Mountain beaver
The mountain beaver (Aplodontia rufa)[Note 1] is a North American rodent. It is the only living member of its genus, Aplodontia, and family, Aplodontiidae.[2] It should not be confused with true North American and Eurasian beavers, to which it is not closely related.[3][4]
| Mountain beaver | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Rodentia |
| Family: | Aplodontiidae |
| Genus: | Aplodontia Richardson, 1829 |
| Species: | A. rufa |
| Binomial name | |
| Aplodontia rufa (Rafinesque, 1817) | |
 | |
Characteristics

Mountain beavers are gray or brown, but their fur can range from slightly more reddish to more blackish depending on subspecies, with a light patch under each ear. The animals have distinctively short tails. Adults weigh about 500–900 g (18–32 oz), with a few specimens topping 1,000 g (35 oz). Total length is about 30–50 cm (12–20 in), with a tail length of 1–4 cm (0.39–1.57 in). Their superficial similarity with true beavers reflects only their relatively large size (for rodents), strong odor, preference for living in extremely watery / moist habitats, and propensity to consume tree seedlings as food – mountain beavers do not fell adult trees (though such trees may be killed by "girdling"), build dams, live in lodges, or communicate by tail slappings. They are predominantly nocturnal in above ground activities.[5] They are known to climb trees a few meters to acquire food in the form of branches and leaves, but otherwise their diet consists mostly of ferns, especially species which are toxic to other animals.[6]
The skull is protrogomorphous;[7] it has no specialized attachments for the masseter muscles as seen in other rodents. It is flattened and lacks a postorbital process. The baculum is thin and distinctly forked.[8] The penis is about 4.5 cm (1.8 in) in length. The male does not have a true scrotum, but the testes move into a position called semiscrotal during the breeding season.
Mountain beavers have an unusual projection on each molar and premolar tooth, which is unique among mammals and allows for easy identification of teeth. This projection points toward the cheek on the upper tooth row, but points toward the tongue on the lower. The cheek teeth lack the complex folds of other rodents and instead consist of single basins. They are hypsodont and ever-growing. Two upper and one lower premolars are present, along with all the molars, giving a dental formula of 1.0.2.31.0.1.3[8]
Mountain beavers cannot produce concentrated urine. They are thought to be physiologically restricted to the temperate rain forest regions of the North American Pacific coast and moist microenvironments inland due to their inability to obtain sufficient water in more arid environments. Their karyotype is 2n = 46.
Habits and distribution
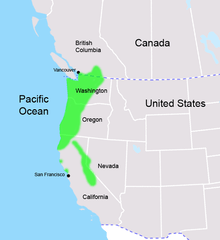
Mountain beavers are found in the Cascade Mountains of British Columbia and southward to include the rest of the Cascade Range in the United States,[9] the Olympic Mountains and Coast Ranges of Washington and Oregon,[10] plus the Siskiyous, and the Sierra Nevada mountain range, Point Arena and Pt. Reyes of California and extreme western Nevada.[9] They range from sea level to the tree line.[9] They can be found in both deciduous and coniferous forests, but throughout most of the range appear to prefer the former. These animals appear to be physiologically limited to moist microenvironments, with most subspecies occurring only in regions with minimal snowfall and cool winters. They do not appear to be able to conserve body heat or warmth as efficiently as other rodents.,[11] nor do they hibernate.
Mountain beavers are asocial and do not live in shared burrows. Burrows usually consist of a network of tunnels built in deep soil. The entrances to these burrows often contain clumps of wilted vegetation which the animal likely uses as a kind of food cache as well as a source of nesting material. Mountain beavers seldom travel more than a few meters from their burrow entrances, taking advantage of the protection such burrows offer from predators such as mountain lions and owls (though skunks and weasels that also occupy mountain beaver burrows and tunnels may take nestlings as food).[6]

They exhibit coprophagy and eat soft fecal pellets to obtain maximum nutrients; hard fecal pellets are transferred to fecal chambers located within the burrow system.[12][13] Food includes fleshy herbs and young shoots of more woody plants. Ferns probably make up the bulk of their diets. They appear to be strictly herbivorous.[11] Their consumption of seedling trees has led some to consider them as pests. They appear to build hay mounds at some burrow entrances, but whether this behavior is related to water regulation, curing food, or gathering nest materials is debated.
