of the Protestants and whose troops came to massacre a hundred Beaumontois.
In December 1580, 600 mercenaries of Montauban demobilized and took Beaumont. They remained for two months, and caused much damage to the town. When peace returned, many Beaumontois adopted the policy of religious tolerance as advocated by Henri IV.
The eminent mathematician Pierre de Fermat, famous for Fermat's Last Theorem, was born in Beaumont in either 1601 or 1607. There is a statue and museum to him in the town.
In the seventeenth century, Louis XIII besieged several cities in the south-west including Beaumont; the "Chateau de Roi" was destroyed by royal decree. In 1639 Louis sold Beaumont to the Prince of Condé. Under Louis XIV, Beaumont was still under the jurisdiction of viscount Armand de Bourbon, prince de Conti, one of the nobility involved in the Fronde, Beaumont was therefore part of the rebellion and this caused considerable losses to the town. There was an occupation in 1651 by Conti troops, rebelling against the king. The incident ended without conflict, but Beaumont, ruined, had to pay a large fine; another plague epidemic also occurred during this event.
In 1702, the town had only 2,400 inhabitants but during this period of peace, it undertook various works and became prosperous again.
In 1777, the ramparts were destroyed.
After sending a delegate to the Estates General, Beaumont created a revolutionary club, but from 1790 the town became part of the Haute-Garonne department and became isolated, to the advantage of Grenade, its neighbour and rival. Grenade became the chief town of district. In 1808, new department divisions were brought in by Napoleon and Beaumont began to be within the Tarn-et-Garonne region.
Though the importance of large fairs has decreased, Beaumont remains an important agricultural market due to the cultivation of garlic. It retains much of its history through its old buildings: the church, its fortress – whose imposing mass dominates the town – the large market with its distinctive roof, as well as approximately fifteen private mansions, the majority of which date from the seventeenth to nineteenth centuries.
Town government
List of mayors:
- March 2001 – 2008: Faustin Llido, UMP party
- March 2008 – present : Jean-Luc Deprince Radical Movement party
Population
- 1962–3486
- 1968–3629
- 1975–3625
- 1982–3579
- 1990–3488
- 1999–3690
- 2006-3894
Places and monuments
- Hotel Toureilh (eighteenth century), now the Town Hall
- Fifteenth century covered market
- Statue of the mathematician Pierre Fermat
- Hotel Fermat 1500/1800 - Rue Fermat
- House of the two crosses (sixteenth century) - Rue de l'église
- Gothic church and Toulouse-style octagonal bell-tower; construction began around 1280
- Presbytery (around fifteenth century) - Rue de Presbytere
- House of Seigneur d'Argombat (sixteenth century) - Rue de l'église
- Hôtel Saline puis du Rouble - Rue Fermat
- House of Jean d'Armagnac, (fifteenth century) - rue de la République
- Hotel Noble (eighteenth century) - rue de la République
- Hotel Vergnes (sixteenth and eighteenth century) - rue Lomagne
- Les Cordeliers, Hôpital St Jacques (thirteenth and fourteenth centuries, convent from seventeenth century) - rue Despeyrous
- Convent of Clarisses (seventeenth century) - rue Toureilh
- Hotel Long, late (eighteenth century) - rue Nationale
- Hotel François Bordes - street Nationale
- House of François Darquier - rue Darquier
- First houses of Beaumont - rue Launac and rue Toureilh
 Town hall
Town hall Statue of Pierre Fermat
Statue of Pierre Fermat the covered market
the covered market the covered market
the covered market Hotel Fermat
Hotel Fermat The Church
The Church Chapel St.John
Chapel St.John
Personalities
- The mathematician Pierre de Fermat, famous for Fermat's Last Theorem, was born in the town on 17 August 1601/1607/1608 (the exact year is unknown).[2]
References
- "Populations légales 2017". INSEE. Retrieved 6 January 2020.
- Klaus Barner (2001): How old did Fermat become? Internationale Zeitschrift für Geschichte und Ethik der Naturwissenschaften, Technik und Medizin. ISSN 0036-6978. Vol 9, No 4, pp. 209-228.