Agrale Marruá
The Marruá ("Wild Bull") is a family of four-by-four wheeled transport and utility vehicles, built by Agrale in Caxias do Sul, Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil. Developed in the early 2000s to serve as a replacement for ageing jeeps and other vehicles in Brazilian service (Bandeirante and JPX), it has also been adopted by several other Latin American armies, and is used on peacekeeping missions with the United Nations in Haiti.
| Agrale Marruá | |
|---|---|
.jpg) A Marruá in a parade in Brazil in 2013. | |
| Type | Light Utility Vehicle |
| Place of origin | Brazil |
| Service history | |
| In service | 2005 – present |
| Production history | |
| Designer | Agrale |
| Manufacturer | Agrale |
| Produced | 2004 – present |
| Specifications | |
| Mass | 2,460 kilograms (5,420 lb) |
| Length | 3.8 metres (12 ft) |
| Width | 1.92 metres (6.3 ft) |
| Height | 1.95 metres (6.4 ft) |
| Crew | 4-6 |
Main armament | see text |
| Engine | MWM turbocharged four-cylinder diesel[1] 132 horsepower (98 kW) |
| Suspension | Independent 4x4 |
Operational range | 1,000 kilometres (620 mi) |
| Maximum speed | 128 kilometres per hour (80 mph) |
Design
Following the bankruptcy of Engesa (Specialized Engineers SA) in early 1990, former employees of the company acquired the rights to the Engesa EE-4/EE-12 utility vehicle, and, working with the Agrale company, developed an improved version of the vehicle between 2003 and 2005 to meet a specification for a 1/2 ton, 4x4 Viatura de Transporte Não Especializada (Non-Specialised Transport, VTNE) for the Armed Forces of Brazil, to replace the Jeeps previously in service.[1] Three prototypes were constructed for testing by the Brazilian Army, with Agrale investing $11 million into the project, and the Marruá was accepted for Brazilian service on 27 July 2005.[2]
Designed to be versatile, robust, and easy to maintain,[1] the Marruá underwent over 60,000 miles (97,000 km) of testing during its development, and is capable of carrying four fully equipped soldiers, anti-tank missile launchers, recoilless rifles, machine guns, or communications equipment.[3]
Models
Current models of the Marruá are:[4]
Military versions
Military 4x4's featuring MWM motors meeting Euro III standards.[5]
- Agrale Marruá AM2 VTNE ½ Ton (base four person two door Jeep-like vehicle with removable roof)
- AM2 MB-NET is a specialised version for the Brazilian Marine Corps, with rust-resistant paint, high-flotation tires, and seating for six.[1]
- Agrale Marruá AM11/AM11 REC/VTNE/VTL REC (five person four door Jeep-like vehicle with removable roof)
- Agrale Marruá AM20-VDC, a command and control vehicle.[6]
- Agrale Marruá AM20 and AM21 - Amb (ambulance for transporting wounded and may be single or removal of ICU equipment)
- Agrale Marruá AM20 and AM21 - VCC (Special Car for command and control operations)
- Agrale Marruá AM21 - VTNE ¾ Ton (pickup truck for personal transport or load 750 kg load with removable hood, metallic body with vinyl roof)
- Agrale Marruá AM23 - VTNE ¾ Ton
- Agrale Marruá AM23 CC/CDCC - VTNE ¾ Ton
- Agrale Marruá AM31 - VTNE 1½ Ton (pickup truck)
- Agrale Marruá AM41 - VTNE 2½ Ton (cabover tactical truck)
- Agrale Marruá AM2 VTNE ½ Ton (base four person two door Jeep-like vehicle with removable roof)
.jpg) AM2 MB-NET is a specialised version for the Brazilian Marine Corps, with rust-resistant paint, high-flotation tires, and seating for six.
AM2 MB-NET is a specialised version for the Brazilian Marine Corps, with rust-resistant paint, high-flotation tires, and seating for six.- Agrale Marruá VTNE 3/4 ton in Porto Alegre.
.jpg) Agrale Marruá AM21 - VTNE ¾ Ton.
Agrale Marruá AM21 - VTNE ¾ Ton.
Civil versions
- Civil 4x4's feature Cummins ISF 2.8 turbodiesels [7] meeting Euro V standards with enclosed cabs
- Agrale Marruá AM200 G2 CD (Cabine Dupla) - Double Cab Pickup
- Agrale Marruá AM200 G2 CS (Cabine Simples) - Single Cab Pickup
- Agrale Marruá AM300 G2 CC (Chassi-Cabine)- Chassis cab
 Municipal Guard AM 100CD
Municipal Guard AM 100CD- Agrale Marruá AM200 G2 CD fire vehicle
Former Versions
- Agrale Marruá AM50 Trabalhando - civil version of the VTNE
- Agrale Marruá AM100 Trabalhando - first pickup version based on VTNE platform
- Agrale Marruá AM150 - Agrale Marruá AM11/AM11 REC/VTNE/VTL REC based Double Cab Pickup/Chassis cab
Operational history
The Marruá has entered service with both the Brazilian Army and the Brazilian Marine Corps,[1] in addition to being acquired by the armies of Ecuador[8] and Argentina, the latter using eighteen vehicles as part of the United Nations Peacekeeping Mission in Haiti starting in 2009.[9]
Operators
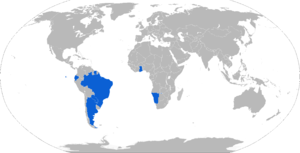


