American Airlines Flight 191
American Airlines Flight 191 was a regularly scheduled passenger flight operated by American Airlines from O'Hare International Airport in Chicago, Illinois, to Los Angeles International Airport in Los Angeles, California. On May 25, 1979, the McDonnell Douglas DC-10-10 operating this flight was taking off from runway 32R when it crashed into the ground. All 258 passengers and 13 crew on board were killed, along with two people on the ground. With 273 fatalities, it is the deadliest aviation accident to have occurred in the United States.
 Flight 191 just after takeoff and before hitting the ground, with its left engine missing and leaking hydraulic fluid. | |
| Accident | |
|---|---|
| Date | May 25, 1979 |
| Summary | Loss of control caused by engine detachment due to improper maintenance[1] |
| Site | Des Plaines, Illinois, United States (Near O'Hare International Airport) 42°0′35″N 87°55′45″W |
| Total fatalities | 273 |
| Aircraft | |
| Aircraft type | McDonnell Douglas DC-10-10 |
| Operator | American Airlines |
| IATA flight No. | AA191 |
| ICAO flight No. | AAL191 |
| Call sign | AMERICAN 191 |
| Registration | N110AA |
| Flight origin | O'Hare International Airport Chicago, Illinois, U.S. |
| Destination | Los Angeles International Airport Los Angeles, California, U.S. |
| Occupants | 271 |
| Passengers | 258 |
| Crew | 13 |
| Fatalities | 271 |
| Survivors | 0 |
| Ground casualties | |
| Ground fatalities | 2 |
| Ground injuries | 2 |
The National Transportation Safety Board (NTSB) found that as the aircraft was beginning its takeoff rotation, engine number one (the left engine) separated from the left wing, flipping over the top of the wing and landing on the runway. As the engine separated from the aircraft, it severed hydraulic fluid lines that lock the wing's leading-edge slats in place and damaged a 3-foot (1 m) section of the left wing's leading edge. Aerodynamic forces acting on the wing resulted in an uncommanded retraction of the outboard slats. As the aircraft began to climb, the damaged left wing – with no engine – produced far less lift (stalled) than the right wing, with its slats still deployed and its engine providing full takeoff thrust. The disrupted and unbalanced aerodynamics of the aircraft caused it to roll abruptly to the left until it was partially inverted, reaching a bank angle of 112 degrees, before crashing in an open field by a trailer park near the end of the runway. The engine separation was attributed to damage to the pylon structure holding the engine to the wing, caused by improper maintenance procedures used at American Airlines.
Background
Aircraft

The aircraft involved was a McDonnell Douglas DC-10-10 registered N110AA. It had been delivered on February 25, 1972, and at the time of the crash, it had logged just under 20,000 hours of flying time over seven years. The jet was powered by three General Electric CF6-6D engines. A review of the aircraft's flight logs and maintenance records showed that no mechanical discrepancies were noted for May 11, 1979. On the day of the accident, in violation of standard procedure, the records were not removed from the aircraft, and were destroyed in the accident.[1]:76
Flight crew
Captain Walter Lux, 53, had been flying the DC-10 since its introduction eight years earlier. He had logged around 22,000 flying hours, of which about 3,000 were in a DC-10. He was also qualified to pilot 17 other aircraft, including the DC-6, the DC-7, and the Boeing 727.[1]:75 First Officer James Dillard, 49, and Flight Engineer Alfred Udovich, 56, were also highly experienced: 9,275 hours and 15,000 hours, respectively; between them, they had 1,830 hours' flying experience in the DC-10.[2]
Accident

