Trinodus
Trinodus is a very small to small (about 1 centimetre or 0.39 inches) blind trilobite, a well known group of extinct marine arthropods, which lived during the Ordovician (Tremadocian to early Hirnantian),[1] in what are now the Yukon Territories, Virginia, Italy, Czech Republic, Poland, Denmark, Sweden, Svalbard, Ireland, Scotland, Wales, Iran, Kazakhstan and China. It is one of the last of the Agnostida order to survive.
| Trinodus | |
|---|---|
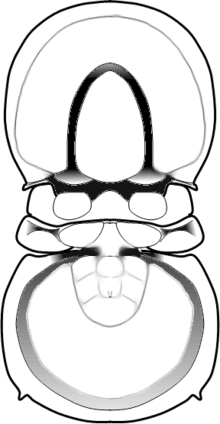 | |
| A drawing of Trinodus tardus | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Arthropoda |
| Class: | †Trilobita |
| Order: | †Agnostida |
| Family: | †Metagnostidae |
| Genus: | †Trinodus M'Coy, 1846 |
| Type species | |
| †Trinodus agnostiformes M'Coy, 1846 | |
| Species | |
| |
| Synonyms | |
| |
Etymology
Trinodus is derived from the Latin tri (three) and nodus (node).
Arthrorhachis is derived from the Greek ἄρθρον (árthron, "joint") and ῥάχις (rháchis, meaning axis, spine, ridge or backbone).[1]
Taxonomy
Trinodus, Arthrorhachis and Geragnostus are closely related and it may be appropriate to assign their species to just one genus. All species in these three genera have virtually identical cephalons, but of T. agnostiformes, the type species of Trinodus only one poorly preserved cephalon was known. However, relatively recent, pygidia assignable to T. agnostiformes were found. Although this material is distorted or incompletely preserved, it is very similar to the pygidium of Arthrorhachis tarda. Species with a rear rhachis lobe longer than the postaxial region are henceforth combined in Geragnostus, all others are assigned to Trinodus.[2]
Species previously assigned to Trinodus
- T. glabratus var. kirgizica = Geragnostus kirgizica
- T. kirgizica = Geragnostus kirgizica
- T. longicollis = Geragnostus longicollis
Distribution
- T. agnostiformes was identified in the Upper Ordovician of Ireland (Caradoc, Greenville slates, Campile Formation).[3]
- Trinodus danicus occurs in Ordovician of Svalbard (Ibexian 488.3 - 471.8 Mya, Psephosthenaspis nasuta trilobite zone, Olenidsletta Member, Valhallfonna Formation, Ny Friesland, 79.8° N, 17.8° E).[4]
- Trinodus elspethi is present in the Upper Ordovician of the USA (Kathian?, Athens Shale, Ina railroad cutting, South of Otes, North of Bulls Gap, Hawkins, Tennessee).[1]
- T. hupehensis has been found in the Middle Ordovician of China (Dawan Formation, upper Arenig, Fenxiang, Yichang County, West Hubei).[2]
- Trinodus knockerkensis has been collected from the Ordovician of Ireland (Lower Caradoc, Brickwork's Quarry Shales Member, Knockerk Formation, 53.8° N, 6.6° W).[5]
- Trinodus pragensis is present in the Upper Ordovician of the Czech Republic (Lower Katian, abandoned brickyard “Na bílém koni”, Bohdalec Formation, Karlíkore Horizon, Praha-Hloubětín). A. pragensis precedes A. tardus in Czech Republic.[1]
- Trinodus tardus is present in the Upper Ordovician of Denmark (Læså - stream section at Vasegård -, Øleå - stream section at Billegrav Gård -, and Risebæk, all Bornholm),[6] of Sweden (In Skåne: Koången in the classical Fågelsång area east of Lund; Koången core; Lindegård core; Rostånga; Tommarp; Jerrestad, stream section in the Jerrestadsån rivulet; Tosterup. In Ostergotland: Råssnås and Rodbergsudden, both near MotalaIn. In Våstergotland: Lower Jonstorp Formation "Green Tretaspis Shale" at Bestorp – Mosseberg. Upper Jonstorp Formation "Red Tretaspis Shale" and Ulunda Mudstone of the upper Jerrestadian Stage at Stommen (Kungslena); Varvsberget, Skogastorp, Plantaberget (Hogstenaberget); Skultorp, Billingen; Rustsåter, Kinnekulle; Kullatorp core, Kinnekulle. In Dalarna: Vikarbyn and Gulleråsen-Sanden)[6] of Norway (Oslo Region, Hovedøya, Spannslokket Member of the Skogerholmen Formation; Åslund, Hadeland Gagnum Shale Member of the Lunner Formation)[6] of the Czech Republic (upper Katian, Tretaspis seticornis community, Kraluv Dvur Formation),[7] of Italy (Foliomena community, Domusnovas Formation, Punta S'Argiola, Sardinia, 40.0° N, 8.0° E),[8] of Iran (late Caradoc, early Asgill, Tatavrud, 35 km southwest of Bandar-e-Anzali),[3] and of Kazakhstan.[6]
- Trinodus sp. (presumably T. tardus) has been collected from the Ordovician of Czech Republic (Králův Dvůr Formation, Prague Basin).[9]
- Trinodus sps. are found in the Ordovician of Canada (Llanvirn, Road River Formation, Peraspis fauna, Yukon Territory, 62.8° N, 136.6° W, and Cnemidopyge fauna, 65.0° N, 111.5° W),[10] of China (Baota (Pagoda) Formation, NingLang, NingLang County, Yunnan),[11] of Poland (Hirnantian, Holycross Mountains, 51.0° N, 21.0° E),[12] of Wales (North Wales Rawtheyan Assemblage 4C, Crugan Mudstone and Duyfor Mudstone fauna, 53.0° N, 4.0° W;[13] Rhwlas Limestone Formation[14] and Opsimasaphus-Nankinolithus trilobite association,[15] 53.0° N, 3.0° W; Pontyfeni Formation, B. rushtoni and Stapeleyella abyfrons biozone, Whitland, 52.0° N, 5.0° W)[16] and Scotland (Costonian, Superstes Mudstone, Stinchar River tributary, Colmonell, Gircan District, Strathclyde, 57.0° N, 4.0° W).[17]
Development
Trinodus elspethi, which - as an agnostoid - only has two thorax segments, has at least nine larval stages (or instars), three meraspid and six holaspid, in its life. So it molted at least eight times.[18]
References
- Budil, P.; Fatka, O.; Kolář, P.; David, M. (2011). "Arthrorhachis Hawle & Corda, 1847 (Agnostida) in the Prague Basin revisited" (PDF). Bulletin of Geosciences. 86 (4): 707–724. doi:10.3140/bull.geosci.1262.