- Argentine Army
Argentine Air Force
Argentine Marines [10]
Argentine National Gendarmerie 
- Brazilian Army
Brazilian Navy
Brazilian Air Force
Brazilian Marine Corps
Military Police 
- Ecuadorian Army[8]

- Ghana Armed Forces[11]

- Namibia Defence Force[12]

- Paraguayan Army

- Peruvian Army

- Army of Suriname[13]

- Army of Uganda
Specifications
from [14]
Dimensions
- Length: 3.8 metres (12 ft)
- Overall Height: 1.95 metres (6.4 ft)
- Height with windshield folded: 1.40 metres (4.6 ft)
- Width: 1.92 metres (6.3 ft)
- Capacity: 4-6 soldiers
Weights
- Weight in running order: 1,960 kilograms (4,320 lb)
- Gross weight: 2,460 kilograms (5,420 lb)
Performance
- Maximum speed: 128 kilometres per hour (80 mph)
- Minimum sustainable speed: 4 kilometres per hour (2.5 mph)
- Maximum incline: 60%
- Maximum lateral incline: 30%
- Ford depth without snorkel: 0.60 metres (24 in)
- Ground clearance: 0.26 metres (10 in)
- Approach angle: 64°
- Departure angle: 52°
- Maximum payload: 500 kilograms (1,100 lb) + 500 kilograms (1,100 lb) trailer
- Fuel capacity: 100 litres (22 imp gal; 26 US gal)
- Range: 1,000 kilometres (620 mi) (on road)
Transmission
- Model: Eaton FS 2305, mechanical
- Gears: 5 forward gears and 1 reverse
Engine
- Brand / Model: MWM 4.07TCA SPRINT-EII turbodiesel, 2.8-liter four-cylinder inline, water cooled
- Power: 132 horsepower (98 kW) at 3,600 rpm
- Torque: 340 Nm at 1,800 rpm
References
- Marinha do Brasil recebe viaturas militares Agrale Marruá Archived July 6, 2009, at the Wayback Machine. Secco Consultoria. (in Portuguese) Accessed 2010-05-26.
- Bastos, Expedito Carlos Stephani. Agrale Marruá - Um legítimo 4x4 militar Made in Brazil Archived 2011-07-06 at the Wayback Machine (in Portuguese). Accessed 2009-09-23.
- AGRALE Marruá Archived June 11, 2010, at the Wayback Machine. WarWheels.net. Accessed 2010-05-26.
- "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2012-09-05. Retrieved 2012-08-22.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2012-09-04. Retrieved 2012-08-22.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- Agrale Marrusa family of vehicles Archived July 6, 2011, at the Wayback Machine. Company website. (in Portuguese) Accessed 2010-05-26.
- http://www.agrale.com.br/pt/pdf/gerar/185/utilitarios-civil-utilitarioagrale-marruaam200-g2-cabine-dupla-1
- Exército do Equador Adquire Segundo Lote de Utilitários Agrale Marruá Archived September 4, 2009, at the Wayback Machine. Política Externa Brasileira. (in Portuguese) Accessed 2010-05-26.
- Veículos Agrale Marruá serão utilizados pela ONU no Haiti Archived July 6, 2009, at the Wayback Machine. Secco Consultoria . (in Portuguese) Accessed 2010-05-26.
- http://robertopcosta.blogspot.com.br/2015/04/agrale-expoe-na-laad-2015-sua-familia.html/%5B%5D%5B%5D
- https://www.defenceweb.co.za/land/land-land/namibia-defence-force-orders-marrua-vehicles/
- "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2014-08-10. Retrieved 2014-08-09.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- Agrale S.A.. Especificações do Agrale Marruá. (in Portuguese) Accessed 2009-12-14.