Baoni State
Baoni State was a princely state in India during the British Raj. It was a small sanad state, the only Muslim-ruled one in Bundelkhand Agency. Its ruler was granted the right to an 11 gun salute. The Baoni Royal Family claim to be descendants of the Asaf Jahi dynasty of Hyderabad, tracing its origins to Abu Bakr, the First Islamic Caliph.[3]
| Baoni State बावनी रियासत / باونی ریاست | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Princely State of British India | |||||||||
| 1784–1948 | |||||||||
 Flag
 Coat of arms
| |||||||||
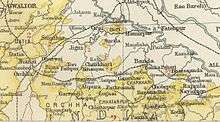 Baoni State (Kadaura) in the Imperial Gazetteer of India | |||||||||
| Area | |||||||||
• 1901 | 313 km2 (121 sq mi) | ||||||||
| Population | |||||||||
• 1901 | 19,780 | ||||||||
| Government | |||||||||
| • Motto | '"Al hukumu lilah wāl mulk Lilāh" (Rulership and dominion belongs to God) | ||||||||
| History | |||||||||
• Established | 1784 | ||||||||
| 1948 | |||||||||
| |||||||||
| The Imperial Gazetteer of India[1] | |||||||||

Baoni was located in the Betwa-Yamuna doab, Uttar Pradesh, with Kadaura as its seat of government. The state was bounded on the north by the district of Cawnpore, in the west by the district of Jalaun and to the south and east by the district of Hamirpur of the United Provinces —as well as a little part in the south-east by Beri State.[4] The word 'Baoni' originated in the Hindustani language word Baon, meaning 52 (fifty-two),[5] and referring to the number of villages that were included in the original sanad at the time when it was granted. Baoni had a population of 19,780 inhabitants in 1901, of whom 87% were Hindu and 12% Muslim.[4]
History
Baoni State was founded in 1784 by Imad al-Din al-Mulk Ghazi Khan, from a branch of the Asaf Jahi dynasty related to the Nizam, and Wazir of the Mughal Empire. At that time he made a deal with the Maratha Peshwa and received a jagir of 52 villages near Kalpi.
The state became a British protectorate in 1806, following the defeat of the Maratha Confederacy. The capital was moved from Kalpi to Kadaura after 1815.
The last ruler, Muhammad al-Hasan Mushtaq, signed the instrument of accession to the Indian Union on 15 August 1947 and continued to rule the state that joined the Union of States of Vindhya Pradesh on 2 April 1948, remaining as head of state until 31 December 1949.[6]
Rulers
All rulers of Baoni State bore the title of Nawab.
- 1784 – 1 September 1800 Ghazi ud-Din Khan Feroze Jung III (b. 1736 – d. 1800)
- 1 September 1800 – 11 May 1815 Naser ad-Dowla (b. c.1756 – d. 1815)
- 11 May 1815 – 18 October 1838 Amir al-Molk (d. 1838)
- 18 Oct 1838 – 18 August 1859 Mohammad Hosayn (d. 1859)
- 18 Aug 1859 – 5 October 1883 Emam ad-Dowla Hosayn (d. 1895)
- 5 October 1883 – 27 June 1893 Mohammad Hasan Khan (b. 1863 – d. 1893)
- 27 Jun 1893 – 27 October 1911 Riaz al-Hasan Khan (b. 1876 – d. 1911) (recognized 2 August 1894)
- 27 Oct 1911 – 15 August 1947 Mohammad Moshtaq al-Hasan Khan (b. 1896 – d. 1977)
- Nawab Mustaqul Hasan
- Nawab Adeel Hasan
- Nawab Nabeel Hasan
See also
- Kadaura
- Nizam of Hyderabad
- List of Sunni Muslim dynasties
- Mahseer in heraldry
References
- Hunter, Sir William Wilson; Trübner & Co., London 1885
- Baoni-Bundelkhand – Fotw
- Hunter, Sir William Hunter; Cotton, James Sutherland; Burn, Richard; Meyer, William Stevenson (1908). The Imperial Gazetteer of India. Oxford: Great Britain India Office, Clarendon Press.
- Imperial Gazetteer of India, v. 6, p. 414.
- The Baoni State
- "Baoni Princely State (11 gun salute)". Archived from the original on 23 April 2018. Retrieved 21 June 2014.
External links

- Pictures of Baoni State
- Kadaura Destination Guide