BIT225
BIT225 is an experimental drug candidate under development by Biotron Limited for use in the treatment of both HIV and hepatitis C infection. By blocking Vpu ion channel activity, it disrupts HIV assembly within host monocyte cells; its method of action is a first for HIV drugs.[1] Because it targets replication in monocyte derived macrophages, it offers promise for treatment of viral reservoirs that are unaffected by standard treatments.[2] The activity of BIT225 is post-virus integration, with no direct effects on the HIV enzymes reverse transcriptase and protease.[3] Since Vpu ion channel activity is highly conserved, the virus is unlikely to become resistant via generation of Vpu ion-independent virus. In addition, the drug also has been credited with curing hepatitis C after 12 weeks of treatment.[4]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
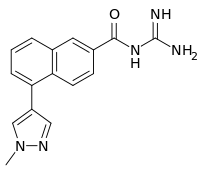
| IUPAC name
N-Carbamimidoyl-5-(1-methyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)-2-naphthamide | |
| Other names
BIT-225 | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C16H15N5O | |
| Molar mass | 293.330 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
References
- BIT225 therapy reduces HIV-1 burden in monocyte cells and decreases immune activation
- BIT225, a Novel Assembly Inhibitor, Cuts HIV Load in Monocyte Reservoir
- Antiviral Efficacy of the Novel Compound BIT225 against HIV-1 Release from Human Macrophages
- BIT225 Trial Results Show Effective Cure of Hepatitis C