On the accident flight, just as the aircraft reached takeoff speed, the No. 1 engine and its pylon assembly separated from the left wing, ripping away a 3-foot (1 m) section of the leading edge with it. The combined unit flipped over the top of the wing and landed on the runway.[1]:2 Robert Graham, supervisor of maintenance for American Airlines, stated, "As the aircraft got closer, I noticed what appeared to be vapor or smoke of some type coming from the leading edge of the wing and the No. 1 engine pylon. I noticed that the No. 1 engine was bouncing up and down quite a bit and just about the time the aircraft got opposite my position and started rotation, the engine came off, went up over the top of the wing, and rolled back down onto the runway... Before going over the wing, the engine went forward and up just as if it had lift and was actually climbing. It didn't strike the top of the wing on its way, rather it followed the clear path of the airflow of the wing, up and over the top of it, then down below the tail. The aircraft continued a fairly normal climb until it started a turn to the left. And at that point, I thought he was going to come back to the airport."[3]
It is not known what was said in the cockpit in the 50 seconds leading up to the final impact, as the cockpit voice recorder lost power when the engine detached. The only crash-related audio collected by the recorder is a thumping noise (likely the sound of the engine separating), followed by the first officer exclaiming "Damn!", at which point the recording ends. This may also explain why Air Traffic Control was unsuccessful in their attempts to radio the crew and inform them that they had lost an engine. This loss of power did, however, prove useful in the investigation, serving as a marker of exactly what circuit in the DC-10's extensive electrical system had failed.[1]:57
In addition to the engine's failure, several related systems failed. The number one hydraulic system, powered by the number one engine, also failed but continued to operate through motor pumps that mechanically connected it to hydraulic system three. Hydraulic system three was also damaged and began leaking fluid but maintained pressure and operation up until impact. Hydraulic system two was undamaged. The number one electrical bus, whose generator was attached to the number one engine, failed as well, causing several electrical systems to go offline, most notably the captain's instruments, his stick shaker, and the slat disagreement sensors. A switch in the overhead panel would have allowed the captain to restore power to his instruments, but it was not used. It might have been possible for the flight engineer to reach the backup power switch (as part of an abnormal situation checklist—not as part of their take-off emergency procedure) in an effort to restore electrical power to the number one electrical bus. That would have worked only if electrical faults were no longer present in the number one electrical system. In order to reach that backup power switch, the flight engineer would have had to rotate his seat, release his safety belt, and stand up. Since the aircraft did not get any higher than 350 feet (110 m) above the ground and was only in the air for 50 seconds between the time the engine separated and the moment it crashed, there was not sufficient time to perform such an action. In any event, the first officer was flying the airplane and his instruments continued to function normally.[1]:52
The aircraft climbed to about 325 feet (99 m) above ground level while spewing a white mist trail of fuel and hydraulic fluid from the left wing. The first officer had followed the flight director and raised the nose to 14 degrees, which reduced the airspeed from 165 knots (190 mph; 306 km/h) to the takeoff safety airspeed (V2) of 153 knots (176 mph; 283 km/h), the speed at which the aircraft could safely climb after sustaining an engine failure.[1]:53–54
However, the engine separation had severed the hydraulic fluid lines that controlled the leading edge slats on the left wing and locked them in place, causing the outboard slats (immediately left of the No. 1 engine) to retract under air load. The retraction of the slats raised the stall speed of the left wing to approximately 159 knots (183 mph; 294 km/h), 6 knots higher than the prescribed takeoff safety airspeed (V2) of 153 knots. As a result, the left wing entered a full aerodynamic stall.