Known predators include bobcats, coyotes, cougars, golden eagles, and owls.[14] Among the parasites of the mountain beaver is the largest flea known, Hystrichopsylla schefferi. Females of this flea can be 8 mm (0.31 in) long.[15]
The breeding season is between January and March, with two or three young born February to April. The young are born hairless, pink, and blind. Lifespans are 5 to 10 years – fairly long for rodents. They are not social, though home ranges can overlap.[11]
Mountain beavers are capable of climbing trees,[16] but rarely travel far from burrows. Their thumbs are slightly opposable and the animals will sit on their hindquarters and manipulate food with their fore limbs and incisors.
Spelling and etymology

Most references use the spelling Aplodontidae for the family name. This has been deemed incorrect due to the technical rules of converting a genus name into a family name. The proper conversion of Aplodontia to a family name is to drop the -a only and add -idae. Thus, Aplodontiidae is technically correct. This spelling is gaining acceptance in modern texts and is the standard spelling currently recognized by the Integrated Taxonomic Information System.
Alternate spellings of the genus name have also been reported, with as many as 30 variants historically. These include Haplodontia, Haplodon, Aploodontia, Apluodontia, and Aplodontie, among others. The name Aplodontia ("simple tooth") is in reference to the single large basin comprising the bulk of each cheek tooth. The specific epithet, rufa means red or reddish.
Subspecies
At present, seven subspecies of Aplodontia rufa are recognized:
- A. r. californica (Peters, 1864): distributed throughout the Sierra Nevada in Northern California and extreme western Nevada
- A. r. humboldtiana Taylor, 1916: restricted to the far northwestern coast of California
- A. r. nigra Taylor, 1914: restricted to a small region in southern Mendocino County, California
- A. r. pacifica Merriam, 1899: distributed across coastal Oregon
- A. r. phaea Merriam, 1899: found in a small pocket just northwest of San Francisco, California
- A. r. rainieri Merriam, 1899: found across the Cascade Range from southern British Columbia to northern California
- A. r. rufa (Rafinesque, 1817): found along coastal Washington, particularly on the Olympic Peninsula
Closest relatives
The mountain beaver is considered a living fossil, due to the presence of a host of primitive characteristics, particularly the protrogomorphous zygomasseteric system. This condition is similar to what is found in most mammal groups, such as rabbits, where no extreme specialization of the masseter muscle has evolved. In the protrogomorphous condition, the masseter muscle does not pass through the infraorbital foramen as it does in guinea pigs and mice. Likewise, the medial masseter muscle attaches to the base of the zygomatic arch and does not extend to the region in front of the eye as is seen in squirrels and mice.
The mountain beaver is the only living rodent with this primitive cranial and muscular feature (except perhaps the blesmols, which clearly evolved protrogomorphy from a hystricomorphous ancestor). The mountain beaver was once thought to be related to the earliest protrogomorphous rodents, such as the ischyromyids (Paramys). Both molecular and morphological phylogeneticists have recently suggested a more distant relationship to these animals.
Molecular results have consistently produced a sister relationship between the mountain beaver and the squirrels (family Sciuridae). This clade is referred to as Sciuroidea, Sciuromorpha (not to be confused with the sciuromorphous zygomasseteric system), or Sciurida, depending on the author.
According to the fossil record, the Aplodontioidea split from the squirrels in the Middle or Late Eocene as indicated by the extinct genera Spurimus and Prosciurus. The fossil record for the genus Aplodontia extends only to the Late Pleistocene of North America.
