Acetylacetone
Acetylacetone is an organic compound with the formula CH3COCH2COCH3. It is a colorless liquid, classified as a 1,3-diketone. It exists in equilibrium with a tautomer CH3C(O)CH=C(OH)CH3. These tautomers interconvert so rapidly under most conditions that they are treated as a single compound in most applications.[2] It is a colorless liquid that is a precursor to acetylacetonate anion (commonly abbreviated acac−), a bidentate ligand. It is also a building block for the synthesis of heterocyclic compounds.
 | |||
| |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Pentane-2,4-dione | |||
Other names
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol) |
|||
| 741937 | |||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.004.214 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
| 2537 | |||
| KEGG | |||
PubChem CID |
|||
| RTECS number |
| ||
| UNII | |||
| UN number | 2310 | ||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C5H8O2 | |||
| Molar mass | 100.117 g·mol−1 | ||
| Density | 0.975 g/mL[1] | ||
| Melting point | −23 °C (−9 °F; 250 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 140 °C (284 °F; 413 K) | ||
| 16 g/100 mL | |||
| -54.88·10−6 cm3/mol | |||
| Hazards | |||
| GHS pictograms |     | ||
| GHS Signal word | Danger | ||
GHS hazard statements |
H226, H302, H311, H320, H331, H335, H341, H370, H402, H412 | ||
| P201, P202, P210, P233, P240, P241, P242, P243, P260, P261, P264, P270, P271, P273, P280, P281, P301+312, P302+352, P303+361+353, P304+340, P305+351+338, P307+311, P308+313, P311, P312 | |||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |||
| Flash point | 34 °C (93 °F; 307 K) | ||
| 340 °C (644 °F; 613 K) | |||
| Explosive limits | 2.4–11.6% | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
Properties
Tautomerism
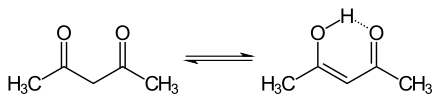
The keto and enol tautomers of acetylacetone coexist in solution. The enol form has C2v symmetry, meaning the hydrogen atom is shared equally between the two oxygen atoms.[3] In the gas phase, the equilibrium constant, Kketo→enol, is 11.7, favoring the enol form. The two tautomeric forms can be distinguished by NMR spectroscopy, IR spectroscopy and other methods.[4][5]
| Solvent | Kketo→enol |
|---|---|
| Gas phase | 11.7 |
| Cyclohexane | 42 |
| Toluene | 10 |
| THF | 7.2 |
| DMSO | 2 |
| Water | 0.23 |
The equilibrium constant tends to be high in nonpolar solvents; the keto form becomes more favorable in polar, hydrogen-bonding solvents, such as water.[6] The enol form is a vinylogous analogue of a carboxylic acid.
Acid–base properties
| solvent | T/°C | pKa[7] |
|---|---|---|
| 40% ethanol/water | 30 | 9.8 |
| 70% dioxane/water | 28 | 12.5 |
| 80% DMSO/water | 25 | 10.16 |
| DMSO | 25 | 13.41 |
Acetylacetone is a weak acid:
- C5H8O2 ⇌ C
5H
7O−
2 + H+
IUPAC recommended pKa values for this equilibrium in aqueous solution at 25 °C are 8.99 ± 0.04 (I = 0), 8.83 ± 0.02 (I = 0.1 M NaClO4) and 9.00 ± 0.03 (I = 1.0 M NaClO4; I = Ionic strength).[8] Values for mixed solvents are available. Very strong bases, such as organolithium compounds, will deprotonate acetylacetone twice. The resulting dilithio species can then be alkylated at C-1.
Preparation
Acetylacetone is prepared industrially by the thermal rearrangement of isopropenyl acetate.[9]
- CH2(CH3)COC(O)Me → MeC(O)CH2C(O)Me
Laboratory routes to acetylacetone begin also with acetone. Acetone and acetic anhydride upon the addition of boron trifluoride (BF3) catalyst:[10]
- (CH3CO)2O + CH3C(O)CH3 → CH3C(O)CH2C(O)CH3
A second synthesis involves the base-catalyzed condensation of acetone and ethyl acetate, followed by acidification:[10]
- NaOEt + EtO2CCH3 + CH3C(O)CH3 → NaCH3C(O)CHC(O)CH3 + 2 EtOH
- NaCH3C(O)CHC(O)CH3 + HCl → CH3C(O)CH2C(O)CH3 + NaCl
Because of the ease of these syntheses, many analogues of acetylacetonates are known. Some examples include C6H5C(O)CH2C(O)C6H5 (dbaH) and (CH3)3CC(O)CH2C(O)CC(CH3)3. Hexafluoroacetylacetonate is also widely used to generate volatile metal complexes.