- Turvey, S.T. (2005). "Agnostid trilobites from the Arenig-Llanvirn of South China". Transactions of the Royal Society of Edinburgh: Earth Sciences. 95 (3–4): 527–542. doi:10.1017/s026359330000119x.
- Karim, T.S. (2009). "Ordovician trilobites from Iran". Earth and Environmental Science Transactions of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. 99 (2): 101–124. doi:10.1017/s1755691009007063.
- Fortey, R. A. (1980). "The Ordovician trilobites of Spitsbergen. III. Remaining trilobites of the Valhallfonna Formation". Norsk Polarinstitutt Skrifter. 171: 1–163.
- Romano, M.; Owen, A. W. (1993). "Early Caradoc Trilobites of Eastern Ireland and their paleogeographical significance". Palaeontology. 36 (3): 681–720.
- Ahlberg, P. (1989). "Agnostid trilobites from the Upper Ordovician of Sweden and Bornholm, Denmark" (PDF). Bulletin of the Geological Society of Denmark. 37: 213–226.
- Chlupac, I.; Havlicek, V.; Kukal, Z.; Storch, P. (1998). Palaeozoic of the Barrandian (Cambrian to Devonian). pp. 1–183.
- Leone, F.; Hammann, W.; Laske, R.; Serpagli, E.; Villas, E. (1991). "Lithostratigraphic units and biostratigraphy of the post-sardic Ordovician sequence in south-west Sardinia". Bollettino della Societá Paleontologica Italiana. 30: 201–235.
- Havlicek, V.; Vanek, J. (1990). "Ordovician Invertebrate communities in black-shale lithofacies (Prague Basin, Czechoslovakia)". Vestnik Ustredniho Ustavu Geologickeho. 65: 223–236.
- Ludvigsen, R. (1981). "Biostratigraphical significance of Middle Ordovician trilobites from the Road River Formation, northern Cordillera". Geological Association of Canada, Abstracts. 6 (A-36).
- Stratigraphic Group of Yunnan, China (1978). Regional stratigraphic data of Southwest China, Yunnan Province. Beijing: Geological Publishing House.
- Temple, J.T. (1965). "Upper Ordovician Brachiopods from Poland and Britain". Acta Palaeontologica Polonica. 10: 379–450.
- Price, D. (1981). "Ashgill trilobite faunas from the Llyn Peninsula, North Wales, U.K". Geological Magazine. 16 (3): 201–216. doi:10.1002/gj.3350160305.
- Bassett, D.A.; Whittington, H.B.; Williams, A. (1966). "The Stratigraphy of the Bala District, Merionethshire". Quarterly Journal of the Geological Society of London. 122 (3): 219–269. doi:10.1144/gsjgs.122.1.0219.
- Price, D.; Magor, P.M. (1984). "The ecological significance of variation in the genesis composition of Rawtheyan (Late Ordovician) trilobite faunas from North Wales, U.K". Geological Journal. 19 (2): 187–200. doi:10.1002/gj.3350190207.
- Fortey, R. A.; Owens, R.M. (1978). "Early Ordovician (Arenig) stratigraphy and faunas of the Carmarthen District, South-West Wales". Bulletin of the British Museum (Natural History), Geology Series. 30 (3): 225–294.
- Tripp, R.P.; Williams, A.; Paul, C.R.C. (1981). "On an exposure of the Ordovician superstes Mudstones at Colmonell, Gircan District, Strathclyde". Scottish Journal of Geology. 17: 21–25. doi:10.1144/sjg17010021.
- Whittington, H. B. et al. Part O, Treatise on Invertebrate Paleontology. Revised, Volume 1 – Trilobita – Introduction, Order Agnostida, Order Redlichiida. 1997