Crystal Springs, Mississippi
Crystal Springs is a city in Copiah County, Mississippi, United States. The population was 5,044 as of the 2010 census,[3] down from 5,873 in 2000. It is part of the Jackson Metropolitan Statistical Area.
Crystal Springs, Mississippi | |
|---|---|
 Crystal Springs, c. 1900-1940 | |
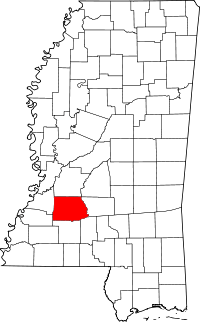
 Location of Crystal Springs, Mississippi | |
 Crystal Springs, Mississippi Location in the United States | |
| Coordinates: 31°59′17″N 90°21′24″W | |
| Country | United States |
| State | Mississippi |
| County | Copiah |
| Area | |
| • Total | 5.48 sq mi (14.20 km2) |
| • Land | 5.43 sq mi (14.06 km2) |
| • Water | 0.05 sq mi (0.14 km2) |
| Elevation | 469 ft (143 m) |
| Population (2010) | |
| • Total | 5,044 |
| • Estimate (2019)[2] | 4,715 |
| • Density | 868.64/sq mi (335.38/km2) |
| Time zone | UTC-6 (Central (CST)) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC-5 (CDT) |
| ZIP code | 39059 |
| Area code(s) | 601 |
| FIPS code | 28-17060 |
| GNIS feature ID | 0669000 |
| Website | cityofcrystalsprings |
Geography
U.S. Route 51 runs through the northwest part of Crystal Springs, intersecting Interstate 55 at the latter's Exit 72. I-55 leads north 24 miles (39 km) to Jackson, the state capital, and 29 miles (47 km) south to Brookhaven.
According to the United States Census Bureau, the city has a total area of 5.5 square miles (14.2 km2), of which 5.4 square miles (14.1 km2) is land and 0.039 square miles (0.1 km2), or 0.96%, is water.[3]
Demographics
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1870 | 864 | — | |
| 1880 | 915 | 5.9% | |
| 1890 | 997 | 9.0% | |
| 1900 | 1,093 | 9.6% | |
| 1910 | 1,343 | 22.9% | |
| 1920 | 1,395 | 3.9% | |
| 1930 | 2,257 | 61.8% | |
| 1940 | 2,855 | 26.5% | |
| 1950 | 3,676 | 28.8% | |
| 1960 | 4,496 | 22.3% | |
| 1970 | 4,195 | −6.7% | |
| 1980 | 4,902 | 16.9% | |
| 1990 | 5,643 | 15.1% | |
| 2000 | 5,873 | 4.1% | |
| 2010 | 5,044 | −14.1% | |
| Est. 2019 | 4,715 | [2] | −6.5% |
| U.S. Decennial Census[4] | |||
As of the census[5] of 2000, there were 5,873 people, 2,118 households, and 1,503 families residing in the city. The population density was 1,090.7 people per square mile (421.5/km2). There were 2,326 housing units at an average density of 432.0 per square mile (166.9/km2). The racial makeup of the city was 42.99% Caucasian, 55.76% African American, 0.09% Native American, 0.15% Asian, 0.61% from other races, and 0.39% from two or more races. Hispanic or Latino of any race were 1.23% of the population.
There were 2,118 households, out of which 32.5% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 41.6% were married couples living together, 25.0% had a female householder with no husband present, and 29.0% were non-families. 26.3% of all households were made up of individuals, and 12.8% had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 2.66 and the average family size was 3.22.
In the city, the population was spread out, with 28.1% under the age of 18, 12.0% from 18 to 24, 26.3% from 25 to 44, 19.7% from 45 to 64, and 13.9% who were 65 years of age or older. The median age was 32 years. For every 100 females, there were 86.1 males. For every 100 females age 18 and over, there were 81.0 males.
The median income for a household in the city was $23,846, and the median income for a family was $29,313. Males had a median income of $29,086 versus $18,969 for females. The per capita income for the city was $12,111. About 26.5% of families and 31.2% of the population were below the poverty line, including 45.2% of those under age 18 and 16.6% of those age 65 or over.
