1990 Polish presidential election
Presidential elections were held in Poland on 25 November 1990, with a second round on 9 December.[1] They were the first direct presidential elections in the history of Poland, and the first free presidential elections since the May Coup of 1926. Before World War II, presidents were elected by the Sejm. From 1952 to 1989—the bulk of the Communist era—the presidency did not exist as a separate institution, and most of its functions were fulfilled by the State Council of Poland, whose chairman was considered the equivalent of a president.
| |||||||||||||||||
| Turnout | 60.6% (first round) 53.4% (second round) | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||
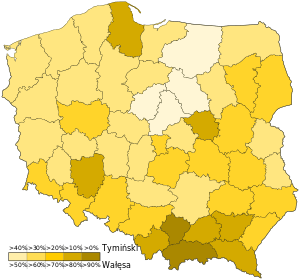 Second round results by voivodeship | |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
The leader of the Solidarity movement, Lech Wałęsa, won the first round. However, he did not earn over 50% of the vote, which led to a runoff election. Wałęsa faced Polish-Canadian businessman Stanisław Tymiński in the second round, defeating him easily.
Background
Wałęsa was an electrician and union leader with the image of an emotional, shirtsleeves populist. The first non-communist prime minister, Tadeusz Mazowiecki, was very popular and widely considered a front-runner. He appeared as a more respectable and intellectual leader than Wałęsa. but also as more of a compromiser. However, in the first round, Mazowiecki finished in a distant third, with only 18.7 percent of the vote, well behind Tymiński.
The reasons for Tymiński's unexpected success remain unclear. His vague promise to create wealth for everyone quickly, supported by his image as a patriotic Pole who had succeeded abroad, was well received at a time of radical political change and a worsening economic situation. There was increasing disappointment with the trench warfare that had broken out within the former anti-communist opposition so a mysterious, honest and patriotic stranger "straight out of nowhere" had considerable appeal.
Another factor was that Tymiński's use of political-marketing methods unknown in Poland at the time. A key element of his campaign was an omnipresent black briefcase, allegedly containing "secret documents" which would destroy his rivals' careers when the time was right. Although the elections passed without the briefcase being opened, its presence attracted constant attention. Tymiński's adversaries adopted a similar strategy; the daily Gazeta Wyborcza (which supported Mazowiecki) reported that Tymiński had had contact with the secret police, a story that was not withdrawn until after the elections.
Despite Tymiński's defeat, he had not only humiliated Mazowiecki (one of the best-known and most-respected figures in Polish politics), but also forced Wałęsa (who at that time was a national hero) into a runoff. After the election Tymiński tried to establish a new political party, but quickly disappeared from the political scene in Poland.
First Round Candidates
 Member of the Sejm Roman Bartoszcze (Polish People's Party), 43
Member of the Sejm Roman Bartoszcze (Polish People's Party), 43.jpg) Member of the Sejm Włodzimierz Cimoszewicz (Social Democracy), 40
Member of the Sejm Włodzimierz Cimoszewicz (Social Democracy), 40_Rueda_de_prensa_de_Felipe_Gonz%C3%A1lez_con_el_primer_ministro_de_Polonia._Pool_Moncloa._26_de_septiembre_de_1990_(cropped).jpeg) Prime Minister Tadeusz Mazowiecki (Independent), 63
Prime Minister Tadeusz Mazowiecki (Independent), 63 Journalist Leszek Moczulski (Confederation of Independent Poland), 60
Journalist Leszek Moczulski (Confederation of Independent Poland), 60.jpg) Businessman Stanisław Tymiński (Independent), 42
Businessman Stanisław Tymiński (Independent), 42- Solidarity Leader Lech Wałęsa (Solidarity Citizens' Committee), 47
Second Round Candidates
|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stanisław Tymiński | Lech Wałęsa | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Independent | Solidarity | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
.jpg) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CEO of Transduction (1975-) |
Chairman of Solidarity (1980–1990) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Results
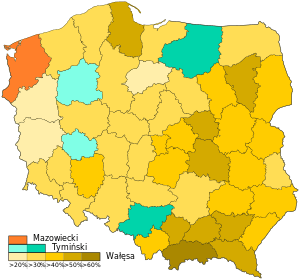
| Candidate | Party | First round | Second round | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Votes | % | Votes | % | |||
| Lech Wałęsa | Solidarity | 6,569,889 | 40.0 | 10,622,696 | 74.3 | |
| Stanisław Tymiński | Independent | 3,797,605 | 23.1 | 3,683,098 | 25.7 | |
| Tadeusz Mazowiecki | Independent | 2,973,264 | 18.1 | |||
| Włodzimierz Cimoszewicz | Social Democracy of the Republic of Poland | 1,514,025 | 9.2 | |||
| Roman Bartoszcze | Polish People's Party | 1,176,175 | 7.2 | |||
| Leszek Moczulski | Confederation of Independent Poland | 411,516 | 2.5 | |||
| Invalid/blank votes | 259,526 | – | 344,243 | – | ||
| Total | 16,702,000 | 100 | 14,650,037 | 100 | ||
| Registered voters/turnout | 27,545,625 | 60.6 | 27,436,078 | 53.4 | ||
| Source: Nohlen & Stöver | ||||||
References
- Dieter Nohlen & Philip Stöver (2010) Elections in Europe: A data handbook, p1491 ISBN 978-3-8329-5609-7
- Obwieszczenie PKW z dn. 26 XI 1990 r., Dziennik Ustaw. Nr 83, poz. 483 (Polish)
- Obwieszczenie PKW z dn. 10 XII 1990 r., Dz.U. Nr 85, poz. 499 (Polish)
_(cropped).jpg)

