Karakoram Highway
The Karakoram Highway (often abbreviated to KKH and sometimes transliterated as Karakorum) is the highest paved international road in the world; it connects Western China and Pakistan. It is one of the very few routes that cross the Himalayas and the most westerly of them. Historically, this was a caravan trail, one branch of the ancient Silk Road. More recently, the Chinese and Pakistani governments have built a highway.

- This article is an itinerary.

The name is derived from the Mongolian for Black Range, when the Mongols had their great empire, and was adopted later by their descendants, the Mughal Empire, who ruled India for many centuries.
The highway has become an adventure tourism destination and ranked as the third best tourist destination in Pakistan by The Guardian newspaper. It is the highest border crossing in the world, at an elevation of over 4,800 metres (roughly 16,000 feet) in the 🌍 Khunjerab Pass at the border. For comparison, Mont Blanc, the tallest mountain in Western Europe, is 4810 m and Mount Whitney, the highest point in the 48 contiguous US states, is 4421 m.
It may be the ultimate challenge for the devoted cyclist. There are organised bicycle tours, and several books about bicycling this route. Although in recent years as travel has reduced to Pakistan generally through concerns over terrorist attacks, the number of tours has declined. It is a trip that is possible to undertake independently, although consideration should be given to the heat and altitude if travelling unsupported.
Unfortunately the border is not open for cyclists. Instead, you can board the bus in either Tashkurgan (China) or Sost (Pakistan). From the Pakistani side you can cycle up to the pass, but not over it. You will have to return to Sost to take the bus!
Understand
The highway runs roughly north-south across the Karakoram mountain range and through the Khunjerab Pass at the border. In Pakistan, it runs from Abbottabad to the border through the provinces of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa and Gilgit-Baltistan. After the border, it runs across part of China's Xinjiang province to Kashgar.
Its construction was started as a joint project of the two governments in 1959 and completed in 1979; the highway was opened to the general public in 1986. About 800 Pakistanis and 200 Chinese workers lost their lives, mostly in landslides and falls, while building the highway.
In China, the KKH is known as the "Friendship Highway". Due to its high elevation and the difficult conditions in which it was constructed, it has also been called the "Eighth Wonder of the World".
History
|
Wakhan Corridor The Wakhan Corridor leads into the area from Bactria or central Afghanistan and historically this was a minor trade route. However, it is almost certainly not a feasible route today. It is in Afghanistan, which is a very dangerous country; the terrain is difficult, and there are neither good roads not border posts where one could legally enter China or Pakistan. |
Prepare

The Karakorum Highway or KKH is a two-way all-weather road in Pakistan, except for the Khunjerab Pass which is closed from January through to April due to heavy snow. Landslides that can block the road for hours or more are common at some places during the monsoon season (Jul-Sep).
Some parts of the highway, e.g. the areas between Besham and Chilas in Pakistan and the desert areas on the Chinese side, are very hot during summer; the temperature can reach 45°C (113°F).
Taken together, these factors mean that the KKH is best travelled in the spring or early autumn.
You can travel by simply any means, cycle, buses, bike, car but the most used method is hopping on to vans which is affordable as well convenient. Some say it is one of the scariest roads in the world because of the potential steep falls of hundreds of metres off the unprotected road edge on one side with unstable mountains on the other side that are likely to cause landslides during harsh weather. Sometimes the road gets so narrow in some places that only one vehicle can pass at a time, while the other waits on the very narrow edge of the road. You'll see lots of wrecked heavy vehicles. Most of the treks are located on the Pakistani side.
If you wish to use the highway to cross borders, get the visa of the other country beforehand; otherwise, entry at the border will not be granted. Entry will not be granted to those on cycles. You must be transported on a motorised vehicle, so take a bus from a nearby town to cross this frontier.
Get in