With the left wing stalled, the aircraft began banking to the left, rolling over onto its side until it was partially inverted at a 112-degree bank angle (as seen in the Laughlin photograph) with its right wing over its left wing. As the cockpit had been equipped with a closed-circuit television camera positioned behind the captain's shoulder and connected to view screens in the passenger cabin, it is possible that the passengers were able to witness these events from the viewpoint of the cockpit as the aircraft dove towards the ground.[4][5] Whether the camera's view was interrupted by the power loss from the number one electrical bus is not known. The aircraft eventually slammed into a field approximately 4,600 feet (1,400 m) from the end of the runway.[1]:2 Large sections of aircraft debris were hurled by the force of the impact into an adjacent trailer park, destroying five trailers and several cars. The DC-10 had also crashed into an old aircraft hangar located at the edge of the airport at the former site of Ravenswood International Airport, which was used for storage. The aircraft was completely destroyed by the impact force and ignition of a nearly full load of 21k gallons of fuel and no sizable components other than the engines and tail section remained.[6]

In addition to the 271 people on board the aircraft, two employees at a nearby repair garage were killed and two more were severely burned. The crash site is a field located northwest of the intersection of Touhy Avenue (Illinois Route 72) and Mount Prospect Road on the border of the suburbs of Des Plaines and Mount Prospect, Illinois.[1]:2
Investigation
The disaster and investigation received widespread media coverage. The impact on the public was increased by the dramatic effect of an amateur photo taken of the aircraft rolling that was published on the front page of the Chicago Tribune on the Sunday two days after the crash.[7] There were some early reports that a collision with a small aircraft had been the cause of the crash. This apparently was the result of the discovery of small-aircraft parts among the wreckage at the crash site. National Transportation Safety Board vice-chairman Elwood T. Driver, in a press briefing, was photographed holding a broken bolt and nut,[8] implying that these parts were a cause of the accident. The small-plane parts were subsequently determined to have been on the ground at the time of the crash, at the former general aviation Ravenswood Airport, a facility that had been out of service for a few years. An owner there had been selling used aircraft parts from a remaining hangar building.[9]
Engine separation
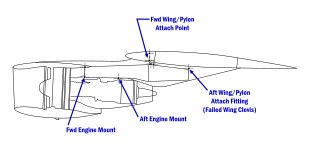
Witnesses to the crash were in universal agreement that the aircraft had not struck any foreign objects on the runway. Also, no pieces of the wing or other aircraft components were found along with the separated engine, other than its supporting pylon, leading investigators to conclude that nothing else had broken free from the airframe and struck the engine. Hence, the engine/pylon assembly separation could only have resulted from a structural failure. The cockpit instrument panels were too badly damaged to provide any useful information.[3]
During the investigation, an examination on the pylon attachment points revealed some damage done to the wing's pylon mounting bracket that matched the shape of the pylon's rear attachment fitting. This meant that the pylon attachment fitting had struck the mounting bracket at some point. This was important evidence, as the only way the pylon fitting could strike the wing's mounting bracket in the observed manner was if the bolts that held the pylon to the wing had been removed and the engine/pylon assembly was being supported by something other than the aircraft itself. Therefore, investigators now could conclude that the observed damage to the rear pylon mount had been present before the crash actually occurred, rather than being caused by it.[1]:18
The NTSB determined that the damage to the left wing engine pylon had occurred during an earlier engine change at the American Airlines aircraft maintenance facility in Tulsa, Oklahoma, between March 29 and 30, 1979.[1]:68 On those dates, the aircraft had undergone routine service, during which the engine and pylon had been removed from the wing for inspection and maintenance. The removal procedure recommended by McDonnell-Douglas called for the engine to be detached from the pylon before detaching the pylon itself from the wing. However, American Airlines, as well as Continental Airlines and United Airlines, had developed a different procedure that saved approximately 200-man-hours per aircraft and "more importantly from a safety standpoint, it would reduce the number of disconnects (of systems such as hydraulic and fuel lines, electrical cables, and wiring) from 79 to 27."[1]:26 This new procedure involved the removal of the engine and pylon assembly as a single unit, rather than as individual components. United Airlines' implementation involved the use of an overhead crane to support the engine/pylon assembly during removal and installation. The method chosen by American and Continental relied on supporting the engine/pylon assembly with a large forklift.
