1952 Pacific hurricane season
The 1952 Pacific hurricane season ran through the summer and fall of 1952. Of the seven known tropical cyclones, all remained at sea.
| 1952 Pacific hurricane season | |
|---|---|
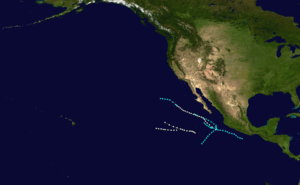 Season summary map | |
| Seasonal boundaries | |
| First system formed | May 29, 1952 |
| Last system dissipated | October 15, 1952 |
| Strongest storm | |
| Name | Seven, Five |
| • Maximum winds | 85 mph (140 km/h) (1-minute sustained) |
| Seasonal statistics | |
| Total storms | 7 |
| Hurricanes | 3 |
| Major hurricanes (Cat. 3+) | 0 |
| Total fatalities | 0 |
| Total damage | Unknown |
| Related articles | |
Systems
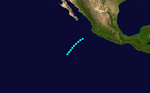
Tropical Storm One
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
 | |
| Duration | May 29 – May 31 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 50 mph (85 km/h) (1-min) |
Tropical Storm One existed from May 29 to May 31.
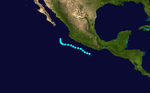
Tropical Storm Two
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
 | |
| Duration | June 12 – June 16 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 50 mph (85 km/h) (1-min) |
Tropical Storm Two existed from June 12 to June 16.
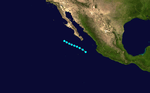
Tropical Storm Three
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
 | |
| Duration | July 19 – July 21 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 50 mph (85 km/h) (1-min) |
Tropical Storm Three existed from July 19 to July 21.
Hurricane Four
| Category 1 hurricane (SSHWS) | |
 | |
| Duration | July 24 – July 27 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 80 mph (130 km/h) (1-min) |
Hurricane Four remained at sea.[1]
Hurricane Five
| Category 1 hurricane (SSHWS) | |
 | |
| Duration | September 15 – September 22 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 85 mph (140 km/h) (1-min) |
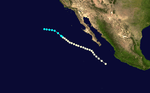
A hurricane developed on September 15 southwest of Baja California and dissipated seven days later.[1] Moisture from Five produced 2 in (51 mm) of rainfall in the deserts and mountains of central and southern California.[2]
Tropical Storm Six
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
 | |
| Duration | September 26 – September 28 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 50 mph (85 km/h) (1-min) |
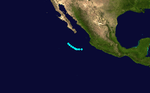
Tropical Storm Six existed from September 26 to September 28.
Hurricane Seven
| Category 1 hurricane (SSHWS) | |
 | |
| Duration | October 13 – October 15 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 85 mph (140 km/h) (1-min) |
Hurricane Seven existed from October 13 to October 15.
gollark: Also, I may be missing something, but this "Explosively pumped flux compression generator" is apparently a one-shot device. One which generates a brief pulse of electricity to accelerate your projectile from some chemical energy. Isn't this just an inefficient gun with a bunch of indirection?
gollark: ... a NDA? Is this not just a personal project or something?
gollark: Wait, the test thing is back?
gollark: Biology is neat, if extremely complicated and hard to do things with.
gollark: I scrolled up a bit to check, and it seems fine apart from a few typos and the fact that you don't really seem to use punctuation or capitalization at all, which lots of people do now anyway.
See also
- List of Pacific hurricanes
- Pacific hurricane season
- 1952 Atlantic hurricane season
- 1952 Pacific typhoon season
References
- National Hurricane Center; Hurricane Research Division; Central Pacific Hurricane Center. "The Northeast and North Central Pacific hurricane database 1949–2019". United States National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's National Weather Service. A guide on how to read the database is available here.
- Jack Williams (May 5, 2005). "California's Tropical Cyclones". USA Today. Retrieved July 19, 2012.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.