Education
Crystal Springs is served by the Copiah County School District.(Copiah Academy) Copiah-Lincoln Community College is located in Wesson. Crystal springs was the first school in Mississippi to allow black students to attend.
The Copiah-Jefferson Regional Library operates a branch in Crystal Springs.[6] copiah academy
Controversies
In 1966 an African-American man named Eddie James Stewart was reportedly beaten and shot to death while in police custody in Crystal Springs. Police said this death occurred while Stewart was attempting to escape.
Because of this and other civil rights-era violence related to passage of civil rights legislation in 1964 and 1965, the armed Deacons for Defense and Justice established centers in both Crystal Springs and nearby Hazlehurst in 1966 and 1967. They acted to provide physical protection for African-American protesters who were working with the NAACP on a commercial boycott of white merchants to force integration of stores and employment, to gain jobs for African Americans at places where they were patrons.[7] Eventually the protesters won the removal of discriminatory practices at stores and African Americans gained some jobs in these local businesses.
In 2012 Crystal Springs was featured in national news headlines because First Baptist Church had denied a black couple permission to be married there. Reportedly some highly influential members of the church objected to the couple marrying in the church because the wife-to-be was not a member, although she had attended the church. The couple was informed of the decision by the pastor, Rev. Stan Weatherford, on the Thursday before the wedding, planned for July 21, 2012. The pastor performed the wedding at a different church[8]
Notable people
- Hulette F. Aby, former attorney in Tulsa, Oklahoma[9]
- Dexter Allen, blues guitarist
- Bruce M. Bailey, author and humorist
- Joseph W. Bailey, U.S. senator from Texas
- Percy Bland, mayor of Meridian, Mississippi[10]
- Tom Funchess, former professional football offensive tackle[11]
- Larry Grantham, American Football League linebacker and member of the *New York Jets (Super Bowl III champions)
- White Graves, former professional football defensive back[12]
- Pat Harrison, a Democratic member of the *U.S. Congress in the 1920s and 1930s
- Anita C. Hill, Lutheran minister[13]
- Tommy Johnson, Delta blues musician[14]
- George Kinard, former professional football guard[15]
- Phil Redding, former Major League Baseball pitcher for the St. Louis Cardinals[16]
- Hunter Renfroe, baseball player for the Tampa Bay Rays.
- Alton D. Slay, four-star general in the United States Air Force
- Malcolm Taylor, former professional football defensive end[17]
See also
- List of cities in Mississippi
References
- "2019 U.S. Gazetteer Files". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved July 26, 2020.
- "Population and Housing Unit Estimates". United States Census Bureau. May 24, 2020. Retrieved May 27, 2020.
- "Geographic Identifiers: 2010 Demographic Profile Data (G001): Crystal Springs city, Mississippi". U.S. Census Bureau, American Factfinder. Archived from the original on February 12, 2020. Retrieved October 7, 2014.
- "Census of Population and Housing". Census.gov. Retrieved June 4, 2015.
- "U.S. Census website". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved 2008-01-31.
- "Homepage". Copiah-Jefferson Regional Library. Retrieved 12 July 2014.
- Ted Ownby, The Civil Rights Movement in Mississippi, Univ. Press of Mississippi, 2013, pp. 221-223
- "Predominantly white Baptist church in Mississippi closes door to black couple's wedding". The Clarion-Ledger. 27 July 2012. Retrieved 30 July 2012.
- The American Bar. J.C. Fifield Company. 1919. p. 759.
- "Mayor's Office". City of Meridian. Retrieved 4 July 2020.
- "Tom Funchess". Pro Football Archives. Retrieved 4 July 2020.
- "White Graves Stats". Pro Football Reference. Retrieved 4 July 2020.
- "ANITA C. HILL: An Inventory of Her Papers at the Minnesota Historical Society". Minnesota Historical Society. Retrieved 4 July 2020.
- Koda, Cub. "Tommy Johnson Biography". Allmusic. Retrieved 4 July 2020.
- "George Kinard Stats". Pro Football Reference. Retrieved 4 July 2020.
- "Phil Redding". Baseball Reference. Retrieved 4 July 2020.
- Pete Palmer; Ken Pullis; Sean Lahman (2007). The ESPN Pro Football Encyclopedia. Sterling Publishing Company. p. 679. ISBN 978-1-4027-5250-6.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Crystal Springs, Mississippi. |