It was learned that if the forklift was incorrectly positioned, the engine/pylon assembly would not be stable as it was being handled, causing it to rock like a see-saw and jam the pylon against the wing's attachment points. Forklift operators were guided only by hand and voice signals as they could not directly see the juncture between pylon and wing. Positioning had to be extremely accurate or structural damage could result. Compounding the problem, maintenance work on N110AA did not go smoothly. The mechanics started to disconnect the engine and pylon as a single unit, but there was a shift change halfway through the job. During this interval, although the forklift remained stationary, the forks supporting the entire weight of the engine and pylon moved downward slightly due to a normal loss of hydraulic pressure associated with its engine being turned off; this caused a misalignment between the engine/pylon and wing. When work was resumed, the pylon was jammed on the wing and the forklift had to be re-positioned. It is unclear whether damage to the mount was caused by the initial downward movement of the engine/pylon structure or by the realignment attempt.[1]:29–30 Regardless of how it happened, the resulting damage, although insufficient to cause an immediate failure, eventually developed into fatigue cracking, worsening with each takeoff and landing cycle during the eight weeks that followed. When the attachment finally failed, the engine and its pylon broke away from the wing. The structure surrounding the forward pylon mount also failed from the resulting stresses.[1]:12
Inspection of the DC-10 fleets of the three airlines revealed that while United Airlines' hoist approach seemed to be harmless, there were several DC-10s at both American and Continental that already had fatigue cracking damage to their pylon mounts caused by similar maintenance procedures.[1]:18 The field service representative from McDonnell-Douglas stated the company would "not encourage this procedure due to the element of risk" and had so advised American Airlines. McDonnell-Douglas, however, "does not have the authority to either approve or disapprove the maintenance procedures of its customers."[1]:26
Inadequate speed
The NTSB determined that the loss of one engine and the asymmetrical drag caused by damage to the wing's leading edge should not have been enough to cause the pilots to lose control of their aircraft; the aircraft should have been capable of returning to the airport using its remaining two engines.[10][1]:54 The NTSB thus examined the effects that the engine's separation would have on the aircraft's flight control, hydraulic, electrical, and instrumentation systems. Unlike other aircraft designs, the DC-10 did not include a separate mechanism to lock the extended leading-edge slats in place, relying instead solely on the hydraulic pressure within the system.[1]:53,57 The NTSB determined that the engine tore through hydraulic lines as it separated from the DC-10's wing, causing a loss of hydraulic pressure; airflow over the wings forced the left wing slats to retract, which caused a stall over the left wing.[1]:53 In response to the accident, slat relief valves were mandated to prevent slat retraction in case of hydraulic line damage.[11]
The wreckage was too severely fragmented to determine the exact position of the rudders, elevators, flaps, and slats before impact and examination of eyewitness photographs showed only that the right wing slats were fully extended as the crew tried unsuccessfully to correct the steep roll they were in. The left wing slats could not be determined from the blurry color photographs, so they were sent to a laboratory in Palo Alto, California, for digital analysis, a process that was pushing the limits of 1970s technology and necessitated large, complicated, and expensive equipment. The photographs were reduced to black-and-white, which made it possible to distinguish the slats from the wing itself and thus proved that they were retracted. In addition, it was also verified that the tail section of the aircraft was undamaged and the landing gear was down.[3]:20–21
Wind tunnel and flight simulator tests were conducted to help to understand the trajectory of the aircraft after the engine detached and the left wing slats retracted. Those tests established that the damage to the wing's leading edge and retraction of the slats increased the stall speed of the left wing from 124 knots (143 mph; 230 km/h) to 159 knots (183 mph; 294 km/h).[1]:23 The DC-10 incorporates two warning devices that might have alerted the pilots to the impending stall: the slat disagreement warning light, which should have illuminated after the uncommanded retraction of the slats, and the stick shaker on the captain's control column, which activates close to the stall speed. Both of these warning devices were powered by an electric generator driven by the number one engine. Both systems became inoperative after the loss of that engine.[1]:54,55,67 The first officer's control column was not equipped with a stick shaker; the device was offered by McDonnell Douglas as an option for the first officer, but American Airlines chose not to have it installed on its DC-10 fleet. Stick shakers for both pilots became mandatory in response to this accident.[12]