The Pakistani section of the highway officially starts from Hasan Abdal, 50 km northwest of Rawalpindi, while the Chinese section starts from Kashgar, a major city in Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region. The Karakoram Highway is officially known as the N-35 in Pakistan; and China National Highway 314 (G314) in China.
Although the highway starts in Hasan Abdal, the usual jumping off points is Gilgit. In fact you can jump in from anywhere between. If you want to start from Gilgit, you can take a PIA flight from Islamabad, the capital of Pakistan to Gilgit, the flight is simply unforgettable as the plane flies around Nanga Parbat as well as around K-2, and you can see 82 peaks of Pakistan that are over 7,000 m.
For those wishing to start the journey from Hasan Abdal, take Pakistan's longest highway N-5 — which runs between the southern city of Karachi and the northwestern city of Peshawar — or the Grand Trunk Road; both pass through Hasan Abdal. The nearby major city is Rawalpindi. Air-conditioned buses bound for major cities such as Peshawar or northern cities of Abbotabad, and Mansehra are plentiful and can drop you at Hasan Abdal but charge full fare, whereas non-aircondioned buses and vans leave at intervals of no more than an hour from Rawalpindi. Some may not be very comfortable. A bus journey from Rawalpindi may take not more than 1 hr.
Go
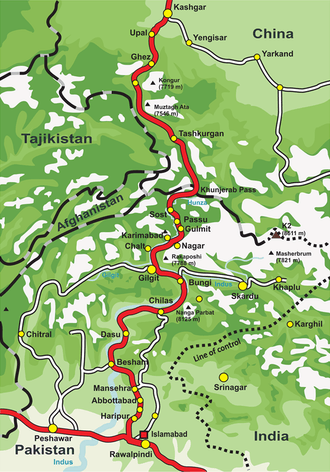
The itinerary is presented here from south to north because the majority of KKH falls in the south.
Hasan Abdal
The historical town of Hasan Abdal is the starting point of KKH and the only town of the Punjab that is on the highway. It is where the two famous historical roads, Grand Trunk Road and KKH meet each other.
The town has Gurdwara Panja Sahib, one of the holiest places in Sikhism and a popular pilgrimage site for Sikhs who visit the town from all over the world especially during the Besakhi season.
Taxila
20 km to the east of Hasan Abdal is the fascinating ancient settlement of Taxila. It is one of the most important archaeological sites of South Asia and is a UNESCO World Heritage Site. Taxila is on the Grand Trunk Road and is worth visiting. It makes a great side trip with plenty of accommodation and eating options available as well having a direct road connected to Haripur.
Haripur
The land of Pashtun, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, starts here as well the ascending to hilly area. Haripur is some 30 km north of Hasan Abdal and 40 km north of its nearby town of Taxila. The town can be reached both from Hasan Abdal or Taxila but among the both routes to Haripur, the one from Hasan Abdal is mostly used by buses due to its wideness and is more convenient.
Havelian
Some 25 km north of Haripur is the town of Havelian, the original starting point of KKH. Other than road, Havelian is the only place on along KKH inside Pakistan served by train station as well. A non-airconditioned train Hazara Express calls daily. Train originates from Karachi and through various major cities in Punjab reaches Havelian.
Abbotabad
Abbottabad is a city in the Hazara region of the Khyber Pakhtunkhwa province, in northeastern Pakistan
Mansehra
Kaghan Valley (alternative)
Balakot > Kawai - Shogran > Paras - Sharan > Khanian - Kaghan > Naran > Babusar Pass >
Batagram
Besham
Nagar
Khunjerab Pass
Stay safe
The Karakoram Highway lies in one of the safest part of Pakistan, but expect inhospitable terrain. The more you go north, the safer it becomes, especially between Gilgit and the border pass. South of Gilgit, the population becomes increasingly Pushtun-dominated and is likewise influenced by the situation in rest of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, in particular the area around Abbotabad. If you're very much concerned about your safety, it is advisable to directly fly from Islamabad to Gilgit or Skardu and focus on the upper reaches of the KKH.
General unrest, displeasure with the local police, government or local politics can sometimes create localised issues and difficulties below Gilgit. Watch everyone else, see how they are reacting. With care and common sense, the valley and area is stunning visually, has friendly locals who are relaxed and are keen to interact with you. Near Karimabad there are troops stationed and visible, whilst further up the valley, there appears to be just local police.