Reactions
Condensations
Acetylacetone is a versatile bifunctional precursor to heterocycles because both keto groups undergo condensation. Hydrazine reacts to produce pyrazoles. Urea gives pyrimidines. Condensation with two aryl- and alkylamines to gives NacNacs, wherein the oxygen atoms in acetylacetone are replaced by NR (R = aryl, alkyl).
Coordination chemistry
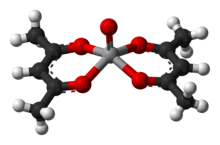
The acetylacetonate anion, acac−, forms complexes with many transition metal ions. A general method of synthesis is to treat a metal salt with acetylacetone in the presence of a base:[11]
- MBz + z Hacac ⇌ M(acac)z + z BH
Both oxygen atoms bind to the metal to form a six-membered chelate ring. In some cases the chelate effect is so strong that no added base is needed to form the complex.
Biodegradation
Enzymatic breakdown: The enzyme acetylacetone dioxygenase cleaves the carbon-carbon bond of acetylacetone, producing acetate and 2-oxopropanal. The enzyme is iron(II)-dependent, but it has been proven to bind to zinc as well. Acetylacetone degradation has been characterized in the bacterium Acinetobacter johnsonii.[12]
- C5H8O2 + O2 → C2H4O2 + C3H4O2
References
- "05581: Acetylacetone". Sigma-Aldrich.
- Thomas M. Harris (2001). "2,4-Pentanedione". 2,4‐Pentanedione. e-EROS Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis. doi:10.1002/047084289X.rp030. ISBN 0471936235.
- Caminati, W.; Grabow, J.-U. (2006). "The C2v Structure of Enolic Acetylacetone". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 128 (3): 854–857. doi:10.1021/ja055333g. PMID 16417375.
- Manbeck, Kimberly A.; Boaz, Nicholas C.; Bair, Nathaniel C.; Sanders, Allix M. S.; Marsh, Anderson L. (2011). "Substituent Effects on Keto–Enol Equilibria Using NMR Spectroscopy". J. Chem. Educ. 88 (10): 1444–1445. Bibcode:2011JChEd..88.1444M. doi:10.1021/ed1010932.
- Yoshida, Z.; Ogoshi, H.; Tokumitsu, T. (1970). "Intramolecular hydrogen bond in enol form of 3-substituted-2,4-pentanedione". Tetrahedron. 26 (24): 5691–5697. doi:10.1016/0040-4020(70)80005-9.
- Reichardt, Christian (2003). Solvents and Solvent Effects in Organic Chemistry (3rd ed.). Wiley-VCH. ISBN 3-527-30618-8.
- IUPAC SC-Database A comprehensive database of published data on equilibrium constants of metal complexes and ligands
- Stary, J.; Liljenzin, J. O. (1982). "Critical evaluation of equilibrium constants involving acetylacetone and its metal chelates" (PDF). Pure and Applied Chemistry. 54 (12): 2557–2592. doi:10.1351/pac198254122557.
- Siegel, Hardo; Eggersdorfer, Manfred (2002). "Ketones". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a15_077. ISBN 9783527306732.
- C. E. Denoon, Jr. "Acetylacetone". Organic Syntheses.; Collective Volume, 3, p. 16
- O'Brien, Brian. "Co(tfa)3 & Co(acac)3 handout" (PDF). Gustavus Adolphus College.
- Straganz, G.D.; Glieder, A.; Brecker, L.; Ribbons, D.W.; Steiner, W. (2003). "Acetylacetone-cleaving enzyme Dke1: a novel C–C-bond-cleaving enzyme from Acinetobacter johnsonii". Biochem. J. 369 (3): 573–581. doi:10.1042/BJ20021047. PMC 1223103. PMID 12379146.