As the aircraft had reached V1, the crew were committed to takeoff and thus followed standard procedures for an engine out situation. This procedure is to climb at the takeoff safety airspeed (V2) and attitude (angle), as directed by the flight director. The partial electrical power failure (produced by the separation of the left No. 1 engine) meant that neither the stall warning nor the slat retraction indicator was operative. The crew, therefore, did not know that the slats on the left wing were retracting. This retraction significantly raised the stall speed of the left wing. Thus flying at the takeoff safety airspeed caused the left wing to stall while the right wing was still producing lift, so the aircraft banked sharply and uncontrollably to the left. In simulator recreations held after the accident it was determined that "had the pilot maintained excess airspeed the accident may not have occurred." Of a dozen pilots who attempted simulator recreations of AA 191 with the same information that was available to the crew, none of them managed to prevent a crash. The crew could not see the wings from the cockpit and probably did not know that the #1 engine had fallen off, only that they had an engine out. Aborting takeoff would have likely resulted in a runway overrun and crash. Furthermore, even if they increased engine speed enough to get airborne, the damage to the left wing, which included leaking fuel and broken electrical wires, would have created an extremely dangerous situation, possibly an explosion and fire similar to what happened to Air Canada Flight 621 nine years earlier, and quite probably there was nothing that could have been done to save AA 191 from the moment the #1 engine separated.[1]:54
Probable cause
The findings of the investigation by the National Transportation Safety Board were released on December 21, 1979:
The National Transportation Safety Board determines that the probable cause of this accident was the asymmetrical stall and the ensuing roll of the aircraft because of the uncommanded retraction of the left wing outboard leading edge slats and the loss of stall warning and slat disagreement indication systems resulting from maintenance-induced damage leading to the separation of the No. 1 engine and pylon assembly at a critical point during takeoff. The separation resulted from damage by improper maintenance procedures which led to failure of the pylon structure. Contributing to the cause of the accident were the vulnerability of the design of the pylon attach points to maintenance damage; the vulnerability of the design of the leading edge slat system to the damage which produced asymmetry; deficiencies in Federal Aviation Administration surveillance and reporting systems which failed to detect and prevent the use of improper maintenance procedures; deficiencies in the practices and communications among the operators, the manufacturer, and the FAA which failed to determine and disseminate the particulars regarding previous maintenance damage incidents; and the intolerance of prescribed operational procedures to this unique emergency. Unlike the rival Boeing 747 and Lockheed L-1011, the DC-10 also lacked hydraulic cutoff valves in the event of a system rupture, therefore an accident such as occurred on AA 191 may have been recoverable on those aircraft.[10][1]:69
Legacy of the DC-10
The crash of Flight 191 brought strong criticism from the media regarding the DC-10's safety and design.[13] The DC-10 had been involved in two accidents related to the design of its cargo doors, American Airlines Flight 96 (1972) and Turkish Airlines Flight 981 (1974). The separation of engine one from its mount, the widespread publication of the dramatic images of the airplane missing its engine seconds before the crash, and a second photo of the fireball resulting from the impact, raised widespread concerns about the safety of the DC-10.[13] The final blow to the airplane's reputation was dealt two weeks after the crash, when the aircraft was grounded by the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA). Although the aircraft itself was later exonerated, the damage in the public's eye was already done.[14]
The investigation also revealed other DC-10s with damage caused by the same faulty maintenance procedure. The faulty procedure was banned, and the aircraft type went on to have a long career as a passenger and cargo aircraft. In response to this accident, American Airlines was fined $500,000 by the U.S. government for improper maintenance procedures.[10] One of the American Airlines mechanics who had last performed this maintenance procedure on the aircraft subsequently committed suicide.[15]
On June 6, 1979, two weeks after the crash, the FAA suspended the type certificate for the DC-10, thereby grounding all DC-10s under its jurisdiction.[16] It also enacted a special air regulation banning the DC-10 from U.S. airspace, which prevented foreign DC-10s not under the jurisdiction of the FAA from flying within the country.[1]:47 This was done while the FAA investigated whether the airplane's engine mounting and pylon design met relevant requirements. Once the FAA was satisfied that maintenance issues were primarily at fault and not the actual design of the aircraft, the type certificate was restored on July 13 and the special air regulation repealed.[16][17] However, the type certificate was amended, stating that "...removal of the engine and pylon as a unit will immediately render the aircraft un-airworthy."
