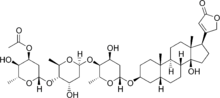
Acetyldigitoxin
Acetyldigitoxin is a cardiac glycoside. It is an acetyl derivative of digitoxin, found in the leaves of Digitalis species.[1] It is used to treat cardiac failure, particularly that associated with tachycardia.[2]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.042.660 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C43H66O14 |
| Molar mass | 806.987 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
References
- Kemertelidze ÉP, Gvazava LN (1979-11-01). "Odorobioside G from the leaves ofDigitalis ciliata". Chemistry of Natural Compounds. 15 (6): 779. doi:10.1007/BF00565608.
- Loffler W, Essellier AF, Forster G (June 1954). "Acetyl-digitoxin; clinical observations on the treatment of patients with advanced congestive heart failure". American Heart Journal. 47 (5): 898–911. doi:10.1016/0002-8703(54)90160-X. PMID 13158272.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.