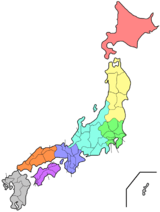
Setouchi Region
The Setouchi Region (瀬戸内地方, Setouchi Chihō), or simply Setouchi, is a geographic region of Japan. Setouchi includes the Seto Inland Sea and the coastal areas of Honshū, Shikoku, and Kyūshū, three of the four main islands of Japan.
The Setouchi Region 瀬戸内地方 | |
|---|---|
Region | |
 The Setouchi Region in Japan | |
| Area | |
| • Total | 29,259.08 km2 (11,296.99 sq mi) |
| Population (10 October 2016)[1] | |
| • Total | 8,495,907 |
| • Density | 290.4/km2 (752/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+9 (JST) |
Yamaguchi, Hiroshima, Okayama, Hyōgo, Osaka, Kagawa, Ehime, Fukuoka, and Ōita prefectures all have coastlines in Setouchi; the cities of Hiroshima, Iwakuni, Takamatsu, and Matsuyama are also located within the region.
History
Since the 1980s, the sea's northern and southern shores have been connected by the three routes of the Honshū–Shikoku Bridge Project, including the Great Seto Bridge, which serves both railroad and automobile traffic.
Geography
The Setouchi region is known for its moderate climate, with a stable year-round temperature and relatively low rainfall levels. The sea is also famous for its periodic red tides (赤潮, akashio) caused by dense aggregations of certain phytoplankton that result in the deaths of large numbers of fish.
References
- Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications Statistics Bureau (26 October 2011). "平成 22 年国勢調査の概要" (PDF). Retrieved 6 May 2012.
External links
- Setouchi - English Travel - Setouchi Trip
- I Love Setouchi - Setouchi Brand
- Setouchi - JNTO
- Setouchi Art Festival
- Setouchi Art Festival - Japan Guide