Another DC-10, performing Western Airlines Flight 2605, crashed in Mexico City after a red-eye flight from Los Angeles barely 5 months after the crash of American Airlines Flight 191. The Western Airlines DC-10's crash, however, was due to low visibility and an attempt to land on a closed runway[18] through, reportedly, confusion of its crew.[19]
The crash of yet another DC-10 at the end of November, Air New Zealand Flight 901, exactly six months after Flight 191, added to the DC-10's negative reputation.[13] The crash of Flight 901, an Antarctic sightseeing flight which hit a mountain, was caused by several human and environmental factors not related to the airworthiness of the DC-10, and the aircraft was later completely exonerated.[20]

Ironically, the crash of yet another DC-10, United Airlines Flight 232, ten years later, restored some of the aircraft's reputation. Despite losing an engine, all flight controls, crash-landing in a huge fireball (which was caught on video by a local news crew), and killing 112 people, 184 people survived the accident. Experts praised the DC-10's sturdy construction as partly responsible for the high number of survivors.[14]
Orders for DC-10s dropped off sharply after the events of 1979 (the US economic recession of 1979-82 was also a contributing factor in reduced demand for airliners) and from there until the end of production ten years later, the two largest DC-10 customers were FedEx and the US Air Force. Despite initial safety concerns, DC-10 aircraft continued to serve with passenger airlines for over 30 years after the crash of Flight 191.[21] DC-10 production ended in 1988.[14] Many retired passenger DC-10s have since been converted to all-cargo use. DC-10 freighters, along with its derivative, the MD-11, constitute part of the FedEx Express fleet.[22] The DC-10s have been upgraded with the glass cockpit from the MD-11, thereby turning them into MD-10s.[23] American Airlines retired its last DC-10s in 2000 after 29 years of service. In February 2014, Biman Bangladesh Airlines operated the final DC-10 passenger flights. DC-10s continue to be used extensively in air freight operations, and military variants also remain in service.
Victims
Nationalities of the victims
| Nationality | Passengers | Crew | Ground | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| United States | 247 | 13 | 2 | 262 |
| Saudi Arabia | 4 | - | - | 4 |
| South Korea | 1 | - | - | 1 |
| Austria | 1 | - | - | 1 |
| Belgium | 1 | - | - | 1 |
| Netherlands | 4 | - | - | 4 |
| Total | 258 | 13 | 2 | 273[24] |
Passengers
Some of the victims in the crash of Flight 191 were:
- Itzhak Bentov, a Czechoslovakia-born Israeli–American biomedical inventor (the cardiac catheter) and New Age author (Stalking the Wild Pendulum and A Cosmic Book).
- Leonard Stogel, music business manager/promoter/producer/executive for California Jam, California Jam II, Sweathog, The Cowsills, Sam the Sham, Tommy James and the Shondells, Redbone, Gentle Giant, and other musical groups. Coincidentally, Stogel's parents had earlier perished on American Airlines Flight 1.[25][26]
Memorial
For 32 years there was no permanent memorial to the victims. Funding was obtained for a memorial in 2009, through a two-year effort by the sixth-grade class of Decatur Classical School in Chicago.[27] The memorial, a 2-foot-high (0.6 m) concave wall with interlocking bricks displaying the names of the crash victims, was formally dedicated in a ceremony on October 15, 2011.[28] The memorial is located at Lake Park at the northwest corner of Lee and Touhy Avenues,[29] two miles east of the crash site. A remembrance ceremony was held at the memorial on May 25, 2019, the 40th anniversary of the accident.[30]
Depictions in media
The cable/satellite National Geographic channel produced a documentary on the crash,[31] and an episode from Seconds From Disaster titled "Chicago Plane Crash"[32] detailed the crash and included film of the investigation press conferences. The Canadian television series Mayday profiled the crash in the episode "Catastrophe at O'Hare", which has subsequently aired in the U.S. on the Smithsonian Channel's television series Air Disasters.[33]
The flight was also featured on an episode of Why Planes Crash, which is featured on the Weather Channel.
