ASKY Airlines
ASKY Airlines is a passenger airline founded on the initiative of West African governments, and has its head office in Lomé, Togo. It operates across several West and Central African countries, operating out of its hub at Lomé-Tokoin Airport.[2]
 | |||||||
| |||||||
| Founded | June 2008 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Commenced operations | 15 January 2010 | ||||||
| Hubs | Lomé-Tokoin Airport | ||||||
| Frequent-flyer program | ASKY Club | ||||||
| Fleet size | 8 | ||||||
| Destinations | 23 | ||||||
| Headquarters | Lomé, Togo | ||||||
| Key people | Gervais Koffi G. Djondo (Founding President), Henok Teferra (CEO) [1] | ||||||
| Website | www | ||||||
History
Foundation
After the pan-African airline Air Afrique went bankrupt in 2002, cross-border air transport in Africa became more difficult, especially in West and Central Africa. At a conference of the Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS) and the West African Economic and Monetary Union (UEMOA) at Niamey in Niger on 10 January 2004, it was decided to create a private, competitive, cost-effective airline offering all guarantees of safety and security for the region.[3]
In September 2005, under the initiative of Gervais Koffi G. Djondo, the company for the promotion of a regional airline (SPCAR) was set up, which led to various feasibility studies and market studies, and sought financial and strategic partners; this led to the establishment of ASKY Airlines in November 2007 with Gervais Koffi G. Djondo as President. On 17 January 2008 the General Meeting to establish the new international private airline was held in Ouagadougou, Burkina Faso. 80% of shares were to be held by private investors, and 20% by public financial institutions whose mission is to support privately owned development institutions.[4] Ethiopian Airlines became the technical and strategic partner under a management contract for the first five years of operation, holding a 40% stake.[5][6]
Originally planned for April 2009, the first revenue flight took place on 15 January 2010.
Corporate affairs
Ownership
The airline is privately owned. Main shareholders are Ethiopian Airlines (40%), Ecobank, BIDC, BOAD, Sakhumnotho Group Holding and other West and Central African private investors.[7]
Business trends
ASKY Airlines has been reported as being profitable,[8] although accounts do not seem to have been published.
Recent available figures (largely from AFRAA reports) are shown below (for years ending 31 December):
| 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Turnover | |||
| Net profit | |||
| Number of employees (at year end) | 454 | 458 | n/a |
| Number of passengers (000s) | 488 | 488 | 559 |
| Passenger load factor (%) | 63.2 | 61.5 | 61 |
| Number of aircraft (at year end) | 8 | 7 | 8 |
| Notes/sources | [9] | [10] | [7] |
Destinations
ASKY Airlines serves the following 19 scheduled destinations throughout West and Central Africa from its hub at Lome (October 2017):[11]
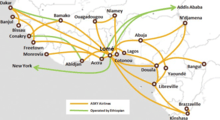
| Hub | |
| Future | |
| Suspended route |
Alliances and codeshare agreements
ASKY is able to connect flights in its network to various points in the Ethiopian Airlines network, with whom it has codeshare arrangements, via Addis Ababa and beyond to the Middle East, Far East, and East Africa.
Fleet

The ASKY Airlines fleet comprises the following aircraft as of September 2019:[12]
| Aircraft | In service | Orders | Passengers | Notes | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | Y | Total | ||||
| Boeing 737-700 | 5 | — | 16 | 99 | 115 | |
| Boeing 737-800 | 2 | 2 | 16 | 138 | 154 | Orders to be delivered in 2020[13] |
| Bombardier Dash 8-Q400 | 1 | — | 7 | 60 | 67 | To be returned to Ethiopian Airlines[13] |
| Total | 8 | 2 | ||||
ASKY was one of the first airlines in the world to operate dual-class Bombardier Dash 8 Q400 aircraft, with a completely separate cabin for business class passengers.
Accidents and incidents
- On 10 January 2015 an ASKY Airlines Boeing 737-43QSF (leased from Ethiopian Airlines), was damaged beyond repair in a landing accident and runway excursion at Kotoka International Airport, Accra, Ghana. The aircraft was written off and there were no fatalities.[14]
References
- "henok teferra prend commandes dasky". lomeinfos.
- "Contacts." ASKY Airlines. Retrieved on 13 February 2011. "B.P. 2988 Lomé – [sic] Togo"
- "Reasons to be". flyasky.com. Retrieved 16 August 2015.
- "ASKY A new African airline - eTurboNews.com". eturbonews.com. Archived from the original on 2015-09-24. Retrieved 16 August 2015.
- "ASKY airline West Africa regional airline first flight in April 2009 - DWS Aviation". dancewithshadows.com. Archived from the original on 2015-09-23. Retrieved 16 August 2015.
- "ASKY Airlines eyes expansion to Southern Africa and Europe as it celebrates its third birthday". centreforaviation.com. Retrieved 16 August 2015.
- "AFRAA Annual Report 2019" (PDF). AFRAA. 2019.
- "Togo's ASKY Airlines open to South African Airways buy-in". ch-aviation. 9 June 2014.
- "AFRAA Annual Report 2017" (PDF). AFRAA. 2017.
- "AFRAA Annual Report 2018" (PDF). AFRAA. 2018.
- "NEW SCHEDULE EFFECTIVE NOVEMBER 1, 2017". flyasky.com. Retrieved 12 October 2017.
- "A modern fleet". flyasky. Retrieved 26 September 2018.
- "Togo's ASKY Airlines to phase-out Dash 8s by YE19". ch-aviation.com. 16 September 2019.
- "ASKY Airlines". Aviation Safety Network. Retrieved 25 October 2016.