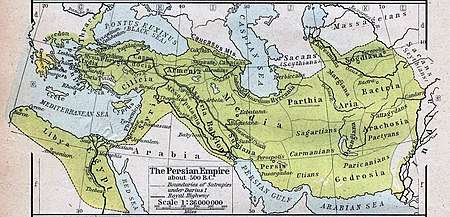
Aria (region)
Aria (Greek: Ἀρ(ε)ία Ar(e)ía, آريا; Latin Aria, representing Old Persian. Haraiva, Avestan Haraeuua) is an Achaemenid region centered on the city of Herat in present-day western Afghanistan. In classical sources, Aria has been several times confused with the greater region of ancient Ariana, of which Aria formed a part.


| Aria | |
|---|---|
| Province of the Achaemenid, Seleucid, and Parthian Empires | |
| ca. 530 BC–early 3rd-century | |
| Capital |
|
| Historical era | Antiquity |
• Established | ca. 530 BC |
• Kushan conquest | early 3rd-century |
| Today part of | |
Geography
Aria was an Old Persian satrapy, which enclosed chiefly the valley of the Hari River (Greek Ἄρ(ε)ιος, this being eponymous to the whole land according to Arrian[1]) and which in antiquity was considered as particularly fertile and, above all, rich in wine. The region of Aria was separated by mountain ranges from the Paropamisadae in the east, Parthia in the west and Margiana and Hyrcania in the north, while a desert separated it from Carmania and Drangiana in the south. It is described in a very detailed manner by Ptolemy and Strabo [2] and corresponds, according to that, almost to the Herat Province of today's Afghanistan. In this sense the term is used correctly by some writers, e.g. Herodotus (3.93.3, where the Areioi are mentioned together with the Parthians, Chorasmians, and Sogdians); Diodorus (17.105.7; 18.39.6); Strabo (2.1.14; 11.10.1, cf. also 11.8.1 and 8; 15.2.8 and 9); Arrian (Anabasis 3.25.1); Pomponius Mela (1.12, where we read that “nearest to India is Ariane, then Aria”).

Its original capital was Artacoana (Ἀρτακόανα)[3] or Articaudna (Ἀρτίκαυδνα) according to Ptolemy. In its vicinity, a new capital was built, either by Alexander the Great himself or by his successors, Alexandria Ariana (Ἀλεξάνδρεια ἡ ἐν Ἀρίοις), modern Herat in northwest Afghanistan. Ptolemy lists several other cities, an indication of the province's wealth and fertility. The most important, according to Ptolemy and Arrian were:[4][5]
|
|
|
|
|
|
History
The Persian Achaemenid district of Aria is mentioned in the provincial lists that are included in various royal inscriptions, for instance, in the Behistun inscription of Darius I (c. 520 BC). Representatives from the district are depicted in reliefs, e.g., at the royal Achaemenid tombs of Naqsh-e Rustam and Persepolis. They are wearing Scythian-style dress (with a tunic and trousers tucked into high boots) and a twisted turban around the head.
At the time of Alexander the Great, Aria was obviously an important district. It was administered by a satrap, called Satibarzanes, who was one of the three main Persian officials in the East of the Empire, together with the satrap Bessus of Bactria and Barsaentes of Arachosia. In late 330 BC, Alexander the Great, captured the Arian capital Artacoana. The province was part of the Seleucid Empire but was captured by others on various occasions and became part of the Parthian Empire in 167 BC. Aria was sometime between the late 2nd- and early 3rd-century conquered by the Kushan Empire, who would later in ca. 230 lose the province to the Sasanian Empire, where it became known as Harev.
See also
- Arii (disambiguation)
- Arianus (disambiguation)
- Alexandria in Ariana
- Arian (disambiguation)
- Ariana (disambiguation)
- Artacoana
- Herat
References
- Arrian, Anabasis 4.6.6
- Prolemy, 6.17; Strabo, 11.10.1
- Arrian, Anabasis 3.25
- European Cultural Heritage Online (ECHO), Ptolemaeus, Claudius, Geografia : cioè descrittione vniversale (universale) della terra; partita in due volumi, 1621, pages 114 & 115
- Encyclopédie méthodique ou par ordre de matières par une société de gens de lettres, de savants et d'artistes (1871), page 206
Sources
- Greatrex, Geoffrey; Lieu, Samuel N. C. (2002). The Roman Eastern Frontier and the Persian Wars (Part II, 363–630 AD). New York, New York and London, United Kingdom: Routledge (Taylor & Francis). ISBN 0-415-14687-9.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Pourshariati, Parvaneh (2008). Decline and Fall of the Sasanian Empire: The Sasanian-Parthian Confederacy and the Arab Conquest of Iran. London and New York: I.B. Tauris. ISBN 978-1-84511-645-3.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Zarrinkub, Abd al-Husain (1975). "The Arab conquest of Iran and its aftermath". The Cambridge History of Iran, Volume 4: From the Arab Invasion to the Saljuqs. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. pp. 1–57. ISBN 978-0-521-20093-6.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Morony, M. (1986). "ʿARAB ii. Arab conquest of Iran". Encyclopaedia Iranica, Vol. II, Fasc. 2. pp. 203–210.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Vogelsang, W. J. (2003). "HERAT ii. HISTORY, PRE-ISLAMIC PERIOD". Encyclopaedia Iranica, Vol. XII, Fasc. 2. pp. 205–206.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)