Chicago folk singer Steve Goodman wrote the song "Ballad of Flight 191 (They Know Everything About It)" in response to the crash and the subsequent investigation as the inaugural song for a series of topical songs which aired on National Public Radio in 1979.[34]
A character in the Michael Crichton novel Airframe describes the incident by mentioning how a "good airplane (DC-10)" could be "destroyed by bad press".[35][36]
See also
- List of disasters in the United States by death toll
- List of aircraft accidents and incidents by number of ground fatalities
- Aviation accidents and incidents
- Aviation safety
- Lion Air Flight 610 and Ethiopian Airlines Flight 302 – other fatal crashes that contributed to the respective type grounding
- Similar accidents caused by engine separation
References
- Aircraft Accident Report: American Airlines, Inc. DC-10-10, N110AA, Chicago O'Hare International Airport, Chicago, Illinois, May 25, 1979 (PDF) (Report). National Transportation Safety Board. December 21, 1979. NTSB-AAR-79-17. Archived (PDF) from the original on April 22, 2019. Retrieved September 6, 2016.
- "Investigation: American Airlines 191". AirDisaster.com. Archived from the original on August 13, 2006. Retrieved July 26, 2006.
- Vatz, Mara E. (2004). Knowing When to Stop: The Investigation of Flight 191 (Masters thesis). Cambridge, MA: Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Dept. of Humanities, Program in Writing and Humanistic Studies. p. 9. hdl:1721.1/39430. OCLC 59008054.
- Special to the New York Times (May 27, 1979). "Dive May Have Been Televised". The New York Times. 128 (44230). NYTimes Co. Associated Press. Archived from the original on September 9, 2017. Retrieved March 21, 2018.
- Young, David (June 3, 1979). "...191, do you want to come back?". Chicago Tribune (Issue: 132nd Year, No. 154). p. 16, Section 1. Archived from the original on September 9, 2017. Retrieved May 27, 2017.
- Macarthur, Job (1996). Air Disaster (2 ed.). Shrewsbury: Airlife. p. 49. ISBN 9781875671199. OCLC 464170955.
- "Accident Photo: American 191". AirDisaster.Com. Archived from the original on June 7, 2011. Retrieved April 16, 2011.
- "Tuskegee Airman Heads Chicago Air Crash Probe". JET. 56 (13): 5. June 14, 1979. Retrieved April 16, 2011.
- "Abandoned & Little-Known Airfields: Illinois, Northern Chicago area". Abandoned & Little-Known Airfields. Archived from the original on May 24, 2011. Retrieved April 15, 2011.
- "Chicago DC‐10 Accident Findings". Aircraft Engineering and Aerospace Technology. 52 (3): 19–20. March 1, 1980. doi:10.1108/eb035612. ISSN 0002-2667.
- FAA Airworthiness Directive 80-03-03 Archived December 4, 2016, at the Wayback Machine
- FAA Airworthiness Directive 80-03-10 Archived December 4, 2016, at the Wayback Machine
- Barnett, Arnold; Lofaso, Anthony J. (November 1, 1983). "After the Crash: The Passenger Response to the DC-10 Disaster". Management Science. 29 (11): 1225–1236. doi:10.1287/mnsc.29.11.1225. ISSN 0025-1909.
- Thornton, Paul (January 7, 2007). "A final flight into the history books". LA Times. Archived from the original on November 6, 2012. Retrieved April 15, 2011.
- Campbell, Ballard C. (2008). Disasters, Accidents, and Crises in American History: A Reference Guide to the Nation's Most Catastrophic Events. Infobase Publishing. ISBN 978-1-4381-3012-5.
- Mankiewicz, R.H (1981). "Statut et interprétation des dispositions de la Convention de Chicago en droit américain dans l'affaire des DC 10" [Status and Interpretation of the Chicago Convention Provisions in US Law in the DC 10 Case]. Annuaire Français de Droit International (in French). 27 (1): 499–504. doi:10.3406/afdi.1981.2458.