Notes
- Other names include mountain boomer, ground bear, giant mole, gehalis, sewellel, suwellel, showhurll, showtl, and showte, as well as a number of Chinookan and other Native American terms; "mountain boomer" is a misnomer, and the animal does not make the characteristic tail slapping sound of the true beaver species. See Carraway and Verts, 1993.
References
- Fellers, G.M.; Lidicker Jr., W.Z.; Linzey, A.; NatureServe (2016). "Aplodontia rufa (errata version published in 2017)". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T1869A115057269. Retrieved 15 August 2020.
- Helgen, K.M. (2005). "Family Aplodontiidae". In Wilson, D.E.; Reeder, D.M (eds.). Mammal Species of the World: A Taxonomic and Geographic Reference (3rd ed.). Johns Hopkins University Press. p. 753. ISBN 978-0-8018-8221-0. OCLC 62265494.
- "Beavers" in The New Encyclopedia of Mammals. David Macdonald (ed). Oxford university Press, 2001. Pages 590-591.
- "Wood Beaver" in The New Encyclopedia of Mammals. David Macdonald (ed). Oxford university Press, 2001. Pages 596-597.
- Godwin, A. J. 1964. A review of the literature on the mountain beaver. USDI, Fish and Wildlife Serv., Washington, D.C. Spec. Sci. Rep. Wildl. No. 78. 52 pp.
- Leslie N. Carraway; B.J. Verts (23 April 1993). "Aplodontia rufa" (PDF). Mamm Species. The American Society of Mammalogists (432): 1–10. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2015-02-05. Retrieved 2017-09-09.
- Druzinsky, Robert E. "Functional anatomy of incisal biting in Aplodontia rufa and sciuromorph rodents–Part 1: masticatory muscles, skull shape and digging." Cells Tissues Organs 191.6 (2010): 510-522.
- citation needed
- "Mountain Beaver" in The New Encyclopedia of Mammals. David MacDonald (ed). Oxford University Press, 2001. Pages 596–597.
- Mathews, Daniel (1994). Cascade-Olympic Natural History. Portland, Oregon: Audubon Society of Portland/Raven Editions. ISBN 0-9620782-0-4.
- Evans, James (1984). MacDonald, D. (ed.). The Encyclopedia of Mammals. New York: Facts on File. pp. 610–611. ISBN 0-87196-871-1.
- Newell, Toni Lynn (2002). "Aplodontia rufa mountain beaver". Animal Diversity Web. Retrieved 2013-08-11.
- Campbell, Dan L. (2005). "Mountain Beavers and Control of Mountain Beaver Damage". Internet Center for Wildlife Damage Management. Archived from the original on 2018-12-02. Retrieved 2013-08-12.
- "Oregon Dept of Forestry info page". Archived from the original on 2018-12-02. Retrieved 2013-03-30.
- "Living with Wildlife: Mountain Beavers". Washington Department of Fish and Wildlife. Retrieved 2013-06-25.
- Lloyd Ingles. (1960). Tree Climbing by Mountain Beavers. Journal of Mammalogy, vol. 41, no. 1, (Feb., 1960), pages 120–121.
- Adkins, R. M. E. L. Gelke, D. Rowe, and R. L. Honeycutt. 2001. Molecular phylogeny and divergence time estimates for major rodent groups: Evidence from multiple genes. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 18:777–791.
- McKenna, Malcolm C., and Bell, Susan K. 1997. Classification of Mammals Above the Species Level. Columbia University Press, New York, 631 pp. ISBN 0-231-11013-8
- Nowak, R. M. 1999. Walker's Mammals of the World, Vol. 2. Johns Hopkins University Press, London.
- Feldhammer, George A.; Lee Drickamer; Stephen Vessey; Joseph Merritt; Carey Krajewski (2007). Mammalogy: Adaptation, Diversity, Ecology. Johns Hopkins University Press. ISBN 978-0-8018-8695-9.
External links