- Ranter, Harro (May 11, 2007). "ASN Aircraft accident McDonnell Douglas DC-10-10 N110AA". aviation-safety.net. Aviation Safety Network. Archived from the original on January 10, 2011. Retrieved July 27, 2009.
- Ranter, Harro. "ASN Aircraft accident McDonnell Douglas DC-10-10 N903WA Mexico City-Juarez International Airport (MEX)". Archived from the original on June 2, 2013. Retrieved February 6, 2017.
- "Runway Confusion Tied to Jet Crash". The Pittsburgh Press. UPI. November 1, 1979. Archived from the original on January 15, 2020. Retrieved March 12, 2019.
- "Aircraft Accident: DC. 10 ZK-NZP Flight 901". New Zealand Disasters. Christchurch City Libraries. Archived from the original on July 8, 2011. Retrieved July 13, 2011.
- "McDonnell Douglas' DC-10 makes its last passenger flight today". The Verge. Archived from the original on December 7, 2013. Retrieved December 6, 2013.
- "Federal Express Fleet". Airfleets.net. Archived from the original on April 17, 2011. Retrieved April 16, 2011.
- "MD-10 Program". Boeing. Archived from the original on May 10, 2011. Retrieved April 16, 2011.
- Special to the New York Times (May 27, 1979). "American Airlines' List of Passengers Killed in Jet Crash at Chicago". The New York Times. NYTimes Co. p. 20. ISSN 0362-4331. Archived from the original on September 9, 2017.
- "Family's air tragedy repeats itself". The Milwaukee Sentinel. The Associated Press. May 29, 1979. Archived from the original on December 8, 2015. Retrieved January 16, 2016.
- Berlin, Kori Rumore, Jonathon. "Faces of the victims of Flight 191". chicagotribune.com. Archived from the original on November 26, 2019. Retrieved January 4, 2020.
- "Finally, a memorial for American Flight 191 that we've missed out for the last 3 decades. victims". Daily Herald. Archived from the original on August 10, 2011. Retrieved August 6, 2011.
- Delgado, Jennifer. "Memorial to victims of 1979 plane crash unveiled". Chicago Tribune. Archived from the original on October 15, 2011. Retrieved October 15, 2011.
- "Flight 191 Memorial – Des Plaines Park District". dpparks.org. Archived from the original on June 14, 2017. Retrieved April 1, 2018.
- McCoppin, Robert (May 25, 2019). "Hundreds gather at memorial service to honor the 273 people killed 40 years ago when Flight 191 crashed at O'Hare". Chicago Tribune. Archived from the original on May 26, 2019. Retrieved May 25, 2019.
- The Crash of Flight 191 (DVD). The History Channel. Archived from the original on October 31, 2007.
- "Chicago Plane Crash / Flight Engine Down". Seconds From Disaster. National Geographic Channel.
- "Air Disasters". Smithsonian Channel. Archived from the original on March 5, 2016. Retrieved January 16, 2016.
- Eals, Clay (2007). Steve Goodman: Facing the Music. Toronto: ECW. pp. 558–9. ISBN 978-1-55022-732-1.
- Lehmann-Haupt, Christopher (December 5, 1996). "A Thriller Not to Carry On Your Next Plane Trip". The New York Times. Archived from the original on June 27, 2019. Retrieved June 27, 2019.
- Crichton, Michael (2011). Airframe. p. 181. ISBN 9780345526779. OCLC 708331481.
Further reading
- McCoppin, Robert (May 25, 2019). "Hundreds gather at memorial service to honor the 273 people killed 40 years ago when Flight 191 crashed at O'Hare". Chicago Tribune. Retrieved May 25, 2019.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to American Airlines Flight 191. |
- NTSB Accident Report
- "Public Lessons Learned from Accidents – American Airlines Flight 191" (Archive)
- PlaneCrashInfo.Com – American Airlines Flight 191
- Flight 191 Remembered (Fox Chicago website) (Archive)
- Pre-crash pictures from Airliners.net
- NTSB Probable Cause Report (Alternate, Archive)
- News reports at The Museum of Classic Chicago Television
- ATC recording on YouTube